purpose: draft a document for the provost to plan for charting the future goal 3.12 “develop a comprehensive strategy to increase awareness and development of e-textbooks and open educational resources (OERs)”
\\STCLOUDSTATE\HuskyNet\DeptFiles\LRS\ETextbooks
SCSU goal: to reduce the cost of textbooks as an affordable learning initiative. Amount of reduction is undetermined
my notes based on the material below:
- best, most applicable source for the purpose of this research: U of Alberta Committee’s notes on the learning environment:
http://www.governance.ualberta.ca/en/GeneralFacultiesCouncil/CommitteeontheLearningEnvironm/~/media/Governance/Documents/GO05/LEA/15-16/WEB/Item-4-eTextbook-Subcommittee-Report-CLE-TLAT.pdf
the Canadians are using (citing) Acker (Ohio) in their research.
- best, most applicable source in terms of the logistics on e-texbooks creation and its pedagogical argumentation is this document from New Zealand: https://akoaotearoa.ac.nz/download/ng/file/group-7/guidelines-for-developing-interactive-etextbooks-on-net-tablets.pdf
- According to Bossaler et al (2014), it might be worth considering that SCSU (MnSCU?) must go first through implementing of e-text[books] in courses first by using publisher materials and then by using “in-house” produce. At this point, SCSU does NOT have an aligned policy of integrating e-texts in courses across campus. Lack of such experience might make a strategy for adoption of e-textbooks much more complex and difficult to implement
- stats are colored in green for convenience. Stats regarding the increase in textbook costs are re-printed from author to author: e.g. Acker (2011, p. 42). Murey and Perez (2011, p. 49 (bottom) – 50 (up)) reports stats from 2009 and projections for 2013 regarding etexbook adotion. Same authors, p. 50 second paragraph reports good stats regarding texbooks’ price increase : US$1122 per year for textbooks in 2010.
- Wimmer at al (2014) presents a lucid graphic of the structure of the publishing process (see bottom of this blog entry for citation and perm link).
- Wimmer at al (2014) discusses copyright and permissions, which is of interest for this research (p. 85)
- regarding in-house creation of e-textbooks, see (Distance education, e-learning, education and training, 2015). It very much follow the example of SUNY, which Keith was laying out: a team of faculty charged with creation the e-textbook for mass consumption.
Besides the SUNY model Keith is envisioning for MnSCU (comparable), there is the option of clustering OER sources: e.g. NASTA as per Horejsi (2013), CourseSmart. FlatWorld Knowledge (Murrey and Perez, 2011) etc.
- Hamedi & Ezaleila (2015) present an entire etextbook program. Article has been ordered through ILL. Same with Joseph (2015).
- Open Educational Resources in Acker (2015, p. 44-47). Also in Murey and Perez (2011, p. 51).
Also in ICWL (Conference) (13th : 2014 : Tallinn, E., & Cao, Y. (2014): OpenDSA
- Different models of pricing also in Acker (2015, p. 48). Keith touched on that
- students learn equally well from etextbooks as from paper ones: Taylor (2011)
- pedagogy
responses from colleagues:
Scott Robison, sarobison@mail.plymouth.edu: sparc-liboer@arl.org listserv
Jeff Gallant, Jeff.Gallant@usg.edu: David Ernst with the U and Ashley Miller from Ohio State U: dernst@umn.edu. Ashley’s is miller.6275@osu.edu.
definition e-textbook and
an electronic version of a printed book that can be read on a computer or handheld device designed specifically for this purpose.
-
a dedicated device for reading electronic versions of printed books.
Definition of: e-book
my note: there is no good definition about e-textbook in terms of the complexity, which e-textbook on campus might involve.
Considering Wimmer et al (2014) account on their campus experience in publishing e-textbook, a textbook may involve an LMS (Canvas) and blog (WordPress). Per my proposal during the F2F meeting, and following Rachel’s suggestion about discrimination of the different types of e-textbooks, here is an outline of e-textbook definition:
*******************
working definition for e-textbook for the purposes of SCSU:
e-textbook is a compilation of textual, multimedia and interactive material, which can be viewed on various electronic devices. E-textbook can: 1. be purchased from a publisher; 2. compiled in HTML format on faculty or group web space; 3. compiled on the content module of LMS (BB, D2L, Canvas, Moodle, etc.) 4. compiled on LMS (BB, D2L, Canvas, Moodle, etc.) and including all interactive materials: e.g. hyperlinks to MediaSpace multimedia, quizzes, etc.; 5. compiled on special apps, such as iBook Author, eCub, Sigil.
*******************
e-book
(Electronic-BOOK) The electronic counterpart of a printed book, which can be viewed on a desktop computer, laptop, smartphone, tablet or e-book reader (e-reader). When traveling, a huge number of e-books can be stored in portable units, dramatically eliminating weight and volume compared to paper. Electronic bookmarks make referencing easier, and e-book readers may allow the user to annotate pages.
Although fiction and non-fiction books come in e-book formats, technical material is especially suited for e-book delivery because it can be searched. In addition, programming code examples can be copied, which is why CD-ROMs that contained examples or the entire text were often packaged inside technical paper books.
E-Book Formats
Wimmer, Morrow, & Weber: Collaboration in eTextbook Publishing
There are several e-book formats on the market, including EPUB, Mobipocket (PRC, MOBI), eReader (PDB), Kindle (AZW, KF8) and Apple iBook (EPUB variation). Many e-readers also accept generic formats, including Adobe PDF and plain text (TXT).
——————
Electronic Textbooks or Paper Textbooks: What Are Students Reading?
According to a United States Government report, textbook prices have increased at over twice the rate of inflation in the last couple of decades. According to another report, the average student spends between $700 and $1,000 per year on textbooks while the cost of e-textbooks can be as much as 50% lower than paper textbooks.
Oxford dictionary, an electronic book or e-book is “an electronic version of a printed book that can be read on a computer or handheld device designed specifically for this purpose.” An e-textbook is defined as an e-book used for instructional or educational purposes and often includes features such as bookmarking, searching, highlighting, and note-taking as well as built-in dictionaries and pronunciation guides, embedded video-clips, embedded hyperlinks, and animated graphics.
E-textbooks have moved from occasional usage to a mainstream technology on college campuses. According to the Association of American Publishers, sales of e-books hit over $90 million; this is up over 200% when compared to the same month the previous year. When the cost of textbooks and the availability of formats are considered, the use of an e-textbook in the classroom may be the reasonable choice.
—————–
A
digital textbook is a digital book or
e-book intended to serve as the text for a class. Digital textbooks may also be known as
e-textbooks or
e-texts. Digital textbooks are a major component of technology-based education reform. They may serve as the texts for a traditional face-to-face class, an online course or degree.
The concepts of
open access and
open source support the idea of
open textbooks, digital textbooks that are free (gratis) and easy to distribute, modify and update
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_textbook—————-
Exploring Students’ E-Textbook Practices in Higher Education
- Authors: by Aimee Denoyelles, John Raible and Ryan Seilhamer Published: Monday, July 6, 2015. Instructional Designers, University of Central Florida
According to the United States Government Accountability Office, prices have increased 82 percent from 2002 to 2012.3 This cost sometimes drives students to
delay or avoid purchasing textbooks. Digital materials such as e-textbooks may offer a more cost-effective alternative.
4 Also, the expectation for digital materials is gaining strength in the K–12 sector.
5 For example, Florida school districts set a goal to spend at
least half of classroom material funding on digital materials by the 2015–2016 school year. Given that 81 percent of first-time-in-college (FTIC) undergraduate students hailed from a Florida public high school during the fall 2014 semester at the University of Central Florida (UCF), it is important to anticipate student expectations of digital materials. Finally, the availability of digital materials has risen exponentially with the incredible popularity of mobile devices.
Key Issues
Despite the advantages that e-textbooks pose, such as interactive features and accessibility on mobile devices, several barriers exist regarding implementation in higher education, namely non-standardization of the platform, limited use by students, and the unclear role of the instructor in adoption.
a survey questionnaire in 2012 that explored basic usage and attitudes regarding e-textbooks.
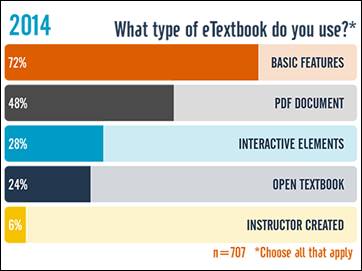
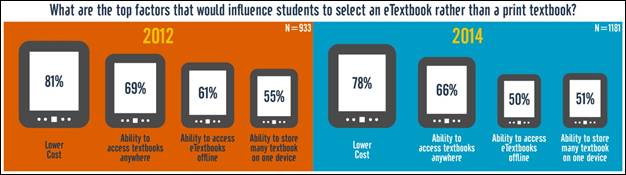
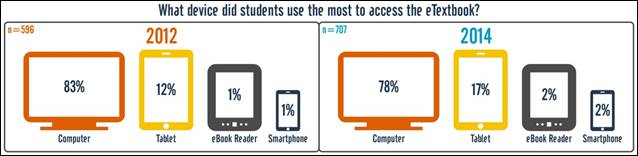
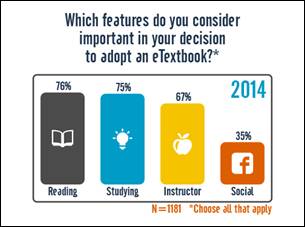

—————————–
Bossaller, J., & Kammer, J. (2014). Faculty Views on eTextbooks: A Narrative Study. College Teaching, 62(2), 68-75. doi:10.1080/87567555.2014.885877
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dkeh%26AN%3d95094045%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
Implementing eTexts into a Course:
- planning
- developing
- implementing
- delivering
This qualitative study gives insight into the experiences instructors have when working with publishers to integrate electronic content and technology into their courses.
Baek, E., & Monaghan, J. (2013). Journey to Textbook Affordability: An Investigation of Students’ Use of eTextbooks at Multiple Campuses. International Review Of Research In Open And Distance Learning, 14(3), 1-26.
http://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1017493
the Advisory Committee on Student Financial Assistance (2007) reported that textbook prices represent a significant barrier to students’ accessibility to textbooks. The report concluded that textbooks cost between $700-$1000 per year; textbook prices have risen much faster than other commodities; and that college aid fails to cover textbook expenses. Textbook costs are equivalent to 26% of tuition costs for an average four-year public university student and 72% of tuition costs for an average community college student. In fact, the California State Auditor (2008) reported that textbook costs grew more rapidly than student fees in academic year 2007–08.


++++++++++++
Wimmer, E. e., Morrow, A. a., & Weber, A. a. (2014). Collaboration in eTextbook Publishing: A Case Study.Collaborative Librarianship, 6(2), 82-86.
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dllf%26AN%3d108762075%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite

Distance education, e-learning, education and training. (2015). Clinical Chemistry & Laboratory Medicine, 53s557-s559. doi:10.1515/cclm-2015-5015
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3daph%26AN%3d102854748%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
the creation of an interactive e-book called “Practical Clinical Chemistry: core concepts” was accomplished using the
Apple Macintosh platform and the iBooks Author software. Digital content, including videos, was developed for the
project and embedded within the final package. In order to limit the size of the final files, some content was uploaded
onto Youtube so that the user could access these via the internet.
The e-book, 200MB in size, was uploaded onto the Apple ITunes site and made available in 51 countries via the
iBooks store. This prototype is the first interactive digital textbook available in clinical chemistry and contains “4-
dimensional” content including digital images, videos, interactive presentations, real-time data generation as well as
review questions with instant feedback and assessment.
Hamedi, M., & Ezaleila, S. (2015). Digital Textbook Program in Malaysia: Lessons from South Korea. Publishing Research Quarterly, 31(4), 244-257. doi:10.1007/s12109-015-9425-4
Joseph, R. (2015). Higher Education Book Publishing-from Print to Digital: A Review of the Literature. Publishing Research Quarterly, 31(4), 264-274. doi:10.1007/s12109-015-9429-0
the author reflects the process on a state level (Ohio).
Marcoux, E. “. (2012). Best of the Best Planning. Teacher Librarian, 39(4), 69-70.
Taylor, A. K. (2011). Students Learn Equally Well From Digital as From Paperbound Texts. Teaching Of Psychology, 38(4), 278-281. doi:10.1177/0098628311421330
Much of the research related to digital texts has focused ontechnical aspects of readability (see Dillon, 1992, for a review) and limitations of digital media for note-taking, underlining, or highlighting text (Brown, 2001). However, the important—and unanswered—question from a teaching perspective is, ‘‘Can students learn as well from digital texts as from paperbound textbooks?’’ Few published studies have addressed this ques-tion directly, and even fewer studies have examined this ques-tion among college students.
Murray, M. C., & Pérez, J. (2011). E-Textbooks Are Coming: Are We Ready?. Issues In Informing Science & Information Technology, 849-60.
read the entire article, good data.
CourseSmart. FlatWorld Knowledge,
Horejsi, M. (2014). Textbooks 2.0. Science Teacher, 81(3), 8. http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3daph%26AN%3d94603788%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
++++++++++++++
pedagogy
two Eastern Europeans (Moldova, Serbia) raise serious concerns about electronic textbooks
Španović, S. (2010). PEDAGOGICAL ASPECTS OF E-TEXTBOOKS. Odgojne znanosti. 12(2). 459-470.
Railean, E. (2015). https://prezi.com/sbidiadctrzo/beyond-textbook-digital-textbook-use-and-development/
http://www.governance.ualberta.ca/en/GeneralFacultiesCouncil/CommitteeontheLearningEnvironm/~/media/Governance/Documents/GO05/LEA/15-16/WEB/Item-4-eTextbook-Subcommittee-Report-CLE-TLAT.pdf :
- (Un)desirable features in etextbooks
- How etextbooks might affect course delivery
- Pilot projects that can help build institutional expertise
- Address how and where insights gained from pilot projects will be collected and
- made available
- People resources (e.g., instructional designers) that will be needed to assist
- instructors to use this technology
ICWL (Conference) (13th : 2014 : Tallinn, E., & Cao, Y. (2014). New horizons in web based learning: ICWL 2014 international workshops, SPeL, PRASAE, IWMPL, OBIE, and KMEL, FET, Tallinn, Estonia, August 14-17, 2014, revised selected papers. Cham: Springer.
++++++++++++++++++++
MnSCU will by as Content Authoring Tool – SoftChalk. Here is a promo from Softchalk (my bold):
NEW SoftChalk Create 10 and SoftChalk Cloud eBook publishing features will arrive on April 25th! Come check out the latest enhancements at our upcoming webinars!
Sleek Designer Headers and Callout Boxes – Add some new pizazz to your SoftChalk lessons!
Three New Quiz Types – Test your students’ understanding with Sentence Completion, Multiple Blanks and Feedback Questions.
Polished New QuizPopper and Activity displays – With an enhanced interface for instructors and students.
Accessibility enhancements – Make your lessons available to everyone with even more accessibility enhancements.
NEW SoftChalk Cloud eBook creation and publishing – Includes a totally re-vamped, easier eBook creation and management. New SoftChalk eReader apps available for free download in the iOS, Android, Chromebook and Windows app stores. (Cloud Only)
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
The future of textbooks looks like this
February 22nd, 2016
are any faculty really going digital? Which content distributors will thrive? What are the implementation concerns? And when will going digital really happen?
two massive surveys and reports by the National Association of College Stores (NACS) and the Independent College Bookstore Association (ICBA) in partnership with the Campus Computing Survey (CCS),
Universal Design for Libraries and Librarians
Instructors: Jessica Olin, Director of the Library, Robert H. Parker Library, Wesley College; and Holly Mabry, Digital Services Librarian, Gardner-Webb University
Offered: April 11 – May 27, 2016
A Moodle based web course with asynchronous weekly content lessons, tutorials, assignments, and groups discussion.
Register Online, page arranged by session date (login required)
Universal Design is the idea of designing products, places, and experiences to make them accessible to as broad a spectrum of people as possible, without requiring special modifications or adaptations. This course will present an overview of universal design as a historical movement, as a philosophy, and as an applicable set of tools. Students will learn about the diversity of experiences and capabilities that people have, including disabilities (e.g. physical, learning, cognitive, resulting from age and/or accident), cultural backgrounds, and other abilities. The class will also give students the opportunity to redesign specific products or environments to make them more universally accessible and usable.
Takeaways
By the end of this class, students will be able to…
- Articulate the ethical, philosophical, and practical aspects of Universal Design as a method and movement – both in general and as it relates to their specific work and life circumstances
- Demonstrate the specific pedagogical, ethical, and customer service benefits of using Universal Design principles to develop and recreate library spaces and services in order to make them more broadly accessible
- Integrate the ideals and practicalities of Universal Design into library spaces and services via a continuous critique and evaluation cycle
Here’s the Course Page
Jessica Olin is the Director of the Library, Robert H. Parker Library, Wesley College. Ms. Olin received her MLIS from Simmons College in 2003 and an MAEd, with a concentration in Adult Education, from Touro University International. Her first position in higher education was at Landmark College, a college that is specifically geared to meeting the unique needs of people with learning differences. While at Landmark, Ms. Olin learned about the ethical, theoretical, and practical aspects of universal design. She has since taught an undergraduate course for both the education and the entrepreneurship departments at Hiram College on the subject.
Holly Mabry received her MLIS from UNC-Greensboro in 2009. She is currently the Digital Services Librarian at Gardner-Webb University where she manages the university’s institutional repository, and teaches the library’s for-credit online research skills course. She also works for an international virtual reference service called Chatstaff. Since finishing her MLIS, she has done several presentations at local and national library conferences on implementing universal design in libraries with a focus on accessibility for patrons with disabilities.
Dates:
February 29 – March 31, 2016
Costs:
- LITA Member: $135
- ALA Member: $195
- Non-member: $260
Technical Requirements:
Moodle login info will be sent to registrants the week prior to the start date. The Moodle-developed course site will include weekly new content lessons and is composed of self-paced modules with facilitated interaction led by the instructor. Students regularly use the forum and chat room functions to facilitate their class participation. The course web site will be open for 1 week prior to the start date for students to have access to Moodle instructions and set their browser correctly. The course site will remain open for 90 days after the end date for students to refer back to course material.
Registration Information:
Register Online, page arranged by session date (login required)
OR
Mail or fax form to ALA Registration
OR
call 1-800-545-2433 and press 5
OR
email registration@ala.org
Making Media Accessible by Adding Captions and Audio
To register for one or both of these Webinars, go to http://easi.cc/clinic.htm
EASI Webinar part 1: Making Media Accessible by Adding Captions and Audio
Presenter: Susanne Van Dorpe Mistric, Instructor/Coordinator Distance Learning – Individualized Learning Center Wade Technical Community College
Monday Feb. 1 at 11 Pacific, noon Mountain, 1 Central and 2 PM Eastern
Susanne provides beginner-level training for WTCC staff on adding captions and audio description to Media. The goal is to take people with little technical skill in how to create descriptions of audio content and then synchronize it with the media. Students also need to be aware of how ane when to add audio descriptions as well
EASI Webinar part 2: Making Media Accessible by Adding Captions and Audio
Presenter: Susanne Van Dorpe Mistric, Instructor/Coordinator Distance Learning – Individualized Learning Center Wade Technical Community College
Monday Feb. 8 at 11 Pacific, noon Mountain, 1 Central and 2 PM Eastern
Susanne provides more advanced-level training for WTCC staff who already have the basic awareness of accessibility and familiarity with the tools to provide this. This will enhance their awareness of how and when to add accessible features especially to meet the requirements of content in more advanced courses.
More on the subject in this IMS blog entry:
subtitles screencast coursecapture
According to the Team 5 meeting notes of 9/22/2015, presented to the library administration, under individual updates, e. Pedagogy, Active Learning/Interactivity/Focused Engagement, there are six points, including ‘flipped classroom,’ as proposed by Chris Inkster, but nothing about my proposal, which can be outlined as “changing the pedagogy of library instruction to fit the increased environment of mobile devices.” It makes the absence of my proposal even more bizarre considering that:
– during a meeting of Team 5 on Sept 23, I was questioned about my proposal and i delivered renewed explainations
– the webinar ONLINE GENERATION IS TRANSFORMING LIBRARIES: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/09/22/online-generation-is-transforming-libraries/, as referred by Chris Inkster, is discussing exactly the need of pedagogical changes proposed by me.
Thus, since past proposals submitted by me were cut/ignored in a similar fashion as well as this one, I am formally entering it in a medium, which will bear the time stamp and the seal, so my proposal is not bastardized in the future and everyone can refer to the original idea, shall misunderstandings occur.
From: Miltenoff, Plamen
Sent: Monday, September 21, 2015 5:33 PM
To: Inkster, Christine D. <cinkster@stcloudstate.edu>; Gruwell, Cindy A. <cagruwell@stcloudstate.edu>; Gorman, Michael S. <msgorman@stcloudstate.edu>; Hubbs, Susan <shubbs@stcloudstate.edu>
Subject: Miller Center 218 – Remodel – TWO Questions
Good evening,
I will pick up from the correspondence below and share my thoughts thereafter.
- Several weeks ago, Cisco announced a technology, which will allow the institutional IT to assign preference of teaching content over personal usage. In my understanding, the news signals that questions about accessibility need to be accordingly rephrased. It also craves transparency on the SCSU IT.
- I have difficulties following Henry May’s ideas because of: 1. Lack of transparency and 2. Lack of didactical understanding.
The quintessential disparity (cart in front of the ox) is that from the emails below, it seems that the technology is driving didactic. If I need to prove that pedagogy drives technology, not vice versa, then there is a profound problem. I will assume that everyone agrees with pedagogy being in the center and technology is serving it. In that sense, this team and any other faculty unit trying to line up their curricular process to Henry’s vision, becomes preposterous; Henry is the one who has to be listening to the faculty and serve them.
Therefore, trying to adjust [long-term]future plans about pedagogy, by asking technology questions first, is in its best limiting. One needs to come up with a didactic frame and ask the responding questions how to furbish such frame with technology. If one assumes, as it is claimed, that this campus is moving to m-learning (mobile learning), BYOD, BYOx or any other fancy acronym, which de facto reflects the preponderance of mobile devices as main gateway to information used by students, then the pedagogy must be [re]designed for m-learning. In that sense, from a pedagogical point of view, I find perplexing focusing on MC 218 and subduing BYOD/x/mobile learning to the pedagogy, which will be exercised in a room ( MC 218). How is it mobile? Using mobile devices in room full with desktops does not make sense to me. Keep teaching a dynamic content such as library instruction in a confined room, also does not make sense to me.
Here is how I see the pedagogical reconsideration of library instruction must be considered.
In April 214, I proposed a plan, adopted from a Chicago librarian:
http://web.stcloudstate.edu/pmiltenoff/bi/
the plan reflects one of numerous possibilities to change the pedagogy of lecturing in a room (MC 218) to hands-on, real-life construct of knowledge by students on their own (constructivism). The pedagogical foundation is based on the use of personal mobile devices (BYOx), which renders the issue of MC 218 accessibility by wi fi as non-significant, since the hit on the wi fi network will be evenly distributed across the entire building.
The example above is only one of many on curriculum that needs to be changed by adopting gaming and gamification techniques:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/03/19/recommendations-for-games-and-gaming-at-lrs/
the essence of library instruction needs to change from lecturing to facilitation and consultations of students’ own construct and discovery how the library works and can help them; it needs to be a F2F rehearsal of students-librarian virtual relationship, which later on can guide and help students individually then in groups.
In that sense, MC 218 can/should to be considered a hub for activities, which mostly take place across the library. MC 218 can be the center place, where in-depth exercises are performed. Exercises, which require either: 1. Stronger processing power, 2. Intensive typing, or 3. Larger screens. While it needs to be further surveyed, I believe that MC 218 needs to have prevalent presence of dock-type of stations (recharge, dongles to connect to large screens) and other peripherals which can allow students to connect their laptops, tablets and mobile devices, then desktops.
Thank you.
Plamen
These six categories are:
- Textual Works and Musical Compositions
- Still Image Works
- Audio Works
- Moving Image Works
- Software and Electronic Gaming and Learning
- Datasets/Databases
From: Scanlon, Donna [mailto:dscanlon@loc.gov]
Sent: Tuesday, June 24, 2014 6:34 AM
To: ‘lita-l@ala.org’
Subject: [lita-l] Library of Congress Recommended Format Specifications
The Library of Congress announces the availability of its Recommended Format Specifications, a document describing the hierarchies of the physical and technical characteristics of creative formats, both analog and digital, which will best maximize the chances for preservation and continued accessibility of creative content. Creators and publishers have also begun to employ a wide array of intangible digital formats, as well as continuing to change and adapt the physical formats in which they work. The Library needs to be able to identify the formats which are suitable for large-scale acquisition and preservation for long-term access if it is to continue to build its collection and ensure that it lasts into the future.
The Library was able to identify six basic categories of creative output, which represent significant parts of the publishing, information, and media industries, especially those that are rapidly adopting digital production and are central to building the Library’s collections: Textual Works and Musical Compositions; Still Image Works; Audio Works; Moving Image Works; Software and Electronic Gaming and Learning; and Datasets/Databases. Technical teams, made up of experts came from across the institution bringing specialized knowledge in technical aspects of preservation, ongoing access needs and developments in the marketplace and in the publishing world, were established to identify recommended formats for each of these categories and to establish hierarchies of preference among the formats within them.
The Library will be revisiting these specifications on an annual basis. The creation and publication of these recommended format specifications is not intended to serve as an answer to all the questions raised in preserving and providing long-term access to creative content. They do not provide instructions for receiving this material into repositories, managing that content or undertaking the many ongoing tasks which will be necessary to maintain this content so that it may be used well into the future.
The Recommended Format Specifications are available at http://www.loc.gov/preservation/resources/rfs/. For more information, please contact Ted Westervelt [thwe@loc.gov].
Donna Scanlon
Electronic Resources Coordinator
Library of Congress
101 Independence Ave., SE
Washington, DC 20540
eMail: dscanlon@loc.gov
Phone: (202) 707-6235
http://eresources.loc.gov







