Searching for "iste"
Report: Video Captions Benefit Virtually All Students
By Leila Meyer 11/02/16
https://campustechnology.com/articles/2016/11/02/report-video-captions-benefit-virtually-all-students.aspx
The Oregon State University Ecampus Research Unit conducted the national study in collaboration with 3Play Media. The researchers surveyed 2,124 students across 15 public and private universities throughout the United States. Of all respondents, 19 percent reported hearing difficulties, and 37 reported vision difficulties. However, only 13 percent had registered with an office of disability services, and less than 12 percent reported they require academic accommodations.
The study revealed that students find closed captions and video transcripts helpful, whether the student is deaf or hard of hearing or not.
Key findings from the study:
- Almost 100 percent of survey respondents had at least one course — either face-to-face or online — that included some video content;
- 75 percent of students use captions as a learning aid in face-to-face and online classrooms;
- 98.6 percent of students who use captions say they are helpful;
- 71 percent of students without hearing difficulties use captions at least some of the time;
- Students reference video transcripts as a learning aid 85 percent of the time;
- 66 percent of English-as-a-second-language (ESL) students find captions extremely or very helpful;
- 61 percent of students with learning disabilities find captions helpful;
- More than one quarter of students were unsure about the availability of closed captions for video content in their course; and
- Almost one-in-five students were unsure about the availability of video transcripts for their course.
Further details about the study and a link to the full report can be found on 3Play Media’s site.
Please look on the bottom of this blog entry for more resources
Effective Library Signage: Tips, Tricks, & Best Practices Workshop
Mark Aaron Polger and Amy F. Stempler Item Number: 1541-9212
Effective Library Signage: Tips, Tricks, & Best Practices Workshop
A 90-minute workshop, Thursday, January 5, 2017, 2:30pm Eastern/1:30 Central/12:30 Mountain/11:30am PacificLibrary signage represents the first lines of communication between a library user and the library. Are you doing everything to ensure that your signage is user friendly and inviting? Although we have the best intentions, sometimes our signage can be punitive, contradictory, outdated, or passive aggressive.In this new workshop, Mark Aaron Polger and Amy F. Stempler, library professionals who’ve conducted a four yearlong study at the College of Staten Island, CUNY that involved an extensive signage audit and replacement project, will provide you with the top ten tips to follow when preparing new signage for your library. They will discuss what constitutes “bad” and “good” signage and the importance of developing a signage policy to ensure consistency in design and overall language. Other topics that will be addressed will be placement, ADA compliancy, branding, design, verbiage, and the use of images, language, and font. You’ll come out of this workshop with the best practices to assess your current signage and develop improved signage for your institution.Learning Outcomes
After participating in this workshop, you will be able to:
- Identify the best practices when developing new signage
- Distinguish and follow the steps involved in coordinating a signage audit
- Create a signage policy that is appropriate for your institution
About the Instructors
Mark Aaron Polger is the first year experience librarian and information literacy instructor at the College of Staten Island, City University of New York (CUNY). His responsibilities include promoting library services and resources to first year students and providing library instruction and information literacy classes. Polger’s research interests include library marketing, outreach, and user experience design. He has written and presented on topics ranging from library marketing strategies, faculty outreach, Information Literacy outreach, embedded librarianship, library jargon, and library signage. Polger holds a BA in Sociology from Concordia University, an MA in Sociology from the University of Waterloo, a B.Ed. in adult education from Brock University, and an MLIS from the University of Western Ontario. He is currently pursuing his Ph.D. in Curriculum, Instruction, and the Science of Learning at SUNY University at Buffalo.
Amy F. Stempler is an associate professor in the library department at the College of Staten Island, CUNY, where she has worked since 2008. She holds a Bachelor’s Degree and Master’s Degree in History from The George Washington University and a Master’s Degree in Library and Information Science Degree from the Pratt Institute. Stempler is currently the coordinator of library instruction, and has written on library signage, Jewish history, Judaica librarianship, and the role of archives in environmental history.
|
+++++++++++++++++++++
more on signage for libraries:
Polger, M. A., & Stempler, A. F. (2014). Out with the Old, In with the New: Best Practices for Replacing Library Signage. Public Services Quarterly, 10(2), 67-95. doi:10.1080/15228959.2014.904210
authors’ thesis is that library signs are living documents
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dkeh%26AN%3d96086859%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
Stempler, A. F., & Polger, M. A. (2013). Do You See the Signs? Evaluating Language, Branding, and Design in a Library Signage Audit. Public Services Quarterly, 9(2), 121-135. doi:10.1080/15228959.2013.785881
To be effective, signage must be consistent, concise, and free of jargon and punitive language.
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dkeh%26AN%3d87666251%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
+++++++++++++++++
more on the use of signage in the library in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=signage
Flipped/Blended/… Teaching/Learning: FridayLive! Collaborative Development Series
Presenters:
Steve Gilbert, TLT Group
Beth Dailey, TLT Group
Dale Parker, Senior Faculty, Cambridge College
Penny Kuckkahn, Nicolet College, Instructional Designer
Robert Voelker-Morris, Faculty Technology Consultant, University of Oregon
Winona Hatcher, Instructional Designer, Augusta University
Date: 11/11/201616
Time: 1:30 PM ET pre session. 2:00 -3:00 PM ET Main event. 3:00 – 3:30 PM ET After thoughts
Description
This is the third in our Flipped/Blended… Teaching/Learning Collaborative Development Series. Faculty considering the next steps toward flipping/blended..teaching/learning and instructional designers and design consultants will all find something of benefit from this series.
In the spring we explored what it means to flip a classroom and added to the flipped classroom toolkit. Over the summer a team of instructional designers assisted a faculty member in designing a flipped lesson. This collaborative development process is the basis of the series.
The third session in our series focuses on Phase 2: Develop the Plan and Identify Resources. Flipped/Blended Teaching/Learning and Integrating Technology Design Approach
+++++++++++++++++
more on blended teaching and learning in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=blended
Ed Dept. Launches $680,000 Augmented and Virtual Reality Challenge
By David Nagel 11/02/16
https://thejournal.com/articles/2016/11/02/ed-dept.-launches-680000-augmented-and-virtual-reality-challenge.aspx
EdSim Challenge, the competition is aimed squarely at developing students’ career and technical skills — it’s funded through the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act of 2006 — and calls on developers and ed tech organizations to develop concepts for “computer-generated virtual and augmented reality educational experiences that combine existing and future technologies with skill-building content and assessment. Collaboration is encouraged among the developer community to make aspects of simulations available through open source licenses and low-cost shareable components. ED is most interested in simulations that pair the engagement of commercial games with educational content that transfers academic, technical, and employability skills.”
all five finalists prizes of $50,000 to help them further develop their concepts. Finalists will also receive access to expert mentors to help with the process, along with gear and development tools, including Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge, Galaxy Tab S2 9.7″, Gear S3 watch and Gear VR headset, as well as an Oculus Mobile software developer kit. ED noted that other prizes may also be added later.
The submission deadline will be Jan. 17,
Participants must also register on the Luminary Lightbox platform. (Registration is free.)
+++++++++++++++++
more on VR in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+reality
My note:
I listened to the report in my car yesterday. It is another sober reminder for being proactive rather then reactive (or punitive). We must work toward digital literacy and go beyond that comfortably numb stage of information literacy.
An Experiment Shows How Quickly The Internet Of Things Can Be Hacked
http://www.npr.org/sections/alltechconsidered/2016/11/01/500253637/an-experiment-shows-how-quickly-the-internet-of-things-can-be-hacked
We have basic security in place in modern devices that screen out the most obvious attacks. Really getting phished, if you will, is more of a problem where you are tricked in surrendering your password or username to a common service. If you plug in your webcam into your router or to your Wi-Fi, you’re relatively safe.
I think the biggest security concern for folks at home would be if their router actually is old, it might have an easily guessed password that someone could gain control. Most modern devices don’t have that problem, but that certainly is a concern for older devices.
+++++++++++
more on cybersecurity in this blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=cybersecurity
In the wake of NMC release regarding digital literacy, https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/10/25/nmc-on-digital-literacy/ (not coincidence, the author is active with NMC)
ALA is offering a webinar:
Rethinking Digital Literacy to Serve Library Staff and Users eCourse
Paul Signorelli Item Number: 1541-9124
http://www.alastore.ala.org/detail.aspx?ID=11469&zbrandid=4634&zidType=CH&zid=38811756&zsubscriberId=1026665847&zbdom=http://ala-publishing.informz.net
Asynchronous eCourse beginning November 14, 2016 and continuing for 5 weeks (includes an extension of 1 week for Thanksgiving)
Estimated Hours of Learning: 24
Certificate of Completion available upon request
Learning outcomes
After participating in this course, you will be able to:
- incorporate ever-evolving definitions of digital literacy into learning opportunities
- draw upon a variety of digital resources to create digital-learning opportunities
- seek additional resources that you can use in your continuing efforts to keep up with new developments in digital literacy in libraries and other learning organizations
What is digital literacy? Do you know how you can foster digital literacy through formal and informal learning opportunities for your library staff and users?
Supporting digital literacy still remains an important part of library staff members’ work, but sometimes we struggle to agree on a simple, meaningful definition of the term. In this four-week eCourse, training/learning specialist Paul Signorelli will begin by exploring a variety of definitions, focusing on work by a few leading proponents of the need to foster digital literacy among people of all ages and backgrounds. He will explore a variety of digital-literacy resources – including case studies of how we creatively approach digital-literacy learning opportunities for library staff and users, and will explore a variety of digital tools that will help to encourage further understanding of this topic.
Now, who is ready to build their digital-literacy skills and help their users become digital literate as well?
eCourse Outline
Part 1: Digital Literacy: Initial Definitions and Explorations
- An overview of various definitions of digital literacy
- Several components of digital literacy
- Exploring Doug Belshaw’s extensive work on defining and fostering digital literacy
Part 2: Digital Literacy: Crap Detection and Other Skills and Tools
- Exploring Howard Rheingold’s approach to crap detection and other digital literacy/net literacy skills
- Participation, collaboration, creativity, and experimentation as digital-literacy skills
- Building our digital-literacy toolkit
Part 3: Digital Literacy in Learning
- The varying digital literacy needs of our youngest students, of teens, and of adults
- Exploring various online resources supporting our digital-literacy training-teaching-learning efforts
- The myth of the digital native
Part 4: Fostering Digital Literacy: Creating Within a Digital Environment
- Creating a framework to promote digital literacy
- Designing workshops and other learning opportunities
- Keeping up in an evolving digital literacy landscape
How this eCourse Works
The eCourse begins on Monday, November 14, 2016. Your participation will require approximately six hours a week, at times that fit your schedule. All activities take place on the website, and you will be expected to:
- Read, listen to or view online content
- Post to online discussion boards
- Complete weekly assignments or activities
Instructor Paul Signorelli will monitor discussion boards regularly during the four-week period, lead group discussions, and will also answer individual questions. All interaction will take place on the eCourse site, which will be available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. It’s recommended that students log into the site on the first day of class or within a few days for an overview of the content and to begin the first lesson.
User Requirements
Participants will need regular access to a computer with an internet connection for online message boards participation, viewing online video, listening to streaming audio (mp3 files), and downloading and viewing PDFs and PowerPoint files. ALA Editions eCourses are fully compatible with Windows and MacOs.
About the Instructor
Paul Signorelli, co-author of Workplace Learning & Leadership with Lori Reed, is a San Francisco-based writer, trainer, presenter, and consultant exploring, fostering, and documenting innovations in learning. Having earned an MLIS through the University of North Texas (with an emphasis on online learning), he remains active in the American Library Association, the New Media Consortium (educational technology), and the Association for Talent Development (formerly the American Society for Training & Development).
My note: Finally ALA is addressing a huge gap. Namely, letting conservative librarians dress information literacy with the appearance of “digital literacy.”
++++++++++++++++
more on digital literacy in this IMS blog:
Book Announcement: Implementing Mobile Language Learning Technologies in Japan
New book: Implementing Mobile Language Learning Technologies in Japan
by Steve McCarty, Hiroyuki Obari, and Takeshi Sato
Publisher: Springer Singapore / SpringerBriefs in Education (107 pages)
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction: Contextualizing Mobile Language Learning in Japan
Chapter 2 Mobile Language Learning Pedagogy: A Sociocultural Perspective
Chapter 3 Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Case Study:
Smartphone App LINE for EFL Peer Learning
Chapter 4 Osaka Jogakuin University Case Study:
Mobilizing the EFL Curriculum and Campus Infrastructure with iPods and iPads
Chapter 5 Aoyama Gakuin University Case Study:
Blended Learning and Flipped Classrooms utilizing Mobile Devices
Chapter 6 Conclusion: Implementing Language Learning in a Mobile-Oriented Society
Abstract
This book explores theoretical and practical aspects of implementing mobile language learning in university classrooms for English as a Foreign Language in Japan. The technologies utilized, such as smartphones, iPads, and wi-fi, integrate students’ hand-held devices into the campus network infrastructure. The pedagogical aims of ubiquitous mobile learning further incorporate social media, blended learning, and flipped classroom approaches into the curriculum. Chapter 1 defines mobile language learning within dimensions of e-learning and technology-assisted language learning, prior to tracing the development of mobile learning in Japan. Chapter 2 documents the sociocultural theory underpinning the authors’ humanistic approach to implementation of mobile technologies. The sociocultural pedagogy represents a global consensus of leading educators that also recognizes the agency of Asian learners and brings out their capability for autonomous learning. Case studies of universities, large and small, public and private, are organized similarly in Chapters 3 to 5. Institutional/pedagogical and technological context sections are followed by detailed content on the implementation of initiatives, assessment of effectiveness, and recommendations for other institutions. Distinct from a collection of papers, this monograph tells a story in brief book length about theorizing and realizing mobile language learning, describing pioneering and original initiatives of importance to practitioners in other educational contexts.
Authors
Steve McCarty lectures for Kansai University, Osaka Jogakuin University, KIC Graduate School of IT, and the government agency JICA.
Hiroyuki Obari, PhD in Computer Science, is a Professor at the Aoyama Gakuin University College of Economics in Tokyo.
Takeshi Sato is an Associate Professor at the Division of Language and Culture Studies, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology.
Ordering information from Springer
Paperback (ISBN: 978-981-10-2449-8):
http://www.springer.com/us/book/9789811024498
eBook (ISBN: 978-981-10-2451-1) or individual chapters:
http://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-981-10-2451-1
++++++++++++++++++++++
more on mobile technologies in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=mobile+devices
Laptops, Tablets & Smartphones: School-Issued or BYOD? Either Way Works!
Title: Mobile Device Management – Strategies for Success
Date: Wed. 11/09 | 02:00 PM EST // 11:00 AM PDT
Register now
++++++++++++++
more on BYOD in education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=byod
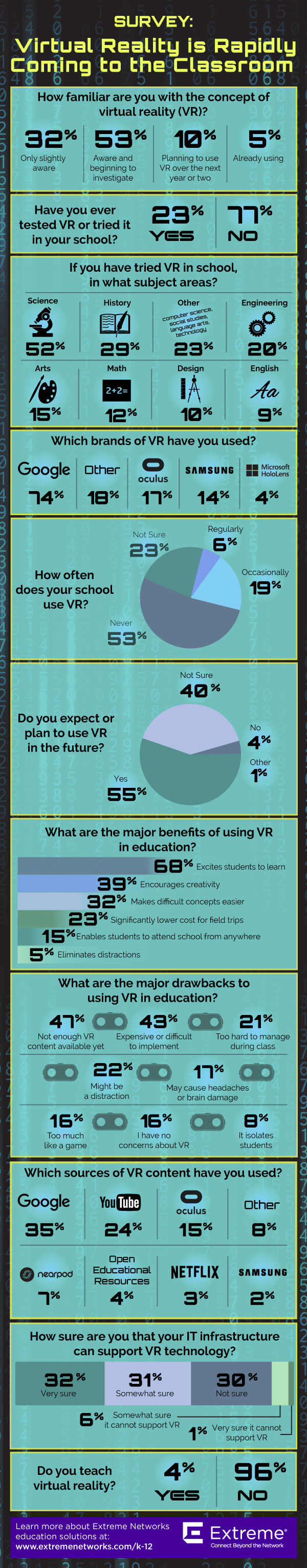
5 ways virtual reality is being used in education right now
By Meris Stansbury
1. For new research: using a state-of-the-art “haptic” floor of aeronautic metal that vibrates and moves to stimulate the physical world for research on how VR has the potential to change the way users feel and behave. There may also be implications for confronting racism, sexism, and aiding in
empathy and humanitarian efforts, says Bailenson.
2. For coding and 3D design:
According to Bob Nilsson, director of Vertical Solutions Marketing for Extreme Networking, the University of Maryland, College Park, now offers a class on virtual reality that gives students the opportunity to design their own interactive world, work with 3D audio and experiment with immersive technology through a combination of hands-on learning and case studies. Also, the University of Georgia is offering similar classes where students design and explore applications for VR. Conrad Tucker, an assistant professor of engineering at Pennsylvania State University, has received funding to build a virtual engineering lab where students hold, rotate, and fit together virtual parts as they would with their real hands.
3. For anatomy and dissection: Said one Extreme Networks survey respondent, “Our students have been developing a VR model of a cow’s anatomy for dissection and study. You have the ability to drill down to the circulatory system, brain, muscle, skeleton, etc. Our applied tech program is using VR in conjunction with Autocad for models of projects they design.”
4. For engagement: A whopping 68 percent of survey respondents said the major benefit of using VR in education is to excite students about the subject matter. 39 percent said it’s great for encouraging creativity.
5. For field trips: Google has eliminated restrictions on Expeditions, their VR field trips program. Google Expeditions was cited in the survey as one of the most popular sources of VR content, but with the complaint that it was a restricted program.
comment:
·
Virtual reality may have its place, but until traditional education moves away from their 20th century teaching methodology and replaces it with educationally innovative, 21st century learning methodology, within a blended and flipped learning environment, virtual reality is currently, much ado about nothing.
Unless any new application is educationally innovative and directly and measurably contributes to effective, efficient, consistent, affordable, relevant advanced student success outcomes for ALL students, future innovations must wait for current innovations to be implemented.
This process of appriate choice and appropriate implemention must start at the top and be beta tested for measured student success before its rolled out system wide.
+++++++++++++++
more on VR in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+reality
Save
A course for librarians who want to explore the institutional application of social media. Based on an established academic course at St. Cloud State University “Social Media in Global Context” (more information at http://web.stcloudstate.edu/pmiltenoff/lib290/ ).
Critically examine the institutional need of social media and juxtapose it to its private use. Discussion about the mechanics of choice for recent and future SM tools. Theoretical introduction to the subculture of social media. How to streamline library SM policies with the goals and mission of the institution. Hands-on exercises on creation and dissemination of textual and multimedia content and patrons’ engagement. Brainstorming on suitable for the institution strategies regarding resources, human and technological, workload share, storytelling, and branding.
This is a blended format web course:
The course will be delivered as 4 separate live webinar lectures, one per week on:
Wednesdays, September 21, 28, October 5 and 12
2:00 – 3:00 pm Central
You do not have to attend the live lectures in order to participate. The webinars will be recorded and distributed through the web course platform, Moodle for asynchronous participation. The web course space will also contain the exercises and discussions for the course.
