Searching for "learning space"
Literature on project based learning for K 12
Keywords | search strategy:
project-based learning, kindergarten to high school, online leaching ? Online learning? Methodology? Online platforms.
старо но точно по темата:
Cathy Cavanaugh, & Kara Dawson. (2010). Design of Online Professional Development in Science Content and Pedagogy: A Pilot Study in Florida. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 19(5), 438–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-010-9210-2
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_proquest_journals_2259584669
flipped classroom зависи от културни особености. това изследване може да важи за Щатите, но не за България:
Raffaghelli, J. (2017). Does Flipped Classroom work? Critical analysis of empirical evidences on its effectiveness for learning. Form@re : Open Journal Per La Formazione in Rete, 17(3). https://doi.org/10.13128/formare-21216
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_doaj_primary_oai_doaj_org_article_589dc480fa9a48cd828561173c625b39
изследване от Турция
Şahin, S., & Baturay, M. (2016). The effect of 5E-learning model supported with WebQuest media on students’ achievement and satisfaction. E-Learning and Digital Media, 13(3-4), 158–175. https://doi.org/10.1177/2042753016672903
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_crossref_primary_10_1177_2042753016672903
изследване от Гърция|
Georgios FESSAKIS, & Stavroula PRANTSOUDI. (2019). Computer Science Teachers’ Perceptions, Beliefs and Attitudes on Computational Thinking in Greece. Informatics in Education, 18(2), 227–258. https://doi.org/10.15388/infedu.2019.11
Lee, D., Huh, Y., Lin, C., & Reigeluth, C. (2018). Technology functions for personalized learning in learner-centered schools. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66(5), 1269–1302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9615-9
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_proquest_journals_2071965296
Brookes, T. (2017). Design challenges: Connecting the classroom to the real world. Teaching Science, 63(4), 16–19. Retrieved from http://eric.ed.gov/ERICWebPortal/detail?accno=EJ1165661
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_proquest_journals_1979139411
училищен библиотекар да работи с преподавател над учебен план много трудно ще стане в съврменна България, но не е невъзможно:
Boyer, B. (2015). Designer Librarian: Embedded in K12 Online Learning. 59(3), 71–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-015-0855-9
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_proquest_journals_1675592618
Educause прогнозира нарастваща роля на instructional designer при съставянето на учебни планове: e.g. https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2019/04/24/2019-educause-horizon-report/; https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/11/09/new-directions-in-instructional-design/; https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2019/01/06/future-of-libraries-with-instructional-design/; https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/01/04/instructional-design-librarian-2/
Lindsey M Swagerty, & Tara Hodge. (2019). fostering creativity and curiosity: developing safer elementary STEM learning spaces. Technology and Engineering Teacher, 78(8), 20–23. Retrieved from https://search.proquest.com/docview/2226390222
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_proquest_journals_2226390222
Tandra L. Tyler-Wood, Deborah Cockerham, & Karen R. Johnson. (2018). Implementing new technologies in a middle school curriculum: a rural perspective. Smart Learning Environments, 5(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-018-0073-y
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_doaj_primary_oai_doaj_org_article_6b4a31d0f8b9471bbe2d291cba18719b
Justin Weidman, & Geoffrey Wright. (2019). promoting construction education in K-12 by using an experiential, student-centered, STEM-infused construction unit. Technology and Engineering Teacher, 79(1), 8–12. Retrieved from https://search.proquest.com/docview/2309762278
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_proquest_journals_2309762278
това е за твоя офис за професионално ориентиране:
Destinations Career Academies Offer Support to Schools, Families Disrupted by Coronavirus (p. 68–). (2020). NewsRX LLC.
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_gale_healthsolutions_A617560083
Schachter, R. (2013). Project-based learning 2.0: technology pushes PBL into fifth gear in K12. 49(12), 60–.
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_gale_infotracacademiconefile_A353319541
Lee, D., Huh, Y., Lin, C., & Reigeluth, C. (2018). Technology functions for personalized learning in learner-centered schools. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66(5), 1269–1302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9615-9
https://mnpals-scs.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01MNPALS_SCS/ppvqcp/cdi_proquest_journals_2071965296
From ResearchGate:
Amissah, P. (2019). ADVANTAGES AND CHALLENGES OF ONLINE PROJECT-BASED LEARNING [MS Media Arts and Technology]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336614010_ADVANTAGES_AND_CHALLENGES_OF_ONLINE_PROJECT-BASED_LEARNING
Ching, Y.-H., & Hsu, Y.-C. (2011). Incorporating peer feedback for learning in a project-based online learning environment. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277987113_Incorporating_peer_feedback_for_learning_in_a_project-based_online_learning_environment
Handoyono, N. A., & Rabiman, R. (n.d.).
(PDF) Improvement of Learning Motivation and Learning Outcomes by Applying The Problem Based-Learning Method. ResearchGate. Retrieved March 22, 2020, from
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338796878_Improvement_of_Learning_Motivation_and_Learning_Outcomes_by_Applying_The_Problem_Based-Learning_MethodTran, T. Q., & Ngoc Tu, T. P. (2019). (PDF) The Important Roles of Project-Based Learning in Teaching English to High School Students.
ResearchGate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333935026_The_Important_Roles_of_Project-Based_Learning_in_Teaching_English_to_High_School_StudentsZakaria, A., Salleh, A., Ismail, Mohd. S., & Ghavifekr, S. (2019).
(PDF) Cultivating Positive Values via Online Project-Based Module (m-PAT). ResearchGate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334044540_Cultivating_Positive_Values_via_Online_Project-Based_Module_m-PATFrom Academia.com
VIA (very important article):
McDougall, J., Readman, M., & Wilkinson, P. (2018). The uses of (digital) literacy. Learning, Media and Technology, 43(3), 263–279. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439884.2018.1462206
2020 Immersive Learning Technology
https://www.jff.org/what-we-do/impact-stories/jfflabs-acceleration/2020-immersive-learning-technology/
2020-Immersion-012420 per Mark Gill’s finding
Technology is rapidly changing how we learn and grow. More and more, tools and platforms that make use of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and extended reality (ER)—collectively known as immersive learning technology—are moving from the niche world of Silicon Valley into retail stores, warehouses, factory floors, classrooms as well as corporate education and training programs. The value is clear: these immersive learning tools help companies, training providers, and educators train workers better, faster, and more efficiently. Of course, the impact doesn’t stop at the bottom line. Immersive learning presents an opportunity to reliably train employees for situations that are expensive to support, challenging to replicate, and even dangerous. And it can be done efficiently, safely, and with better learning outcomes.
1 in every 3 small and mid-size businesses in the U.S. is expected to be piloting a VR employee training program by 2021, seeing their new hires reach full productivity 50% faster as a result.1
The worldwide AR and VR market size is forecast to grow nearly 7.7 times between 2018 and 2022.
14 million AR and VR devices are expected to be sold in 2019
By 2023, enterprise VR hardware and software revenue is expected to jump 587% to $5.5 billion, up from an estimated $800 million in 2018.
Virtual Reality VR A computer-generated experience that simulates reality. VR may include visual, auditory, or tactile experiences.
Augmented Reality AR A live experience of a physical space, where computer-enhanced visualizations, sounds, or tactile experiences overlay the real-world environment.
Mixed Reality MR A blend of virtual experiences and the real world where virtual and augmented experiences are presented simultaneously
Extended Reality ER An immersive experience involving interactions with the real world, virtual reality, augmented reality, as well as other machines or computers adding content to the experience.
Soft Skills Technical Skills Immersive learning technologies can help people develop human skills, such as empathy, customer service, improving diversity and inclusion, and other areas
Technical Skills. Immersive learning technologies enable workers to learn through simulated experiences, providing the opportunity for risk-free repetition of complex or dangerous technical tasks.
+++++++++++++
more on immersive learning in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=immersive+learning
Building a Learning Innovation Network
https://www.insidehighered.com/digital-learning/blogs/technology-and-learning/building-learning-innovation-network
a new interdisciplinary field of learning innovation emerging.
Learning innovation, as conceptualized as an interdisciplinary field, attempts to claim a space at the intersection of design, technology, learning science and analytics — all in the unique context of higher education.
professional associations, such as POD, ELI, UPCEA, (https://upcea.edu/) OLC (https://onlinelearningconsortium.org/), ASU GSV (https://www.asugsvsummit.com/) and SXSW Edu (https://www.sxswedu.com/) — among many other conferences and events put on by professional associations.
A professional community of practice differs from that of an interdisciplinary academic network. Professional communities of practice are connected through shared professional goals. Where best practices and shared experiences form the basis of membership in professional associations, academic networks are situated within marketplaces for ideas. Academic networks run on the generation of new ideas and scholarly exchange. These two network models are different.
+++++++++++
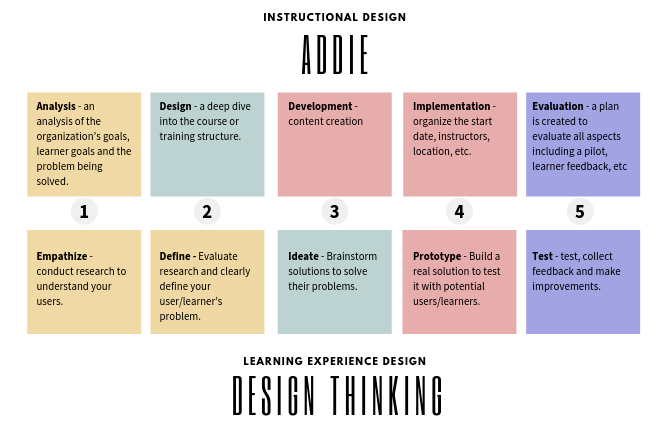
https://elearningindustry.com/learning-experience-design-instructional-design-difference
“Learning Experience Design™ is a synthesis of Instructional Design, educational pedagogy, neuroscience, social sciences, design thinking, and User Experience Design.”
The Process: ADDIE Vs. Design Thinking
++++++++++++++
more on LX design in this iMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=learning+design
How Game-Based Learning Empowers Students for the Future
https://www.edsurge.com/news/2019-01-22-its-2019-so-why-do-21st-century-skills-still-matter
educators’ guide to game-based learning, packed with resources for gaming gurus and greenhorns alike.
How are schools and districts preparing students for future opportunities? What is the impact of game-based learning?
It’s 2019. So Why Do 21st-Century Skills Still Matter?
21st-century trends such as makerspaces, flipped learning, genius hour, gamification, and more.
EdLeader21, a national network of Battelle for Kids.has developed a toolkit to guide districts and independent schools in developing their own “portrait of a graduate” as a visioning exercise. In some communities, global citizenship rises to the top of the wish list of desired outcomes. Others emphasize entrepreneurship, civic engagement, or traits like persistence or self-management.
ISTE Standards for Students highlight digital citizenship and computational thinking as key skills that will enable students to thrive as empowered learners. The U.S. Department of Education describes a globally competent student as one who can investigate the world, weigh perspectives, communicate effectively with diverse audiences, and take action.
Frameworks provide mental models, but “don’t usually help educators know what to do differently,” argues technology leadership expert Scott McLeod in his latest book, Harnessing Technology for Deeper Learning. He and co-author Julie Graber outline deliberate shifts that help teachers redesign traditional lessons to emphasize goals such as critical thinking, authenticity, and conceptual understanding.
1. Wondering how to teach and assess 21st-century competencies? The Buck Institute for Education offers a wide range of resources, including the book, PBL for 21st Century Success: Teaching Critical Thinking, Collaboration, Communication, and Creativity (Boss, 2013), and downloadable rubrics for each of the 4Cs.
2. For more strategies about harnessing technology for deeper learning,listen to the EdSurge podcast featuring edtech expert and author Scott McLeod.
3. Eager to see 21st-century learning in action? Getting Smart offers suggestions for using school visits as a springboard for professional learning, including a list of recommended sites. Bob Pearlman, a leader in 21st century learning, offers more recommendations.
++++++++++++++
more on game- based learning in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=game+based
If This Is the End of Average, What Comes Next?
Todd Rose, the director of the Mind, Brain, and Education program at the Harvard Graduate School of Education, has emerged as a central intellectual figure behind the movement. In particular, his 2016 book, “The End of Average,” is seen as an important justification for and guide to the personalization of learning.
what Rose argues against. He holds that our culture is obsessed with measuring and finding averages—averages of human ability and averages of the human body. Sometimes the average is held to be the ideal.
The jaggedness principle means that many of the attributes we care about are multi-faceted, not of a whole. For example, human ability is not one thing, so it doesn’t make sense to talk about someone as “smart” or “dumb.” That’s unidimensional. Someone might be very good with numbers, very bad with words, about average in using space, and gifted in using of visual imagery.
Since the 1930s, psychologists have debated whether intelligence is best characterized as one thing or many.
But most psychologists stopped playing this game in the 1990s. The resolution came through the work of John Carroll, who developed a third model in which abilities form a hierarchy. We can think of abilities as separate, but nested in higher-order abilities. Hence, there is a general, all-purpose intelligence, and it influences other abilities, so they are correlated. But the abilities nested within general intelligence are independent, so the correlations are modest. Thus, Rose’s jaggedness principle is certainly not new to psychology, and it’s incomplete.
The second (Context Principle) of Rose’s principles holds that personality traits don’t exist, and there’s a similar problem with this claim: Rose describes a concept with limited predictive power as having none at all. The most commonly accepted theory holds that personality can be described by variation on five dimensions
Rose’s third principle (pathways principle) suggests that there are multiple ways to reach a goal like walking or reading, and that there is not a fixed set of stages through which each of us passes.
Rose thinks students should earn credentials, not diplomas. In other words, a school would not certify that you’re “educated in computer science” but that you have specific knowledge and skills—that you can program games on handheld devices, for example. He think grades should be replaced by testaments of competency (my note: badges); the school affirms that you’ve mastered the skills and knowledge, period. Finally, Rose argues that students should have more flexibility in choosing their educational pathways.
=++++++++++++++++
more on personalized learning in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=personalized+learning
New Book Helps Teachers Unlock Secrets of Virtual and Augmented Reality With Lessons, Apps, and Strategies for the Classroom
New Book Helps Teachers Unlock Secrets of Virtual and Augmented Reality With Lessons, Apps, and Strategies for the Classroom
the International Society for Technology in Education to publish a book, titled Learning Transported: Augmented, Virtual and Mixed Reality for All Classrooms, to offer practical insights, lesson plans, and classroom examples so educators can make the most of these experiential worlds.
Definition
Augmented reality superimposes a digital layer on the world around us, often activated by scanning a trigger image or via GPS (think Pokemon Go!). Virtual reality takes users away from the real world, fully immersing students in a digital experience that replaces reality. Mixed reality takes augmented a step further by allowing the digital and real worlds to interact and the digital components to change based on the user’s environment.
Virtual Shapes
DEVICES: iOS, Android, Chromebook, PC, COURSE: Geometry, GRADES: 2-5, 60 minutes
Storytelling
DEVICES: iOS, Android, COURSE: English Language Arts, Speaking and Listening, GRADES: K-1
Augmented and Virtual Reality with EON
DEVICES: iOS, Android, COURSE: Earth and Space Science, GRADE: 4, 45 minutes
Scavenger Hunting as a Classroom Activity
The app offers teachers a unique way to create a scavenger hunt by designing AR messages and leaving them in specific places for students to “discover.”
Waypoint App
The Waypoint App also allows for creation of educational scavenger hunts using augmented reality. Educators can easily add questions that address lesson objectives, set specific locations where the questions are hidden, and then have students hunt for questions by following the map. The hunt is easily shared with students on a variety of platforms, including text messaging and email.
Breakout EDU
Breakout EDU has become a popular game in education. Driven by creativity, teamwork, and problem-solving, the game provides a fun learning experience as it challenges students to compete in solving puzzles. The game centers on a series of questions; each solved question unlocks the next part of the activity. Students work in groups, competing against other groups to open all the locks first.
Key Issues in Teaching and Learning
https://www.educause.edu/eli/initiatives/key-issues-in-teaching-and-learning
A roster of results since 2011 is here.

1. Academic Transformation
2. Accessibility and UDL
3. Faculty Development
4. Privacy and Security
5. Digital and Information Literacies
https://cdn.nmc.org/media/2017-nmc-strategic-brief-digital-literacy-in-higher-education-II.pdf
Three Models of Digital Literacy: Universal, Creative, Literacy Across Disciplines
United States digital literacy frameworks tend to focus on educational policy details and personal empowerment, the latter encouraging learners to become more effective students, better creators, smarter information consumers, and more influential members of their community.
National policies are vitally important in European digital literacy work, unsurprising for a continent well populated with nation-states and struggling to redefine itself, while still trying to grow economies in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent financial pressures
African digital literacy is more business-oriented.
Middle Eastern nations offer yet another variation, with a strong focus on media literacy. As with other regions, this can be a response to countries with strong state influence or control over local media. It can also represent a drive to produce more locally-sourced content, as opposed to consuming material from abroad, which may elicit criticism of neocolonialism or religious challenges.
p. 14 Digital literacy for Humanities: What does it mean to be digitally literate in history, literature, or philosophy? Creativity in these disciplines often involves textuality, given the large role writing plays in them, as, for example, in the Folger Shakespeare Library’s instructor’s guide. In the digital realm, this can include web-based writing through social media, along with the creation of multimedia projects through posters, presentations, and video. Information literacy remains a key part of digital literacy in the humanities. The digital humanities movement has not seen much connection with digital literacy, unfortunately, but their alignment seems likely, given the turn toward using digital technologies to explore humanities questions. That development could then foster a spread of other technologies and approaches to the rest of the humanities, including mapping, data visualization, text mining, web-based digital archives, and “distant reading” (working with very large bodies of texts). The digital humanities’ emphasis on making projects may also increase
Digital Literacy for Business: Digital literacy in this world is focused on manipulation of data, from spreadsheets to more advanced modeling software, leading up to degrees in management information systems. Management classes unsurprisingly focus on how to organize people working on and with digital tools.
Digital Literacy for Computer Science: Naturally, coding appears as a central competency within this discipline. Other aspects of the digital world feature prominently, including hardware and network architecture. Some courses housed within the computer science discipline offer a deeper examination of the impact of computing on society and politics, along with how to use digital tools. Media production plays a minor role here, beyond publications (posters, videos), as many institutions assign multimedia to other departments. Looking forward to a future when automation has become both more widespread and powerful, developing artificial intelligence projects will potentially play a role in computer science literacy.
6. Integrated Planning and Advising Systems for Student Success (iPASS)
7. Instructional Design
8. Online and Blended Learning
In traditional instruction, students’ first contact with new ideas happens in class, usually through direct instruction from the professor; after exposure to the basics, students are turned out of the classroom to tackle the most difficult tasks in learning — those that involve application, analysis, synthesis, and creativity — in their individual spaces. Flipped learning reverses this, by moving first contact with new concepts to the individual space and using the newly-expanded time in class for students to pursue difficult, higher-level tasks together, with the instructor as a guide.
Let’s take a look at some of the myths about flipped learning and try to find the facts.
Myth: Flipped learning is predicated on recording videos for students to watch before class.
Fact: Flipped learning does not require video. Although many real-life implementations of flipped learning use video, there’s nothing that says video must be used. In fact, one of the earliest instances of flipped learning — Eric Mazur’s peer instruction concept, used in Harvard physics classes — uses no video but rather an online text outfitted with social annotation software. And one of the most successful public instances of flipped learning, an edX course on numerical methods designed by Lorena Barba of George Washington University, uses precisely one video. Video is simply not necessary for flipped learning, and many alternatives to video can lead to effective flipped learning environments [http://rtalbert.org/flipped-learning-without-video/].
Myth: Flipped learning replaces face-to-face teaching.
Fact: Flipped learning optimizes face-to-face teaching. Flipped learning may (but does not always) replace lectures in class, but this is not to say that it replaces teaching. Teaching and “telling” are not the same thing.
Myth: Flipped learning has no evidence to back up its effectiveness.
Fact: Flipped learning research is growing at an exponential pace and has been since at least 2014. That research — 131 peer-reviewed articles in the first half of 2017 alone — includes results from primary, secondary, and postsecondary education in nearly every discipline, most showing significant improvements in student learning, motivation, and critical thinking skills.
Myth: Flipped learning is a fad.
Fact: Flipped learning has been with us in the form defined here for nearly 20 years.
Myth: People have been doing flipped learning for centuries.
Fact: Flipped learning is not just a rebranding of old techniques. The basic concept of students doing individually active work to encounter new ideas that are then built upon in class is almost as old as the university itself. So flipped learning is, in a real sense, a modern means of returning higher education to its roots. Even so, flipped learning is different from these time-honored techniques.
Myth: Students and professors prefer lecture over flipped learning.
Fact: Students and professors embrace flipped learning once they understand the benefits. It’s true that professors often enjoy their lectures, and students often enjoy being lectured to. But the question is not who “enjoys” what, but rather what helps students learn the best.They know what the research says about the effectiveness of active learning
Assertion: Flipped learning provides a platform for implementing active learning in a way that works powerfully for students.
9. Evaluating Technology-based Instructional Innovations

What is the total cost of my innovation, including both new spending and the use of existing resources?
What’s the unit I should measure that connects cost with a change in performance?
How might the expected change in student performance also support a more sustainable financial model?
The Exposure Approach: we don’t provide a way for participants to determine if they learned anything new or now have the confidence or competence to apply what they learned.
The Exemplar Approach: from ‘show and tell’ for adults to show, tell, do and learn.
The Tutorial Approach: Getting a group that can meet at the same time and place can be challenging. That is why many faculty report a preference for self-paced professional development.build in simple self-assessment checks. We can add prompts that invite people to engage in some sort of follow up activity with a colleague. We can also add an elective option for faculty in a tutorial to actually create or do something with what they learned and then submit it for direct or narrative feedback.
The Course Approach: a non-credit format, these have the benefits of a more structured and lengthy learning experience, even if they are just three to five-week short courses that meet online or in-person once every week or two.involve badges, portfolios, peer assessment, self-assessment, or one-on-one feedback from a facilitator
The Academy Approach: like the course approach, is one that tends to be a deeper and more extended experience. People might gather in a cohort over a year or longer.Assessment through coaching and mentoring, the use of portfolios, peer feedback and much more can be easily incorporated to add a rich assessment element to such longer-term professional development programs.
The Mentoring Approach: The mentors often don’t set specific learning goals with the mentee. Instead, it is often a set of structured meetings, but also someone to whom mentees can turn with questions and tips along the way.
The Coaching Approach: A mentor tends to be a broader type of relationship with a person.A coaching relationship tends to be more focused upon specific goals, tasks or outcomes.
The Peer Approach:This can be done on a 1:1 basis or in small groups, where those who are teaching the same courses are able to compare notes on curricula and teaching models. They might give each other feedback on how to teach certain concepts, how to write syllabi, how to handle certain teaching and learning challenges, and much more. Faculty might sit in on each other’s courses, observe, and give feedback afterward.
The Self-Directed Approach:a self-assessment strategy such as setting goals and creating simple checklists and rubrics to monitor our progress. Or, we invite feedback from colleagues, often in a narrative and/or informal format. We might also create a portfolio of our work, or engage in some sort of learning journal that documents our thoughts, experiments, experiences, and learning along the way.
The Buffet Approach:
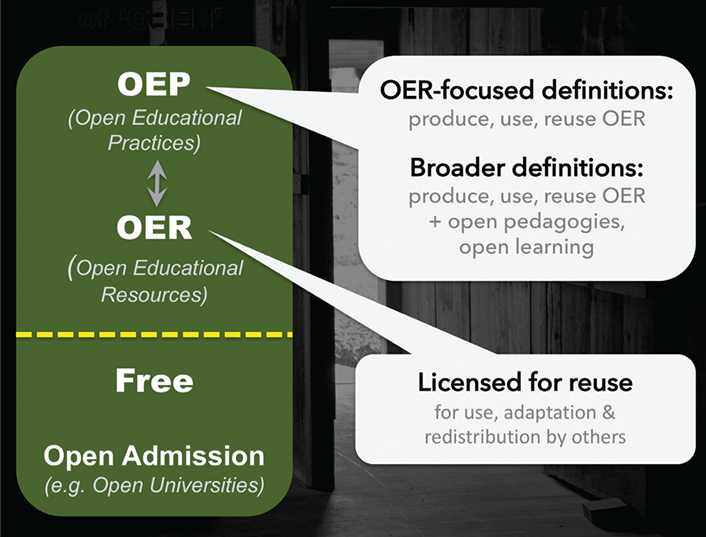
10. Open Education

11. Learning Analytics
12. Adaptive Teaching and Learning
13. Working with Emerging Technology
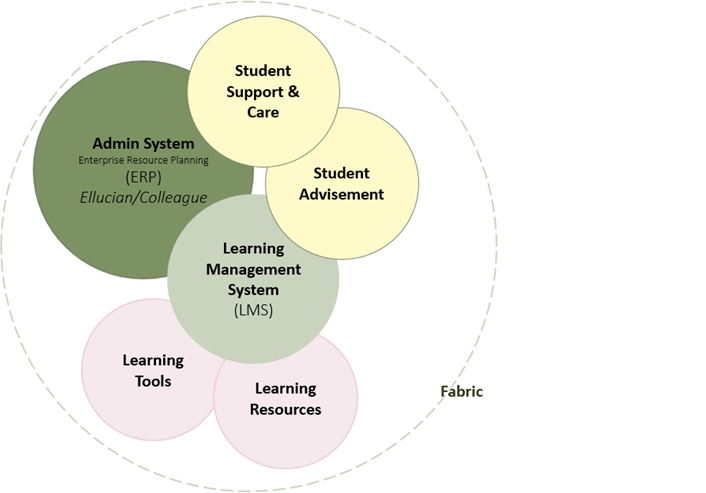
In 2014, administrators at Central Piedmont Community College (CPCC) in Charlotte, North Carolina, began talks with members of the North Carolina State Board of Community Colleges and North Carolina Community College System (NCCCS) leadership about starting a CBE program.
Building on an existing project at CPCC for identifying the elements of a digital learning environment (DLE), which was itself influenced by the EDUCAUSE publication The Next Generation Digital Learning Environment: A Report on Research,1 the committee reached consensus on a DLE concept and a shared lexicon: the “Digital Learning Environment Operational Definitions,
How AR and VR Can Make Students Laugh and Cry Out Loud—and Embed Them in Their Learning
https://www.edsurge.com/news/2018-08-28-how-ar-and-vr-can-make-students-laugh-and-cry-out-loud-and-embed-them-in-their-learning
40 virtual reality headsets with haptic handsets for them to manipulate in the VR/AR space, and I connected them to content from New York Times VR and WITHIN. The content placed students in settings such as on the ground in a refugee crisis or in the midst of the Millions March in New York City.
At the beginning of every class, they would go into this virtual space and engage with the content instead of just reading it. They’d respond to me about what it was like to be immersed in the experience.
The content from the WITHIN app provided one of the more visceral experiences for students.
At the end of the course, for example, students met with a shark tank-type group—investors from the community, business, and industry folks—and pitched them business ideas that would utilize VR to provide a solution to problems that were local, regional, national or even global in scope.
Were you able to measure this success?
The way that I measured it was completion. How many of my students actually got through my class successfully? It was over 85%. My research from the two classes where I used VR and this approach shows students were engaged, and ultimately more successful in my classes.
zSpace https://info.zspace.com/2018-vived-allied-health-promo
Also:
Intro To Haptic Technology
Haptics provide a critical role in making our devices more interactive.
https://www.iotforall.com/intro-to-haptic-technology-tachammer-haptic-actuator/
1. Eccentric Rotating Mass (ERM)
2. Linear Resonant Actuator (LRA)
Apple Taptic Engine
3. Piezoelectric Actuators
4. Forced Impact (Accelerated Ram)
+++++++++++
more on VR in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+reality
Metaliterate Learning for the Post-Truth World to be Published this Fall!
definition:
Metaliteracy is a pedagogical model for ensuring that learners successfully participate in collaborative information environments, including social media and online communities.
Metaliteracy supports reflective learning through metacognitive thinking, the ethical production of new knowledge, the critical consumption of information, and the responsible sharing of verifiable content across media platforms. Through metaliteracy, learners are envisioned as teachers in collaborative social spaces. This book examines the newest version of the Metaliteracy Goals and Learning Objectives, including the four domains of metaliterate learning.
+++++++++++++++
more on metaliteraices in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=metaliteracies
An Imaginary Interview with Lev Vygotsky on Immersive Storytelling and Learning
Ulla, Founder and CEO of ThingLink
https://medium.com/@ulla/an-imaginary-interview-with-lev-vygotsky-on-immersive-storytelling-and-learning-5bbb211c6e50
digital storytelling at the Festival Della Didattica Digitale (Digital Teaching Festival) in Italy.
the trending but undefined concepts of digital storytelling and immersive learning
definition
Storytelling is a logical form of thought. It is an analytical process including perception, labeling, organizing, categorizing real and imaginary objects and their real and imaginary relations in speech.
Q: What do you think immersive documentation technologies such as 360 images and videos can bring to this process?
V: 360 degree media and virtual reality are cultural-historically developed tools that mediate our relationship to the world in a new way. They expand the possible fields of perception transcending space and time. Perception precedes other psychological functions.
Definition
Immersive storytelling can be understood as an activity through which students use language to visualize relations and meaning in 360 degree digital environments. Naming or describing relations between objects in our field of perception using verbal or visual language awakens intellectual processes fundamental to learning.
Q: Would you say immersive storytelling is a form of creative play?
V: That is a possible interpretation. Play is a psychological process through which we create an imaginary situation or place, reflecting or separating objects and their actual meaning, or creating new meanings. The ability to digitally create and modify situations and environments can be understood as a form of play, opening a realm of spontaneity and freedom, connected with pleasure.
Q: Can robots help us learn? Is AI already the More Knowledgeable Other?
V: The More Knowledgeable Other (MKO) refers to anyone or anything who has a better understanding or a higher ability level than the learner, with respect to a particular task, process, or concept. If a robot with artificial intelligence can function as an MKO and support our problem solving, it can expand our Zone of Proximal Development.






