Aug
2018
K12 administrators and data analytics
Data Analytics a Key Skill for Administrators in K–12
++++++++++++
more on data analytics in education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=data+analytics
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
++++++++++++
more on data analytics in education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=data+analytics
Cross-Institution & Cross-Sector Collaboration Long-Term Trend: Driving Ed Tech adoption in higher education for five or more years
Although a variety of collaborations between higher education and industry have emerged, more-explicit frameworks and guidelines are needed to define how these partnerships should proceed to have the greatest impact.
links to the Webinar on the report:
https://events.educause.edu/educause-live/webinars/2018/exploring-the-2018-horizon-report
link to the transcript: https://events.educause.edu/~/media/files/events/educause-live/2018/live1808/transcript.docx
Proliferation of Open Educational Resources Mid-Term Trend: Driving Ed Tech adoption in higher education for the next three to five years
The United States lags on the policy front. In September 2017, the Affordable College Textbook Act was once again introduced in both the US House of Representatives and the Senate “to expand the use of open textbooks
It is unlikely that ACTA will pass, however, as it has been unsuccessfully introduced to two previous Congresses.
The Rise of New Forms of Interdisciplinary Studies
Faculty members, administrators, and instructional designers are creating innovative pathways to college completion through interdisciplinary experiences, nanodegrees, and other alternative credentials, such as digital badges. Researchers, along with academic technologists and developers, are breaking new ground with data structures, visualizations, geospatial applications, and innovative uses of opensource tools.
Growing Focus on Measuring Learning
As societal and economic factors redefine the skills needed in today’s workforce, colleges and universities must rethink how to define, measure, and demonstrate subject mastery and soft skills such as creativity and collaboration. The proliferation of data-mining software and developments in online education, mobile learning, and learning management systems are coalescing toward learning environments that leverage analytics and visualization software to portray learning data in a multidimensional and portable manner
Redesigning Learning Spaces
upgrading wireless bandwidth and installing large displays that allow for more natural collaboration on digital projects. Some are exploring how mixed-reality technologies can blend 3D holographic content into physical spaces for simulations, such as experiencing Mars by controlling rover vehicles, or how they can enable multifaceted interaction with objects, such as exploring the human body in anatomy labs through detailed visuals. As higher education continues to move away from traditional, lecture-based lessons toward more hands-on activities, classrooms are starting to resemble real-world work and social environments
Authentic Learning Experiences
An increasing number of institutions have begun bridging the gap between academic knowledge and concrete applications by establishing relationships with the broader community; through active partnerships with local organizations
Improving Digital Literacy Solvable Challenge: Those that we understand and know how to solve
Digital literacy transcends gaining discrete technological skills to generating a deeper understanding of the digital environment, enabling intuitive and discerning adaptation to new contexts and cocreation of content.107 Institutions are charged with developing students’ digital citizenship, promoting the responsible and appropriate use of technology, including online communication etiquette and digital rights and responsibilities in blended and online learning settings. This expanded concept of digital competence is influencing curriculum design, professional development, and student-facing services and resources. Due to the multitude of elements of digital literacy, higher education leaders must obtain institution-wide buy-in and provide support for all stakeholders in developing these competencies.
Despite its growing importance, it remains a complex topic that can be challenging to pin down. Vanderbilt University established an ad hoc group of faculty, administrators, and staff that created a working definition of digital literacy on campus and produced a white paper recommending how to implement digital literacy to advance the university’s mission: https://vanderbilt.edu/ed-tech/committees/digital-literacy-committee.php
Adapting Organizational Designs to the Future of Work
Technology, shifting information demands, and evolving faculty roles are forcing institutions to rethink the traditional functional hierarchy. Institutions must adopt more flexible, teambased, matrixed structures to remain innovative and responsive to campus and stakeholder needs.
Attempts to avoid bureaucracy also align with a streamlined workforce and cost elimination. Emphasis has been placed on designing better business models through a stronger focus on return on investment. This involves taking a strategic approach that connects financial practice (such as analyzing cost metrics and resource allocation) with institutional change models and goals.124
Faculty roles have been and continue to be impacted by organizational change, as well as by broader economic movements. Reflective of today’s “gig economy,” twothirds of faculty members are now non-tenure, with half working part-time, often in teaching roles at several institutions. This stands as a stark contrast to 1969, when almost 80 percent of faculty were tenured or tenuretrack; today’s figures are nearly inverted. Their wages are applying pressure to traditional organizational structures.Rethinking tenure programs represents another change to organizational designs that aligns with the future of work.
Organizational structures are continuing to evolve on the administrative side as well. With an emphasis on supporting student success, many institutions are rethinking their student services, which include financial aid, academic advising, and work-study programs. Much of this change is happening within the context of digital transformation, an umbrella term that denotes the transformation of an organization’s core business to better meet customer needs by leveraging technology and data.
+++++++++
added Nov 13, 2018
Short-Term, 1-2 years):
(Mid-Term, 3-5 years):
(Long-Term, 5 or more years):
++++++++++++
more on the NMC Horizon Report in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=horizon+report
definition:
Metaliteracy is a pedagogical model for ensuring that learners successfully participate in collaborative information environments, including social media and online communities.
Metaliteracy supports reflective learning through metacognitive thinking, the ethical production of new knowledge, the critical consumption of information, and the responsible sharing of verifiable content across media platforms. Through metaliteracy, learners are envisioned as teachers in collaborative social spaces. This book examines the newest version of the Metaliteracy Goals and Learning Objectives, including the four domains of metaliterate learning.
+++++++++++++++
more on metaliteraices in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=metaliteracies
++++++++++++++++
Jamie Heiman.
All materials on #FakeNews in the IMS blog: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=fake+news
this topic is developed in conjunction with digital literacy discussions.
from psychological perspective: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/03/29/psychology-fake-news/
from legal/ethical perspective: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/03/26/prison-time-for-fake-news/
definition:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/02/18/fake-news-disinformation-propaganda/
mechanics:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/11/22/bots-trolls-and-fake-news/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/07/15/fake-news-and-video/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/04/09/automated-twitter-bots/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/03/25/data-misuse/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/02/10/bots-big-data-future/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/09/19/social-media-algorithms/
exercises in detecting fake news:
(why should we) :
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/12/09/immune-to-info-overload/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/08/13/library-spot-fake-news/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/11/23/fake-news/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/12/14/fake-news-2/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/06/26/fake-news-real-news/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/03/28/fake-news-resources/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/03/15/fake-news-bib/
News literacy education (see digital literacy): https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/06/23/digital-forensics-and-news-literacy-education/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/07/21/unfiltered-news/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/03/13/types-of-misinformation/
Additional ideas and readings:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/11/30/rt-hybrid-war/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/08/23/nmc-digital-literacy/
!*!*!*!*! — this article was pitched by Mark Vargas in the fall of 2013, back then dean of LRS and discussed at a faculty meeting at LRS in the same year—- !*!*!*!
(p. 4) Building strong relationships with faculty and other campus professionals, and establishing collaborative partnerships within and across institutions, are necessary building blocks to librarians’ success. In a traditional liaison model, librarians use their subject knowledge to select books and journals and teach guest lectures.
“Liaisons cannot be experts themselves in each new capability, but knowing when to call in a colleague, or how to describe appropriate expert capabilities to faculty, will be key to the new liaison role.
six trends in the development of new roles for library liaisons
user engagement is a driving factor
what users do (research, teaching, and learning) rather than on what librarians do (collections, reference, library instruction).
In addition, an ALA-accredited master’s degree in library science is no longer strictly required.
In a networked world, local collections as ends in themselves make learning fragmentary and incomplete. (p. 5)
A multi-institutional approach is the only one that now makes sense.
Scholars already collaborate; libraries need to make it easier for them to do so.
but they also advise and collaborate on issues of copyright, scholarly communication, data management, knowledge management, and information literacy. The base level of knowledge that a liaison must possess is much broader than familiarity with a reference collection or facility with online searching; instead, they must constantly keep up with evolving pedagogies and research methods, rapidly developing tools, technologies, and ever-changing policies that facilitate and inform teaching, learning, and research in their assigned disciplines.
In many research libraries, programmatic efforts with information literacy have been too narrowly defined. It is not unusual for libraries to focus on freshman writing programs and a series of “one-shot” or invited guest lectures in individual courses. While many librarians have become excellent teachers, traditional one-shot, in-person instructional sessions can vary in quality depending on the training librarians have received in this arena; and they neither scale well nor do they necessarily address broader curricular goals. Librarians at many institutions are now focusing on collaborating with faculty to develop thoughtful assignments and provide online instructional materials that are built into key courses within a curriculum and provide scaffolding to help students develop library research skills over the course of their academic careers.
And many libraries stated that they lack instructional designers and/or educational technologists on their staff, limiting the development of interactive online learning modules and tutorials. (my note: or just ignore the desire by unites such as IMS to help).
(p. 7). This move away from supervision allows the librarians to focus on their liaison responsibilities rather than on the day-to-day operations of a library and its attendant personnel needs.
effectively support teaching, (1.) learning, and research; (2.) identify opportunities for further development of tools and services; (3.) and connect students, staff, and faculty to deeper expertise when needed.
At many institutions, therefore, the conversation has focused on how to supplement and support the liaison model with other staff.
At many institutions, therefore, the conversation has focused on how to supplement and support the liaison model with other staff.
the hybrid exists within the liaison structure, where liaisons also devote a portion of their time (e.g., 20% or more) to an additional area of expertise, for example digital humanities and scholarly communication, and may work with liaisons across all disciplinary areas. (my note: and at the SCSU library, the librarians firmly opposed the request for a second master’s degree)
functional specialists who do not have liaison assignments to specific academic departments but instead serve as “superliaisons” to other librarians and to the entire campus. Current specialist areas of expertise include copyright, geographic information systems (GIS), media production and integration, distributed education or e-learning, data management, emerging technologies, user experience, instructional design, and bioinformatics. (everything in italics is currently done by IMS faculty).
divided into five areas of functional specialization: information resources and collections management; information literacy, instruction, and curriculum development; discovery and access; archival and special collections; scholarly communication and the research enterprise.
E-Scholarship Collaborative, a Research Support Services Collaborative (p. 8).
p. 9. managing alerts and feeds, personal archiving, and using social networking for teaching and professional development
p. 10. new initiatives in humanistic research and teaching are changing the nature and frequency of partnerships between faculty and the Libraries. In particular, cross-disciplinary Humanities Laboratories (http://fhi.duke.edu/labs), supported by the John Hope Franklin Humanities Institute and the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation-funded Humanities Writ Large project, have allowed liaisons to partner with faculty to develop and curate new forms of scholarship.
consultations on a range of topics, such as how to use social media to effectively communicate academic research and how to mark up historical texts using the Text Encoding Initiative (TEI) guidelines
p. 10. http://www.rluk.ac.uk/news/rluk-report-the-role-of-research-libraries-in-the-creation-archiving-curation-and-preservation-of-tools-for-the-digital-humanities/
The RLUK report identified a wide skills gap in nine key areas where future involvement of liaisons is considered important now and expected to grow
p. 11. Media literacy, and facilitating the integration of media into courses, is an area in which research libraries can play a lead role at their institutions. (my note: yet still suppressed or outright denied to IMS to conducts such efforts)
Purdue Academic Course Transformation, or IMPACT (http://www.lib.purdue.edu/infolit/impact). The program’s purpose is to make foundational courses at Purdue more student-centered and participatory. Librarians are key members of interdepartmental teams that “work with Purdue instructors to redesign courses by applying evidence-based educational practices” and offer “learning solutions” that help students engage with and critically evaluate information. (my note: as offered by Keith and myself to Miguel, the vice provost for undergrads, who left; then offered to First Year Experience faculty, but ignored by Christine Metzo; then offered again to Glenn Davis, who bounced it back to Christine Metzo).
p. 15. The NCSU Libraries Fellows Program offers new librarians a two-year appointment during which they develop expertise in a functional area and contribute to an innovative initiative of strategic importance. NCSU Libraries typically have four to six fellows at a time, bringing in people with needed skills and working to find ongoing positions when they have a particularly good match. Purdue Libraries have experimented with offering two-year visiting assistant professor positions. And the University of Minnesota has hired a second CLIR fellow for a two-year digital humanities project; the first CLIR fellow now holds an ongoing position as a curator in Archives and Special Collections. The CLIR Fellowship is a postdoctoral program that hires recent PhD graduates (non-librarians), allowing them to explore alternative careers and allowing the libraries to benefit from their discipline-specific expertise.
Monday, June 11, 3PM
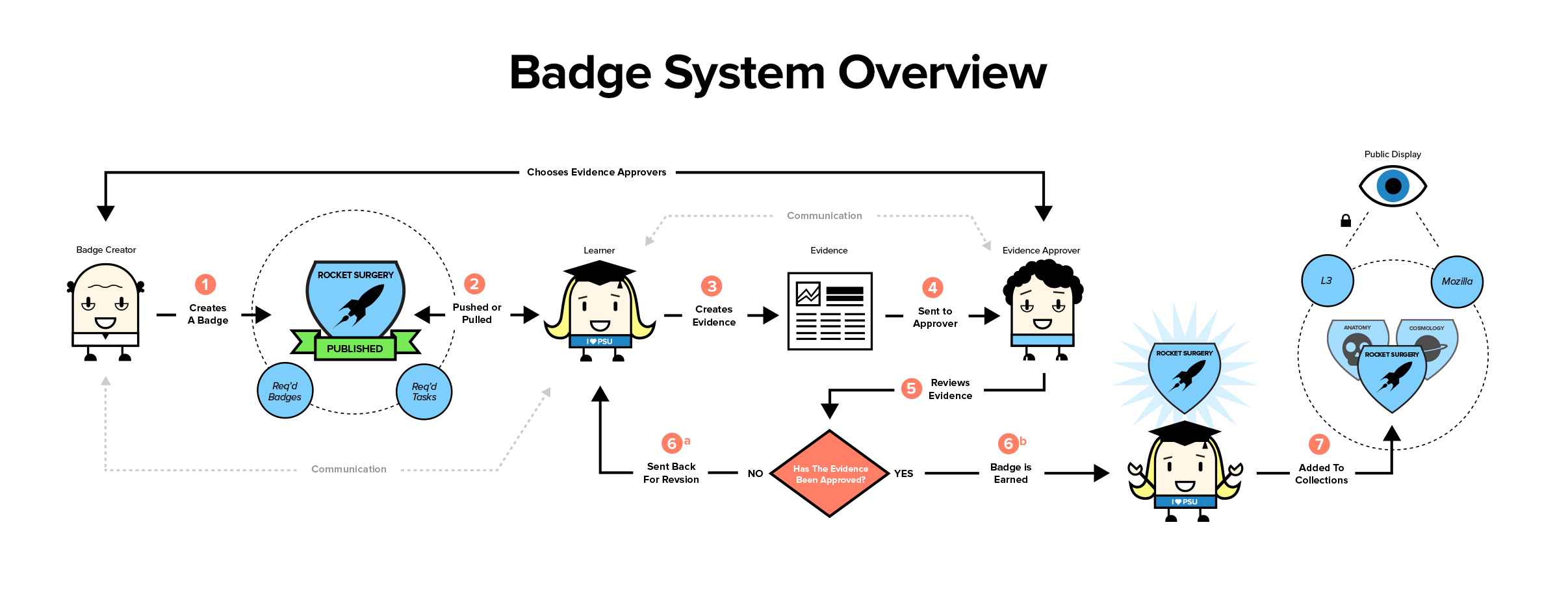
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=badges
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=microcredentialing
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/06/20/colorados-digital-badging-initiative/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/04/11/digital-badges-in-education/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/09/14/badges-blueprint/
++++++++++++++++
From Gail Ruhland:
Guess what … I searched for Brenda Perea (in hopes of maybe getting some information on how they set up their system) … One of her current positions is with Credly … Do we still want to reach out to her?
https://www.linkedin.com/in/brendaperea/
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/new-credential-field-guide-released-brenda-perea/
Johnathan Finkelstein: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=finkelstein
+++++++++++++++
Penn State Digital Badges: https://badgesapp.psu.edu/

http://www.personal.psu.edu/bxb11/blogs/brett_bixler_e-portfolio/2012/07/badges-at-penn-state.html
++++++++++++++++++
https://www.stonybrook.edu/commcms/spd/badges/index.php
October 29, 2015
Kaltura promo: https://learn.esc.edu/media/Ken+Lindblom%2C+Dean+of+the+School+of+Professional+Development%2C+Stony+Brook+University/1_wxhe9l4h
SUNY Micro-Credentialing Task Force Report and Recommendations: http://www.system.suny.edu/media/suny/content-assets/documents/faculty-senate/plenary/Microcredentialing-Report-Final-DRAFT—9-18-17.pdf
page 4, page 12-21
+++++++++++++++++++
+++++++++++++++++
https://www.universitybusiness.com/article/millennial-demand-drives-higher-ed-badging-expansion
Fields in which most badges have been issued:
94%: Institutions offering alternative credentials
1 in 5: Colleges and universities that issue badges
Nearly 2/3: Institutions that cited alternative credentials as an important strategy for the future.
-Source: “Demographic Shifts in Educational Demand and the Rise of Alternative Credentials,” University Professional and Continuing Education Association and Pearson, 2016
#qqml2018_Chania #QQML2018 conf@qqml.net
Where: Cultural Centre Of Chania
ΠΝΕΥΜΑΤΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ ΧΑΝΙΩΝ
https://goo.gl/maps/8KcyxTurBAL2
also live broadcast at https://www.facebook.com/InforMediaServices/videos/1542057332571425/
When: May 24, 12:30AM-2:30PM (local time; 4:40AM-6:30AM, Chicago Central)
Live broadcasts from some of the sessions:
Here is a link to Sebastian Bock’s presentation:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1jSOyNXQuqgGTrhHIapq0uxAXQAvkC6Qb/view
Session 1:
http://qqml.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/SESSION-Miltenoff.pdf
Session Title: Measuring Learning Outcomes of New Library Initiatives Coordinator: Professor Plamen Miltenoff, Ph.D., MLIS, St. Cloud State University, USA Contact: pmiltenoff@stcloudstate.edu Scope & rationale: The advent of new technologies, such as virtual/augmented/mixed reality, and new pedagogical concepts, such as gaming and gamification, steers academic libraries in uncharted territories. There is not yet sufficiently compiled research and, respectively, proof to justify financial and workforce investment in such endeavors. On the other hand, dwindling resources for education presses administration to demand justification for new endeavors. As it has been established already, technology does not teach; teachers do; a growing body of literature questions the impact of educational technology on educational outcomes. This session seeks to bring together presentations and discussion, both qualitative and quantitative research, related to new pedagogical and technological endeavors in academic libraries as part of education on campus. By experimenting with new technologies such as Video 360 degrees and new pedagogical approaches such as gaming and gamification, does the library improve learning? By experimenting with new technologies and pedagogical approaches, does the library help campus faculty to adopt these methods and improve their teaching? How can results be measured, demonstrated?
http://qqml.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/7.5.2018-programme_final.pdf
https://www.academia.edu/Documents/in/Measurement_and_evaluation_in_education
https://www.edsurge.com/news/2016-03-16-the-overselling-of-education-technology
Basically, my response to ed tech is “It depends.” And one key consideration on which it depends is the reason given for supporting it.
ads in education periodicals, booths at conferences, and advocacy organizations are selling not only specific kinds of software but the whole idea that ed tech is de rigueur for any school that doesn’t want to risk being tagged as “twentieth century.”
Other people, particularly politicians, defend technology on the grounds that it will keep our students “competitive in the global economy.” This catch-all justification has been invoked to support other dubious policies, including highly prescriptive, one-size-fits-all national curriculum standards. It’s based on two premises: that decisions about children’s learning should be driven by economic considerations, and that people in other countries should be seen primarily as rivals to be defeated.
But the rationale that I find most disturbing—despite, or perhaps because of, the fact that it’s rarely made explicit—is the idea that technology will increase our efficiency…at teaching the same way that children have been taught for a very long time.
a deeper question: “What kinds of learning should be taking place in those schools?” If we favor an approach by which students actively construct meaning, an interactive process that involves a deep understanding of ideas and emerges from the interests and questions of the learners themselves, well, then we’d be open to the kinds of technology that truly support this kind of inquiry. Show me something that helps kids create, design, produce, construct—and I’m on board. Show me something that helps them make things collaboratively (rather than just on their own), and I’m even more interested—although it’s important to keep in mind that meaningful learning never requires technology, so even here we should object whenever we’re told that software (or a device with a screen) is essential.
more worrisome are the variants of ed tech that deal with grades and tests, making them even more destructive than they already are: putting grades online (thereby increasing their salience and their damaging effects), using computers to administer tests and score essays, and setting up “embedded” assessment that’s marketed as “competency-based.”
we shouldn’t confuse personalized learning with personal learning. The first involves adjusting the difficulty level of prefabricated skills-based exercises based on students’ test scores, and it requires the purchase of software. The second involves working with each student to create projects of intellectual discovery that reflect his or her unique needs and interests, and it requires the presence of a caring teacher who knows each child well.
a recent review found that studies of tech-based personalized instruction “show mixed results ranging from modest impacts to no impact” – despite the fact that it’s remarkably expensive. In fact, ed tech of various kinds has made headlines lately for reasons that can’t be welcome to its proponents. According to an article in Education Week, “a host of national and regional surveys suggest that teachers are far more likely to use tech to make their own jobs easier and to supplement traditional instructional strategies than to put students in control of their own learning.” Last fall, meanwhile, OECD reportednegative outcomes when students spent a lot of time using computers, while Stanford University’s Center for Research on Education Outcomes
Ed tech is increasingly making its way even into classrooms for young children. And the federal government is pushing this stuff unreservedly: Check out the U.S. Office of Education Technology’s 2016 plan recommending greater use of “embedded” assessment, which “includes ongoing gathering and sharing of data,” plus, in a development that seems inevitable in retrospect, a tech-based program to foster a “growth mindset” in children. There’s much more in that plan, too—virtually all of it, as blogger Emily Talmage points out, uncannily aligned with the wish list of the Digital Learning Council, a group consisting largely of conservative advocacy groups and foundations, and corporations with a financial interest in promoting ed tech.
++++++++++++++++
more on technology literacy in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=technology+literacy
By Nicole Krueger Leadership
https://www.iste.org/explore/articleDetail?articleid=2177
A virtual reality headset can take students on an immersive journey to another world. But no matter how cool it is, if that $3,000 piece of equipment enters a classroom and doesn’t provide any real instructional value, it can quickly become a very expensive paperweight.
Most schools don’t do edtech procurement really well yet. Sometimes we buy products that end up in closets because they don’t fit the instructional needs of students, and we end up not being good stewards of taxpayer dollars.
Located in the district’s central office, where hundreds of teachers and staff members stop by each week for professional development, the playground offers a creative space that encourages teachers to explore new tools that have been vetted and approved by the district’s tech department.
In the United States, K-12 schools spend more than $13 billion a year on edtech — often without any idea whether it will make a difference in learning outcomes.
++++++++++++++++
More on ISTE in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=iste
more on digital literacy for ed leaders in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=digital+literacy+EDAD