Tenure Track Position in Gamification Tampere University of Technology
http://www.computeroxy.com/announcement,a2945.html
Tampere University of Technology (TUT) is an active scientific community of 2,000 employees and more than 10,000 students. The University operates in the form of a foundation and has a long-standing tradition of collaboration with other research institutions and business life. Many of the fields of research and study represented at the University play a key role in addressing global challenges. Internationality is an inherent part of all the University’s activities. Welcome to join us at TUT!
The University of Turku is a world-class multidisciplinary research university which offers interesting challenges and a unique vantage point to national and international research and education.
Tenure track (Gamification)
The tenure track position is shared between Tampere University of Technology and the University of Turku. It supports the co-operation in teaching and research in the area of gamification between the two universities.
The professorship is especially associated with the TUT Game Lab (Pori Department, TUT) and the Digital Culture research group of the Cultural Production and Landscape Studies degree programme (School of History, Culture and Arts Studies, UTU). These research groups currently have five on-going research projects related to games and playing.
The TUT Game Lab brings together learning scientists, developers and humanists to conduct research and develop new ways of utilizing games in learning. The aim is to develop and study high-impact digital games that address real world challenges.
The main research objectives of TUT Game Lab are:
– Developing scientifically justified games to demonstrate and conduct research
– Studying the impact of educational games
– Exploring ways to combine learning and assessment in games
– Studying and modelling the playing experience
The Digital Culture research group (UTU) has three research focuses:
– cultural appropriation of technologies
– social media
– game cultures.
The Digital Culture research group specializes in the study of the cultural history of digital games and the uses of digital game histories in contemporary culture (so-called “history culture”). Furthermore, the research group has participated in various digital game exhibition projects as well as practical game design and gamification projects combining digital and non-digital elements. Digital Culture is a part of the Cultural Production and Landscape Studies degree programme which also incorporates two other major subjects: Cultural Heritage Studies and Landscape Studies.
Job description:
We invite applications for one (1) tenure track position in the area of Gamification.
The area of gamification covers:
– research of games and gamification
– games and playing as a cultural phenomenon
– game mechanisms, edugames and pervasive playing
– utilization of games in business, e.g. in new products and services
The emphasis of the position can be tailored according to the specific expertise of the candidate. Suitable educational and research backgrounds for the position include e.g. media studies, cultural studies, information technology and business and management.
The successful candidate is expected to:
– pursue and supervise scientific research in the field
– lead, conduct and develop education in the field
– participate in the activities of the national and international scientific communities
– acquire external funding
– interact with society
– commit to the strategies of TUT and UTU.
The successful candidate will participate in teaching both in the master’s degree programme in Management and Information Technology (TUT) as well as the subject of Digital Culture (UTU) by integrating the gamification theme into the existing course selection, in particular. Supervising theses and conducting doctoral seminars are also essential areas of responsibility.
The position will be filled at the level of Associate Professor.
The successful candidate will be employed by TUT. For more information on TUT’s tenure track career system, please refer to tut.fi/openpositions – Tenure track.
Requirements:
All candidates considered for a tenure track position are expected to:
– hold an applicable doctoral degree
– demonstrate a record of achievement in research that meets high international standards in the field of gamification
– demonstrate the capacity for independent scholarly activity
– possess the teaching skills required for the successful performance of their duties and
– have the ability to co-operate in a multidisciplinary university environment and with industry.
We appreciate experience and a track record in acquiring research funding, along with collaboration and leadership positions in research networks and industry.
For more information on the criteria for each level of TUT’s tenure track, please refer to tut.fi/openpositions – Tenure track.
We offer:
Both TUT and UTU have ambitious and challenging goals in effective, high-quality research, education and social influence. We offer an active research community with a good team spirit, intense cooperation with industry and business, public organizations and students, and opportunities for growth and advancement in academia. Our international cooperation is active and recognized, both in research and education.
We offer the successful candidate an opportunity to contribute to the creation of a new research area that combines gamification with areas such as cultural studies, information technology and business.
TUT offers a wide range of staff benefits, such as occupational health care. Since 2014, TUT has held the European Commission HR Excellence in Research recognition.
For more information, please visit tut.fi/en – About TUT – Careers at TUT
(http://www.tut.fi/en/about-tut/careers-at-tut/index.htm)
(http://www.tut.fi/en/about-tut/quality-assurance/hr-excellence-in-research)
Salary:
The salary will be based on both the job demands and the employee’s personal performance in accordance with the Finnish University Salary System (YPJ).
The advertised position is typically placed on the job demand level 7 (Associate Professor). In addition, the employees receive performance-based salary and they are covered by TUT’s bonus system.
Trial period:
The appointment is subject to the satisfactory completion of a trial period of four months.
Other:
The position will be filled for a fixed-term period of four years. The appointment is expected to begin on 1 December 2016 or as mutually agreed.
The duties are mainly located on the Pori campus in close co-operation with the main campuses in Tampere and Turku.
For the candidates with the most potential for the position, the selection process will involve an external assessment, individual interviews, aptitude assessments and a trial lecture.
For more information, please contact:
Director of University Consortium of Pori, Professor Jari Multisilta, e-mail: jari.multisilta@tut.fi, tel. +358 40 826 2910. Best availability for enquiries: 7 July–15 July and 1 August- 10 August.
In questions concerning the recruitment process, please contact HR Specialist
Eveliina Nurmi, e-mail. eveliina.nurmi@tut.fi, tel. +358 50 3015253. Best availability for enquiries: 15 June – 8 July and 8 August-10 August.
How to apply:
Applications must be submitted through TUT’s online employment system. The closing date for applications is 10 August 2016 (10:00 pm UTC). All applications and supporting documents must be submitted in English.
The applications must include the following documents prepared according to TUT’s instructions:
1. Curriculum Vitae (.doc or .pdf)
2. Research plan
3. List of publications
4. Teaching portfolio
5. References
Additional information on TUT’s tenure track system and attachments to applications.
Webinar: Text and Data Mining: The Way Forward, June 30, 10am (EDT)
LITA announcement. Date: Thursday, June 30, 2016, Time: 10am-11:30am (EDT), Platform: WebEx. Registration required.
a critically important means of uncovering patterns of intellectual practice and usage that have the potential for illuminating facets and perspectives in research and scholarship that might otherwise not be noted. At the same time, challenges exist in terms of project management and support, licensing and other necessary protections.
Confirmed speakers include: Audrey McCulloch, Executive Director, ALPSP; Michael Levine-Clark, Dean of Libraries, University of Denver; Ellen Finnie, Head, Scholarly Communications and Collections Strategies, Massachusetts Institute of Technology; and Jeremy Frey, Professor of Physical Chemistry, Head of Computational Systems Chemistry, University of Southampton, UK.
Audrey McCulloch, Chief Executive, Association of Learned Professional and Society Publishers (ALPSP) and Director of the Publishers Licensing Society
Text and Data Mining: Library Opportunities and Challenges
Michael Levine-Clark, Dean and Director of Libraries, University of Denver
As scholars engage with text and data mining (TDM), libraries have struggled to provide support for projects that are unpredictable and tremendously varied. While TDM can be considered a fair use, in many cases contracts need to be renegotiated and special data sets created by the vendor. The unique nature of TDM projects makes it difficult to plan for them, and often the library and scholar have to figure them out as they go along. This session will explore strategies for libraries to effectively manage TDM, often in partnership with other units on campus and will offer suggestions to improve the process for all.
Michael Levine-Clark, the Dean and Director of the University of Denver Libraries, is the recipient of the 2015 HARRASOWITZ Leadership in Library Acquisitions Award. He writes and speaks regularly on strategies for improving academic library collection development practices, including the use of e-books in academic libraries, the development of demand-driven acquisition models, and implications of discovery tool implementation.
Library licensing approaches in text and data mining access for researchers at MIT
Ellen Finnie, Head, Scholarly Communications & Collections Strategy, MIT Libraries
This talk will address the challenges and successes that the MIT libraries have experienced in providing enabling services that deliver TDM access to MIT researchers, including:
· emphasizing TDM in negotiating contracts for scholarly resources
· defining requirements for licenses for TDM access
· working with information providers to negotiate licenses that work for our researchers
· addressing challenges and retooling to address barriers to success
· offering educational guides and workshops
· managing current needs v. the long-term goal– TDM as a reader’s right
Ellen Finnie is Head, Scholarly Communications & Collections Strategy in the MIT Libraries. She leads the MIT Libraries’ scholarly communications and collections strategy in support of the Libraries’ and MIT’s objectives, including in particular efforts to influence models of scholarly publishing and communication in ways that increase the impact and reach of MIT’s research and scholarship and which promote open, sustainable publishing and access models. She leads outreach efforts to faculty in support of scholarly publication reform and open access activities at MIT, and acts as the Libraries’ chief resource for copyright issues and for content licensing policy and negotiations. In that role, she is involved in negotiating licenses to include text/data mining rights and coordinating researcher access to TDM services for licensed scholarly resources. She has written and spoken widely on digital acquisitions, repositories, licensing, and open access.
Jeremy Frey, Professor of Physical Chemistry, Head of Computational Systems Chemistry, University of Southampton, UK
Text and Data Mining (TDM) facilitates the discovery, selection, structuring, and analysis of large numbers of documents/sets of data, enabling the visualization of results in new ways to support innovation and the development of new knowledge. In both academia and commercial contexts, TDM is increasingly recognized as a means to extract, re-use and leverage additional value from published information, by linking concepts, addressing specific questions, and creating efficiencies. But TDM in practice is not straightforward. TDM methodology and use are fast changing but are not yet matched by the development of enabling policies.
This webinar provides a review of where we are today with TDM, as seen from the perspective of the researcher, library, and licensing-publisher communities.
| Please develop a one hour workshop for faculty on using a new (or old but new to them) technology tool. The aim is not to only show the technical operation, but the pedagogical use of the tool helping faculty think about what this might mean in their own teaching.
Short link: : http://bit.ly/UNCGpres
Alternatives to the pedagogical use of BYOD
Who: students, faculty and staff
Where: TBD
When: Friday, June 17, 2016. 10-11:30 AM |
 |
5 min introduction of workshop presenter Plamen Miltenoff and workshop participants
5 min plan of the workshop
5 min introduction to the topic:
Outline
In financially-sparse times for educational institutions, one viable way to save money is by rethinking pedagogy/methodology and adapt it to the burgeoning numbers of mobile devices (BYOD) owned by students, faculty and staff.
In 5 min,
we will be playing a game, using Kahoot (https://kahoot.it). Kahoot is an application from Norway, which is increasingly popular in K12 and gradually picking momentum at higher ed.
Why Kahoot and not any of the other similar polling apps (AKA formative assessment tools), such as PollEverywhere, PollDaddy etc. (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/01/13/formative-assessment-tools/)?
1. Kahoot has gained momentum; at least one third of your undergraduates have used it in high school and are familiar with the interface.
2. I personally like Kahoot for the kahoots. J
3. I like badges as “badges in gamification.” Let me know, if you want to work on this topic some other time and lets schedule work time after this session (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=badges).
In 10-15 min,
lets try to create an account and build our first kahoot (https://getkahoot.com/). You can use any topic and focus on the features, which Kahoot provides. Split in groups and help each other; if you feel stuck, please let me know and I will do my best to help advance further.
Here are two YouTube lectures how to create an account and a kahoot quiz (5 min) and how to play a kahoot (3 min): https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/06/13/how-to-kahoot/
In 5-10 min,
let’s display 1-2 kahoot’s to the entire audience and think about situations, when and where such kahoots can be used for educational purposes.
Let’s think about the implications, which the use of kahoots on BOYD may trigger in the classroom
Let’s think about the preparation needed for the smooth use of the kahoots (is your WiFi in that particular classroom robust enough to hold the action of 20? 200? Students?
Let’s think about students’ engagement: what constitutes it? would a kahoot on their BYOD will be sufficient to pick their interest and if not, what else must be added to the magic elixir?
In 5 min, lets discuss Kahoot’s similarities with other educational technologies used in the classroom
Let’s assess the potential of Kahoot.
how does it compare
how does it transfer
is it compatible with Canvas
4 Great Curation Tools Created by Teachers for Teachers
http://www.educatorstechnology.com/2016/04/4-great-digital-curation-tools-created.html
April 28, 2016
Edshelf
Edshelf is ‘a socially curated discovery engine of websites, mobile apps, desktop programs, and electronic products for teaching and learning. You can search and filter for specific tools, create shelves of tools you use for various purposes, rate and review tools you’ve used, and receive a newsletter of tools recommended by other educators.
Graphite
a free service from nonprofit Common Sense Education designed to help preK-12 educators discover, use, and share the best apps, games, websites, and digital curricula for their students by providing unbiased, rigorous ratings and practical insights from our active community of teachers
Scoop.it
find out content related to your topics by ‘reviewing your suggestion lists and the topics from other curators
educlipper
social learning platform that allows teachers to curate and share educational content. Some of the interesting features it provides include: ‘Explore top quality education resources for K-12, create clips from the web, Drive, Dropbox, use your camera to capture awesome work that you create in and out of the classroom, create whiteboard recordings, create differentiated groups and share content with them, create Personal Learning Portfolios, create Class Portfolios as a teacher and share Assignments with students, provide quality feedback through video, audio, text, badges, or grades, collaborate with other users on eduClipboards for class projects or personal interests
High Performance Wi-Fi For Today’s Digital Education
Seamless and robust mobile connectivity is a must have in today’s education environment. More student mobile devices, higher performance data rates, greater capacity demands, increasing on-line curriculum and testing require enterprise grade Wi-Fi reliability without the complexities and on-going maintenance. It has to be simple and it has to just work.
In this webinar, you will hear case studies from three different schools, each with their own specific wireless needs, how they addressed them and what recommendation they would each have to ensure your wireless project goes smoothly.
Thank you for registering for High Performance Wi-Fi For Today’s Digital Education. Save this email for details on the webcast.
LIVE WEBCAST DATE: April 07, 2016
LIVE WEBCAST TIME: 02:00 PM EDT
Use the link below to enter the webcast up to 15 minutes before the start.
WEBCAST LINK: http://event.on24.com/wcc/r/1160276/320EAD217540BD94C9056C12601219C3
Vinson Houston
Vice President for Information Technology, Jacksonville State University
 Since 2008, Mr. Vinson Houston has served as vice president for information technology at Jacksonville State University. Prior to that, Mr. Houston served as Director of Telecommunications for JSU, beginning in 2005. Mr. Houston currently serves on the board of directors for the Alabama Supercomputer Authority and is on the CORE Executive Committee that leads initiatives promoting PK-20 collaboration related to using new technologies in the classroom. He holds a B.A. and an M.B.A. from Jacksonville State University.
Since 2008, Mr. Vinson Houston has served as vice president for information technology at Jacksonville State University. Prior to that, Mr. Houston served as Director of Telecommunications for JSU, beginning in 2005. Mr. Houston currently serves on the board of directors for the Alabama Supercomputer Authority and is on the CORE Executive Committee that leads initiatives promoting PK-20 collaboration related to using new technologies in the classroom. He holds a B.A. and an M.B.A. from Jacksonville State University.
Kris Keckler
Executive Director of Information and Accountability, KUSD

Kenosha Unified School District (KUSD) is the 3rd largest district in Wisconsin, with over 40 schools. KUSD’s mission is to provide excellent, challenging learning opportunities and experiences that prepare each student for success. From this role, Kris has the pleasure of directly guiding both the Office of Educational Accountability and the Information Services Department. Kris is a strong advocate for promoting quality integration of technology and data for staff and students alike.
Angela Becker
Network Manager, KUSD

Angela Becker is the Network Manager for Kenosha Unified School District. KUSD serves over 22,200 students and 3,000 staff. Angela supports and maintains the network and wireless infrastructure for 40 district sites which includes a 10Gb internal fiber ring, over 950 access points and 700 network switches as well as provides application and online testing support for the district.
Alex Ender
Network and Systems Administrator, Everest Academy

As the Network and Systems Administrator at Everest Academy, Alex is responsible for planning and implementing network and server upgrades. He has worked both as an administrator and technician for the past 4 years. Never one for a dull moment, Alex also monitors and maintains multiple client networks as a consultant.
purpose: draft a document for the provost to plan for charting the future goal 3.12 “develop a comprehensive strategy to increase awareness and development of e-textbooks and open educational resources (OERs)”
\\STCLOUDSTATE\HuskyNet\DeptFiles\LRS\ETextbooks
SCSU goal: to reduce the cost of textbooks as an affordable learning initiative. Amount of reduction is undetermined
my notes based on the material below:
- best, most applicable source for the purpose of this research: U of Alberta Committee’s notes on the learning environment:
http://www.governance.ualberta.ca/en/GeneralFacultiesCouncil/CommitteeontheLearningEnvironm/~/media/Governance/Documents/GO05/LEA/15-16/WEB/Item-4-eTextbook-Subcommittee-Report-CLE-TLAT.pdf
the Canadians are using (citing) Acker (Ohio) in their research.
- best, most applicable source in terms of the logistics on e-texbooks creation and its pedagogical argumentation is this document from New Zealand: https://akoaotearoa.ac.nz/download/ng/file/group-7/guidelines-for-developing-interactive-etextbooks-on-net-tablets.pdf
- According to Bossaler et al (2014), it might be worth considering that SCSU (MnSCU?) must go first through implementing of e-text[books] in courses first by using publisher materials and then by using “in-house” produce. At this point, SCSU does NOT have an aligned policy of integrating e-texts in courses across campus. Lack of such experience might make a strategy for adoption of e-textbooks much more complex and difficult to implement
- stats are colored in green for convenience. Stats regarding the increase in textbook costs are re-printed from author to author: e.g. Acker (2011, p. 42). Murey and Perez (2011, p. 49 (bottom) – 50 (up)) reports stats from 2009 and projections for 2013 regarding etexbook adotion. Same authors, p. 50 second paragraph reports good stats regarding texbooks’ price increase : US$1122 per year for textbooks in 2010.
- Wimmer at al (2014) presents a lucid graphic of the structure of the publishing process (see bottom of this blog entry for citation and perm link).
- Wimmer at al (2014) discusses copyright and permissions, which is of interest for this research (p. 85)
- regarding in-house creation of e-textbooks, see (Distance education, e-learning, education and training, 2015). It very much follow the example of SUNY, which Keith was laying out: a team of faculty charged with creation the e-textbook for mass consumption.
Besides the SUNY model Keith is envisioning for MnSCU (comparable), there is the option of clustering OER sources: e.g. NASTA as per Horejsi (2013), CourseSmart. FlatWorld Knowledge (Murrey and Perez, 2011) etc.
- Hamedi & Ezaleila (2015) present an entire etextbook program. Article has been ordered through ILL. Same with Joseph (2015).
- Open Educational Resources in Acker (2015, p. 44-47). Also in Murey and Perez (2011, p. 51).
Also in ICWL (Conference) (13th : 2014 : Tallinn, E., & Cao, Y. (2014): OpenDSA
- Different models of pricing also in Acker (2015, p. 48). Keith touched on that
- students learn equally well from etextbooks as from paper ones: Taylor (2011)
- pedagogy
responses from colleagues:
Scott Robison, sarobison@mail.plymouth.edu: sparc-liboer@arl.org listserv
Jeff Gallant, Jeff.Gallant@usg.edu: David Ernst with the U and Ashley Miller from Ohio State U: dernst@umn.edu. Ashley’s is miller.6275@osu.edu.
definition e-textbook and
an electronic version of a printed book that can be read on a computer or handheld device designed specifically for this purpose.
-
a dedicated device for reading electronic versions of printed books.
Definition of: e-book
my note: there is no good definition about e-textbook in terms of the complexity, which e-textbook on campus might involve.
Considering Wimmer et al (2014) account on their campus experience in publishing e-textbook, a textbook may involve an LMS (Canvas) and blog (WordPress). Per my proposal during the F2F meeting, and following Rachel’s suggestion about discrimination of the different types of e-textbooks, here is an outline of e-textbook definition:
*******************
working definition for e-textbook for the purposes of SCSU:
e-textbook is a compilation of textual, multimedia and interactive material, which can be viewed on various electronic devices. E-textbook can: 1. be purchased from a publisher; 2. compiled in HTML format on faculty or group web space; 3. compiled on the content module of LMS (BB, D2L, Canvas, Moodle, etc.) 4. compiled on LMS (BB, D2L, Canvas, Moodle, etc.) and including all interactive materials: e.g. hyperlinks to MediaSpace multimedia, quizzes, etc.; 5. compiled on special apps, such as iBook Author, eCub, Sigil.
*******************
e-book
(Electronic-BOOK) The electronic counterpart of a printed book, which can be viewed on a desktop computer, laptop, smartphone, tablet or e-book reader (e-reader). When traveling, a huge number of e-books can be stored in portable units, dramatically eliminating weight and volume compared to paper. Electronic bookmarks make referencing easier, and e-book readers may allow the user to annotate pages.
Although fiction and non-fiction books come in e-book formats, technical material is especially suited for e-book delivery because it can be searched. In addition, programming code examples can be copied, which is why CD-ROMs that contained examples or the entire text were often packaged inside technical paper books.
E-Book Formats
Wimmer, Morrow, & Weber: Collaboration in eTextbook Publishing
There are several e-book formats on the market, including EPUB, Mobipocket (PRC, MOBI), eReader (PDB), Kindle (AZW, KF8) and Apple iBook (EPUB variation). Many e-readers also accept generic formats, including Adobe PDF and plain text (TXT).
——————
Electronic Textbooks or Paper Textbooks: What Are Students Reading?
According to a United States Government report, textbook prices have increased at over twice the rate of inflation in the last couple of decades. According to another report, the average student spends between $700 and $1,000 per year on textbooks while the cost of e-textbooks can be as much as 50% lower than paper textbooks.
Oxford dictionary, an electronic book or e-book is “an electronic version of a printed book that can be read on a computer or handheld device designed specifically for this purpose.” An e-textbook is defined as an e-book used for instructional or educational purposes and often includes features such as bookmarking, searching, highlighting, and note-taking as well as built-in dictionaries and pronunciation guides, embedded video-clips, embedded hyperlinks, and animated graphics.
E-textbooks have moved from occasional usage to a mainstream technology on college campuses. According to the Association of American Publishers, sales of e-books hit over $90 million; this is up over 200% when compared to the same month the previous year. When the cost of textbooks and the availability of formats are considered, the use of an e-textbook in the classroom may be the reasonable choice.
—————–
A
digital textbook is a digital book or
e-book intended to serve as the text for a class. Digital textbooks may also be known as
e-textbooks or
e-texts. Digital textbooks are a major component of technology-based education reform. They may serve as the texts for a traditional face-to-face class, an online course or degree.
The concepts of
open access and
open source support the idea of
open textbooks, digital textbooks that are free (gratis) and easy to distribute, modify and update
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_textbook—————-
Exploring Students’ E-Textbook Practices in Higher Education
- Authors: by Aimee Denoyelles, John Raible and Ryan Seilhamer Published: Monday, July 6, 2015. Instructional Designers, University of Central Florida
According to the United States Government Accountability Office, prices have increased 82 percent from 2002 to 2012.3 This cost sometimes drives students to
delay or avoid purchasing textbooks. Digital materials such as e-textbooks may offer a more cost-effective alternative.
4 Also, the expectation for digital materials is gaining strength in the K–12 sector.
5 For example, Florida school districts set a goal to spend at
least half of classroom material funding on digital materials by the 2015–2016 school year. Given that 81 percent of first-time-in-college (FTIC) undergraduate students hailed from a Florida public high school during the fall 2014 semester at the University of Central Florida (UCF), it is important to anticipate student expectations of digital materials. Finally, the availability of digital materials has risen exponentially with the incredible popularity of mobile devices.
Key Issues
Despite the advantages that e-textbooks pose, such as interactive features and accessibility on mobile devices, several barriers exist regarding implementation in higher education, namely non-standardization of the platform, limited use by students, and the unclear role of the instructor in adoption.
a survey questionnaire in 2012 that explored basic usage and attitudes regarding e-textbooks.
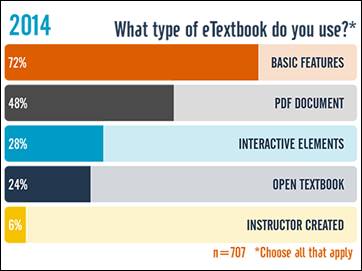
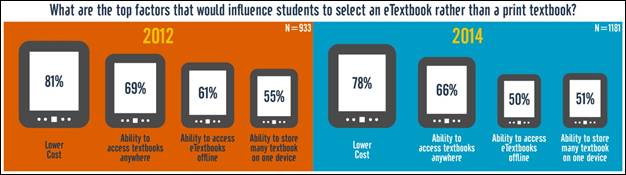
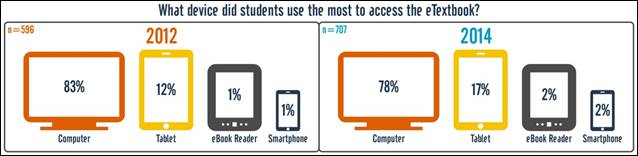
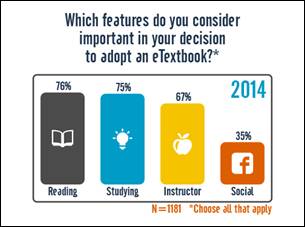

—————————–
Bossaller, J., & Kammer, J. (2014). Faculty Views on eTextbooks: A Narrative Study. College Teaching, 62(2), 68-75. doi:10.1080/87567555.2014.885877
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dkeh%26AN%3d95094045%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
Implementing eTexts into a Course:
- planning
- developing
- implementing
- delivering
This qualitative study gives insight into the experiences instructors have when working with publishers to integrate electronic content and technology into their courses.
Baek, E., & Monaghan, J. (2013). Journey to Textbook Affordability: An Investigation of Students’ Use of eTextbooks at Multiple Campuses. International Review Of Research In Open And Distance Learning, 14(3), 1-26.
http://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1017493
the Advisory Committee on Student Financial Assistance (2007) reported that textbook prices represent a significant barrier to students’ accessibility to textbooks. The report concluded that textbooks cost between $700-$1000 per year; textbook prices have risen much faster than other commodities; and that college aid fails to cover textbook expenses. Textbook costs are equivalent to 26% of tuition costs for an average four-year public university student and 72% of tuition costs for an average community college student. In fact, the California State Auditor (2008) reported that textbook costs grew more rapidly than student fees in academic year 2007–08.


++++++++++++
Wimmer, E. e., Morrow, A. a., & Weber, A. a. (2014). Collaboration in eTextbook Publishing: A Case Study.Collaborative Librarianship, 6(2), 82-86.
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dllf%26AN%3d108762075%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite

Distance education, e-learning, education and training. (2015). Clinical Chemistry & Laboratory Medicine, 53s557-s559. doi:10.1515/cclm-2015-5015
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3daph%26AN%3d102854748%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
the creation of an interactive e-book called “Practical Clinical Chemistry: core concepts” was accomplished using the
Apple Macintosh platform and the iBooks Author software. Digital content, including videos, was developed for the
project and embedded within the final package. In order to limit the size of the final files, some content was uploaded
onto Youtube so that the user could access these via the internet.
The e-book, 200MB in size, was uploaded onto the Apple ITunes site and made available in 51 countries via the
iBooks store. This prototype is the first interactive digital textbook available in clinical chemistry and contains “4-
dimensional” content including digital images, videos, interactive presentations, real-time data generation as well as
review questions with instant feedback and assessment.
Hamedi, M., & Ezaleila, S. (2015). Digital Textbook Program in Malaysia: Lessons from South Korea. Publishing Research Quarterly, 31(4), 244-257. doi:10.1007/s12109-015-9425-4
Joseph, R. (2015). Higher Education Book Publishing-from Print to Digital: A Review of the Literature. Publishing Research Quarterly, 31(4), 264-274. doi:10.1007/s12109-015-9429-0
the author reflects the process on a state level (Ohio).
Marcoux, E. “. (2012). Best of the Best Planning. Teacher Librarian, 39(4), 69-70.
Taylor, A. K. (2011). Students Learn Equally Well From Digital as From Paperbound Texts. Teaching Of Psychology, 38(4), 278-281. doi:10.1177/0098628311421330
Much of the research related to digital texts has focused ontechnical aspects of readability (see Dillon, 1992, for a review) and limitations of digital media for note-taking, underlining, or highlighting text (Brown, 2001). However, the important—and unanswered—question from a teaching perspective is, ‘‘Can students learn as well from digital texts as from paperbound textbooks?’’ Few published studies have addressed this ques-tion directly, and even fewer studies have examined this ques-tion among college students.
Murray, M. C., & Pérez, J. (2011). E-Textbooks Are Coming: Are We Ready?. Issues In Informing Science & Information Technology, 849-60.
read the entire article, good data.
CourseSmart. FlatWorld Knowledge,
Horejsi, M. (2014). Textbooks 2.0. Science Teacher, 81(3), 8. http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3daph%26AN%3d94603788%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
++++++++++++++
pedagogy
two Eastern Europeans (Moldova, Serbia) raise serious concerns about electronic textbooks
Španović, S. (2010). PEDAGOGICAL ASPECTS OF E-TEXTBOOKS. Odgojne znanosti. 12(2). 459-470.
Railean, E. (2015). https://prezi.com/sbidiadctrzo/beyond-textbook-digital-textbook-use-and-development/
http://www.governance.ualberta.ca/en/GeneralFacultiesCouncil/CommitteeontheLearningEnvironm/~/media/Governance/Documents/GO05/LEA/15-16/WEB/Item-4-eTextbook-Subcommittee-Report-CLE-TLAT.pdf :
- (Un)desirable features in etextbooks
- How etextbooks might affect course delivery
- Pilot projects that can help build institutional expertise
- Address how and where insights gained from pilot projects will be collected and
- made available
- People resources (e.g., instructional designers) that will be needed to assist
- instructors to use this technology
ICWL (Conference) (13th : 2014 : Tallinn, E., & Cao, Y. (2014). New horizons in web based learning: ICWL 2014 international workshops, SPeL, PRASAE, IWMPL, OBIE, and KMEL, FET, Tallinn, Estonia, August 14-17, 2014, revised selected papers. Cham: Springer.
++++++++++++++++++++
MnSCU will by as Content Authoring Tool – SoftChalk. Here is a promo from Softchalk (my bold):
NEW SoftChalk Create 10 and SoftChalk Cloud eBook publishing features will arrive on April 25th! Come check out the latest enhancements at our upcoming webinars!
Sleek Designer Headers and Callout Boxes – Add some new pizazz to your SoftChalk lessons!
Three New Quiz Types – Test your students’ understanding with Sentence Completion, Multiple Blanks and Feedback Questions.
Polished New QuizPopper and Activity displays – With an enhanced interface for instructors and students.
Accessibility enhancements – Make your lessons available to everyone with even more accessibility enhancements.
NEW SoftChalk Cloud eBook creation and publishing – Includes a totally re-vamped, easier eBook creation and management. New SoftChalk eReader apps available for free download in the iOS, Android, Chromebook and Windows app stores. (Cloud Only)
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
The future of textbooks looks like this
February 22nd, 2016
are any faculty really going digital? Which content distributors will thrive? What are the implementation concerns? And when will going digital really happen?
two massive surveys and reports by the National Association of College Stores (NACS) and the Independent College Bookstore Association (ICBA) in partnership with the Campus Computing Survey (CCS),
NISO Virtual Conference:
Justifying the Library: Using Assessment to Justify Library Investments
April 20, 11:00am – 5:00pm EST – Learn more and register at: http://www.niso.org/news/events/2016/virtual_conference/apr20_virtualconf/
Assessment exercises for institutional libraries are frequently a double-edged sword; they’re as readily used to justify cuts as they are to bolster budgets. This NISO virtual conference provides expert insights into how data gathered in the normal course of activities can be leveraged to demonstrate value to the parent institution. Data represent the raw material for building your case. What data are available? How is their quality? What is the appropriate context for persuasively presenting that data to deans, provosts and other administrators? This virtual conference will address the very hot topic of library assessment in the context of a changing educational environment and features a complete roster of expert speakers, including:
- Steven J. Bell, Associate University Librarian, Temple University
- Nancy Turner, Assessment and Organizational Performance Librarian, Temple University
- Jocelyn Wilk, University Archivist, Columbia University
- Elisabeth Brown, Director of Assessment & Scholarly Communications Librarian, SUNY-Binghamton
- Ken Varnum, Senior Program Manager for Discovery, Delivery, & Learning Analytics, University of Michigan
- Jan Fransen, Service Lead for Researcher and Discovery Systems, University of Minnesota
- Kristi Holmes, Directer, Galter Health Sciences Library, Northwestern University
- Starr Hoffman, Head, Planning & Assessment, University of Nevada – Las Vegas
- Carl Grant, Chief Technology Officer and Associate University Librarian for Knowledge Services, University of Oklahoma
The preliminary agenda and pricing information for this event may be found at:
http://www.niso.org/news/events/2016/virtual_conference/apr20_virtualconf/
As a bonus, register for the virtual conference and receive an automatic registration for the follow-up training webinar, Making Assessment Work: Using ORCIDS to Improve Your Institutional Assessments, on Thursday, April 28!
http://www.niso.org/news/events/2016/training_thursday/apr28_tt/
Instructors for that session are Alice Meadows (ORCID), Christopher Erdmann (Harvard University) and Merle Rosenzweig (University of Michigan).
For more information about this event, please contact Jill O’Neill (joneill@niso.org).
Other questions for NISO? Get in touch at:
NISO
3600 Clipper Mill Road
Suite 302
Baltimore, MD 21211-1948
Phone: +1.301.654.2512
Email: nisohq@niso.org
More on assessment in this IMS blog:
analytics in education

 Since 2008, Mr. Vinson Houston has served as vice president for information technology at Jacksonville State University. Prior to that, Mr. Houston served as Director of Telecommunications for JSU, beginning in 2005. Mr. Houston currently serves on the board of directors for the Alabama Supercomputer Authority and is on the CORE Executive Committee that leads initiatives promoting PK-20 collaboration related to using new technologies in the classroom. He holds a B.A. and an M.B.A. from Jacksonville State University.
Since 2008, Mr. Vinson Houston has served as vice president for information technology at Jacksonville State University. Prior to that, Mr. Houston served as Director of Telecommunications for JSU, beginning in 2005. Mr. Houston currently serves on the board of directors for the Alabama Supercomputer Authority and is on the CORE Executive Committee that leads initiatives promoting PK-20 collaboration related to using new technologies in the classroom. He holds a B.A. and an M.B.A. from Jacksonville State University.








