Recorded on February 25, 2016
Presenter
Dr. Cynthia Calongne
CTU Doctoral Program | ccalongne@ctuonline.edu
Twitter and Skype: @lyrlobo
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
++++++++++++++++++
https://academicpartnerships.uta.edu/articles/healthcare/pros-cons-competencybased-learning.aspx
The Glossary of Education Reform, “Competency-based learning refers to systems of instruction, assessment, grading, and academic reporting that are based on students demonstrating that they have learned the knowledge and skills they are expected to learn as they progress though their education.”
The benefits, or drawbacks, of competency-based learning (CBL) — also known as competency-based education, mastery-based education, performance-based education, standards-based education and proficiency-based education — are up for debate. Regardless, there are an increasing number of these types of programs, particularly in for-profit colleges.
++++++++++++++++++++++
Problem-based learning is a category of experiential learning that involves students in the process of critical thinking to examine problems that lack a well-defined answer. In problem-based learning, students are given a problem with only preliminary information. They work towards solving the problems themselves, rather than reviewing how others have resolved the situation or problem as in a case study. They do not produce a product as in project-based learning, and students are not necessarily working in the community unless they are gathering data.
Problem-based learning fosters students’ metacognitive skills. They must be consciously aware of what they already know about an area of discovery as well as what they do not know.
Project-based learning is a category of experiential learning where students are presented with a complex problem or question that has multiple potential solutions and possibilities for exploration. However, after studying this problem or question in their teams, students are challenged to develop a plan and create a product or artifact that addresses the problem.
McGraw Hill Plus, a new tool, Focusing first on math and then expanding to ELA and science, its objective is to make personalized learning scalable.
Smith: The modern classroom sits at the intersection of blended learning, competency-based learning and personalized learning.
reimagine instructional time and use technology to scale personalized learning.
First, pulling data into one place is the key fundamental driver that will change the teacher workflow. Second, we need to manipulate that data into some advanced data visualization tools, so it’s easy for teachers to understand and use. Third, we need to be able to visualize student performance and take action on it.
Using these data analytics, we can drive personalized learning based on student performance. And the last thing is the automation of teacher workflow.
eachers get data visualization from different sources, such as an adaptive software solution like our ALEKS program, our Redbird Mathematics, or our recently acquired Achieve3000 Literacy.
a performance- or competency-based approach to education
little evidence that personalized learning improves student learning, in part because so many different approaches are used.
Advocates of competency-based education say they believe public opinion is also shifting their way. They point to a recent national poll showing that 74 percent of voters think the lack of personalized learning in schools is “a problem.”
+++++++++++++
more on competency based ed in this iMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=competency+based
https://www.educause.edu/eli/initiatives/key-issues-in-teaching-and-learning
A roster of results since 2011 is here.

https://cdn.nmc.org/media/2017-nmc-strategic-brief-digital-literacy-in-higher-education-II.pdf
Three Models of Digital Literacy: Universal, Creative, Literacy Across Disciplines
United States digital literacy frameworks tend to focus on educational policy details and personal empowerment, the latter encouraging learners to become more effective students, better creators, smarter information consumers, and more influential members of their community.
National policies are vitally important in European digital literacy work, unsurprising for a continent well populated with nation-states and struggling to redefine itself, while still trying to grow economies in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent financial pressures
African digital literacy is more business-oriented.
Middle Eastern nations offer yet another variation, with a strong focus on media literacy. As with other regions, this can be a response to countries with strong state influence or control over local media. It can also represent a drive to produce more locally-sourced content, as opposed to consuming material from abroad, which may elicit criticism of neocolonialism or religious challenges.
p. 14 Digital literacy for Humanities: What does it mean to be digitally literate in history, literature, or philosophy? Creativity in these disciplines often involves textuality, given the large role writing plays in them, as, for example, in the Folger Shakespeare Library’s instructor’s guide. In the digital realm, this can include web-based writing through social media, along with the creation of multimedia projects through posters, presentations, and video. Information literacy remains a key part of digital literacy in the humanities. The digital humanities movement has not seen much connection with digital literacy, unfortunately, but their alignment seems likely, given the turn toward using digital technologies to explore humanities questions. That development could then foster a spread of other technologies and approaches to the rest of the humanities, including mapping, data visualization, text mining, web-based digital archives, and “distant reading” (working with very large bodies of texts). The digital humanities’ emphasis on making projects may also increase
Digital Literacy for Business: Digital literacy in this world is focused on manipulation of data, from spreadsheets to more advanced modeling software, leading up to degrees in management information systems. Management classes unsurprisingly focus on how to organize people working on and with digital tools.
Digital Literacy for Computer Science: Naturally, coding appears as a central competency within this discipline. Other aspects of the digital world feature prominently, including hardware and network architecture. Some courses housed within the computer science discipline offer a deeper examination of the impact of computing on society and politics, along with how to use digital tools. Media production plays a minor role here, beyond publications (posters, videos), as many institutions assign multimedia to other departments. Looking forward to a future when automation has become both more widespread and powerful, developing artificial intelligence projects will potentially play a role in computer science literacy.
In traditional instruction, students’ first contact with new ideas happens in class, usually through direct instruction from the professor; after exposure to the basics, students are turned out of the classroom to tackle the most difficult tasks in learning — those that involve application, analysis, synthesis, and creativity — in their individual spaces. Flipped learning reverses this, by moving first contact with new concepts to the individual space and using the newly-expanded time in class for students to pursue difficult, higher-level tasks together, with the instructor as a guide.
Let’s take a look at some of the myths about flipped learning and try to find the facts.
Myth: Flipped learning is predicated on recording videos for students to watch before class.
Fact: Flipped learning does not require video. Although many real-life implementations of flipped learning use video, there’s nothing that says video must be used. In fact, one of the earliest instances of flipped learning — Eric Mazur’s peer instruction concept, used in Harvard physics classes — uses no video but rather an online text outfitted with social annotation software. And one of the most successful public instances of flipped learning, an edX course on numerical methods designed by Lorena Barba of George Washington University, uses precisely one video. Video is simply not necessary for flipped learning, and many alternatives to video can lead to effective flipped learning environments [http://rtalbert.org/flipped-learning-without-video/].
Myth: Flipped learning replaces face-to-face teaching.
Fact: Flipped learning optimizes face-to-face teaching. Flipped learning may (but does not always) replace lectures in class, but this is not to say that it replaces teaching. Teaching and “telling” are not the same thing.
Myth: Flipped learning has no evidence to back up its effectiveness.
Fact: Flipped learning research is growing at an exponential pace and has been since at least 2014. That research — 131 peer-reviewed articles in the first half of 2017 alone — includes results from primary, secondary, and postsecondary education in nearly every discipline, most showing significant improvements in student learning, motivation, and critical thinking skills.
Myth: Flipped learning is a fad.
Fact: Flipped learning has been with us in the form defined here for nearly 20 years.
Myth: People have been doing flipped learning for centuries.
Fact: Flipped learning is not just a rebranding of old techniques. The basic concept of students doing individually active work to encounter new ideas that are then built upon in class is almost as old as the university itself. So flipped learning is, in a real sense, a modern means of returning higher education to its roots. Even so, flipped learning is different from these time-honored techniques.
Myth: Students and professors prefer lecture over flipped learning.
Fact: Students and professors embrace flipped learning once they understand the benefits. It’s true that professors often enjoy their lectures, and students often enjoy being lectured to. But the question is not who “enjoys” what, but rather what helps students learn the best.They know what the research says about the effectiveness of active learning
Assertion: Flipped learning provides a platform for implementing active learning in a way that works powerfully for students.

What is the total cost of my innovation, including both new spending and the use of existing resources?
What’s the unit I should measure that connects cost with a change in performance?
How might the expected change in student performance also support a more sustainable financial model?
The Exposure Approach: we don’t provide a way for participants to determine if they learned anything new or now have the confidence or competence to apply what they learned.
The Exemplar Approach: from ‘show and tell’ for adults to show, tell, do and learn.
The Tutorial Approach: Getting a group that can meet at the same time and place can be challenging. That is why many faculty report a preference for self-paced professional development.build in simple self-assessment checks. We can add prompts that invite people to engage in some sort of follow up activity with a colleague. We can also add an elective option for faculty in a tutorial to actually create or do something with what they learned and then submit it for direct or narrative feedback.
The Course Approach: a non-credit format, these have the benefits of a more structured and lengthy learning experience, even if they are just three to five-week short courses that meet online or in-person once every week or two.involve badges, portfolios, peer assessment, self-assessment, or one-on-one feedback from a facilitator
The Academy Approach: like the course approach, is one that tends to be a deeper and more extended experience. People might gather in a cohort over a year or longer.Assessment through coaching and mentoring, the use of portfolios, peer feedback and much more can be easily incorporated to add a rich assessment element to such longer-term professional development programs.
The Mentoring Approach: The mentors often don’t set specific learning goals with the mentee. Instead, it is often a set of structured meetings, but also someone to whom mentees can turn with questions and tips along the way.
The Coaching Approach: A mentor tends to be a broader type of relationship with a person.A coaching relationship tends to be more focused upon specific goals, tasks or outcomes.
The Peer Approach:This can be done on a 1:1 basis or in small groups, where those who are teaching the same courses are able to compare notes on curricula and teaching models. They might give each other feedback on how to teach certain concepts, how to write syllabi, how to handle certain teaching and learning challenges, and much more. Faculty might sit in on each other’s courses, observe, and give feedback afterward.
The Self-Directed Approach:a self-assessment strategy such as setting goals and creating simple checklists and rubrics to monitor our progress. Or, we invite feedback from colleagues, often in a narrative and/or informal format. We might also create a portfolio of our work, or engage in some sort of learning journal that documents our thoughts, experiments, experiences, and learning along the way.
The Buffet Approach:
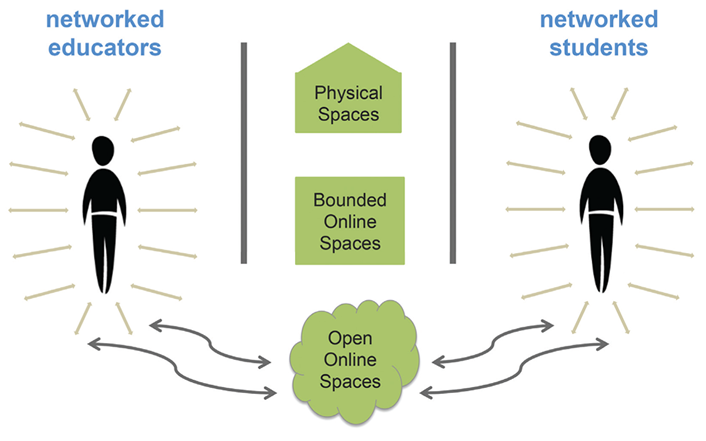
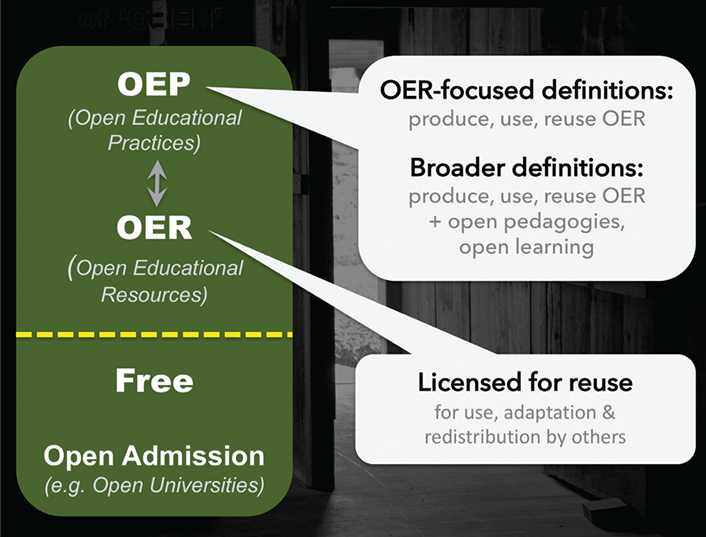

In 2014, administrators at Central Piedmont Community College (CPCC) in Charlotte, North Carolina, began talks with members of the North Carolina State Board of Community Colleges and North Carolina Community College System (NCCCS) leadership about starting a CBE program.
Building on an existing project at CPCC for identifying the elements of a digital learning environment (DLE), which was itself influenced by the EDUCAUSE publication The Next Generation Digital Learning Environment: A Report on Research,1 the committee reached consensus on a DLE concept and a shared lexicon: the “Digital Learning Environment Operational Definitions,
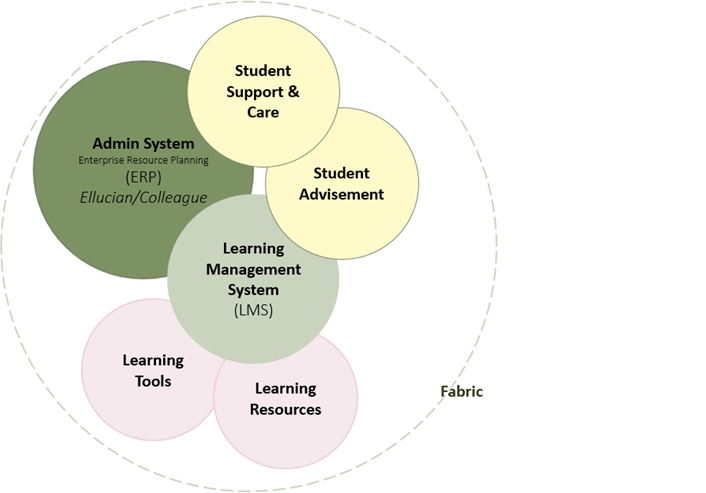
The EDUCAUSE Learning Initiative has just launched its 2018 Key Issues in Teaching and Learning Survey, so vote today: http://www.tinyurl.com/ki2018.
Each year, the ELI surveys the teaching and learning community in order to discover the key issues and themes in teaching and learning. These top issues provide the thematic foundation or basis for all of our conversations, courses, and publications for the coming year. Longitudinally they also provide the way to track the evolving discourse in the teaching and learning space. More information about this annual survey can be found at https://www.educause.edu/eli/initiatives/key-issues-in-teaching-and-learning.
+++++++++++
learning and teaching in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=teaching+and+learning
++++++++++++++++++
According to Weller (2011), a pedagogy of abundance should consider a number of assumptions such as that content often is freely available and abundant. Content further takes on various forms and it is often easy and inexpensive to share information. Content is socially based and since people filter and share content, a social approach to learning is advisable. Further, establishing and preserving connections in a network is easy and they do not have to be maintained on a one-to-one basis. Successful informal groupings occur frequently, reducing the need to formally manage groups.
Resource-based learning. Ryan (as cited in Weller, 2011) defines resource-based learning as “an integrated set of strategies to promote student centred learning in a mass education context, through a combination of specially designed learning resources and interactive media and technologies.”
Problem-based learning. Problem-based learning takes place when learners experience the process of working toward resolving a problem encountered early in the learning process (Barrows & Tamblyn, as cited in Weller, 2011). Students often collaborate in small groups to identify solutions to ill-defined problems, while the teacher acts as facilitator and assists groups if they need help. Problem-based learning meets a number of important requirements such as being learner-directed, using diverse resources and taking an open-ended approach.
Communities of practice. Lave and Wenger’s (as cited in Weller, 2011) concept of situated learning and Wenger’s (as cited in Weller, 2011) idea of communities of practice highlight the importance of apprenticeship and the social role in learning.
My note: this article spells out what needs to be done and how. it is just flabeghasting that research guides are employed so religiously by librarians. They are exactly the opposite concept of the one presented in this article: they are closed, controlled by one or several librarians, without a constant and easy access of the instructor, not to mention the students’ participation
+++++++++++++++++
more on teaching w social media in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=social+media+teaching
Midwest Regional Conference at Notre Dame
http://www.aaeebl.org/?page=notre_dame_2016
The Conference at Notre Dame May 12-13 is intriguing as you can see from some of the session titles below. It’s time to register and book lodging.
Peruse the titles below to get an idea of the dynamism of this eportfolio conference:
Plus 15 other sessions.
The keynote address will be given by Daniel T. Hickey on Open Digital Badges + ePortfolios: Searching for and Supporting Synergy. an internationally-known speaker and leader on the changes in higher education around digital technologies.
Here is a description of another session:
By sharing challenges, practices, and examples of maker portfolios, we highlight the importance of makerspaces and community development in the design of portfolios that capture rich learning.
These are the institutions represented in the program:
The full program will be posted by late Thursday of this week. This is a must-attend event to know about the latest developments in the eportfolio field.
Registration rates (note that AAEEBL members receive a $100 discount on registration; a student rate is available as well):
Registration Fees:
Non-Member Registration
$250 before April 25
$290 after April 25
Member Registration
$150 before Aprial 25
$190 after April 25
Student Registration
$75 before Aprial 25
$115 after April 25
Includes 2 breakfasts, one lunch and one reception. One and a half days of sessions.
Register now. Book lodging. Notre Dame is just outside of Chicago in Northern Indiana. Midway Airport is probably the closest major airport to the Notre Dame campus. Conference facilities at Notre Dame are excellent — lodging and conference space are adjacent.
+++++++++++++++++++++++++
More on badges in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=badges&submit=Search
More on eportfolio in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=eportfolio&submit=Search
| Proportion of Content
Delivered Online |
Type of Course |
Typical Description |
|
0% |
Traditional |
Classroom-based teaching with assignments and activities which students pursue independently of each other. |
|
1 to 29% |
Web Facilitated |
Web resources and technologies are used to facilitate what is essentially a face-to-face course. May use webpages and course management systems (CMS) to post syllabuses, readings and assignments. |
|
30-79% |
Blended / Hybrid |
Course blends online and face-to-face delivery. Substantial parts of the content are delivered online and discussions, team projects and activities and web safaris are used for learning. The number of face-to-face sessions is decreased as the volume of online activity increases. |
|
80+% |
Online |
A course where all, or almost all, of the content is delivered online with no or a very small number of face-to-face meetings. |
Flipped ClassroomCompetency-Based Learningopen learning Gamification Immersive Learning Environments Adaptive Learning and Assessment Systems |
||
++++++++++++++++++
Glossary of Online Learning Terms http://theelearningcoach.com/resources/online-learning-glossary-of-terms/
E-Learning Terms
http://www.bpcc.edu/educationaltechnology/glossary.html
TCC 2016 cordially invites you to join a FREE special pre-conference webinar on competency-based education (CBE).
Unpack CBE
During this session, Diane Singer from Bandman University, and Susan Manning from the University of Wisconsin at Stout, discuss the meaning and processes behind CBE, with a specific eye to how the assessment and recognition of competencies benefit various stakeholders, including business and industry.
Date & time:
March 16, 2:00 PM Hawaii; 6:00 PM Mountain; 8:00 PM Eastern
March 17, 9:00 AM Tokyo & Seoul; 11:00 AM Sydney, Feb. 26
Other timezones:
http://bit.ly/tcc16precon2-unpackCBE
Full information:
http://2016.tcconlineconference.org/unpacking-cbe/
RSVP for this FREE session!
If you wish to participate, please RSVP. A reminder will be sent a few days prior along with instructions to sign-in.
http://bit.ly/tcc2016precon2-rsvp
The 21st Annual TCC Worldwide Online Conference: April 19-21, 2016
TCC, Technology, Colleges and Community, is a worldwide online conference attended by university and college personnel including faculty, academic support staff, counselors, student services personnel, students, and administrators.
More on competency-based learning in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=competency+based+learning&submit=Search
+++++++++++++++++
webinar archived recording:
http://2016.tcconlineconference.org/make-the-future/
Recorded on February 25, 2016
Dr. Cynthia Calongne
CTU Doctoral Program | ccalongne@ctuonline.edu
Twitter and Skype: @lyrlobo