Searching for "mobile learning"
Internet of Things: A Primer for Product Managers
https://medium.com/@delizalde/internet-of-things-a-primer-for-product-managers-5b6bef0a8b9b#.aitrbiy0h
The first step to becoming an IoT Product Manager is to understand the 5 layers of the IoT technology stack.
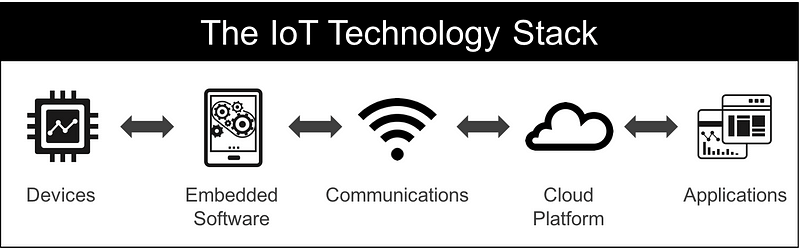
1. Devices
Devices constitute the “things” in the Internet of Things. They act as the interface between the real and digital worlds.
2. Embedded software
Embedded software is the part that turns a device into a “smart device”. This part of the IoT technology stack enables the concept of “software-defined hardware”, meaning that a particular hardware device can serve multiple applications depending on the embedded software it is running.
Embedded Operating System
The complexity of your IoT solution will determine the type of embedded Operating System (OS) you need. Some of the key considerations include whether your application needs a real-time OS, the type of I/O support you need, and whether you need support for the full TCP/IP stack.
Common examples of embedded OS include Linux, Brillo (scaled-down Android), Windows Embedded, and VxWorks, to name a few.
Embedded Applications
This is the application(s) that run on top of the embedded OS and provide the functionality that’s specific to your IoT solution.
3. Communications
Communications refers to all the different ways your device will exchange information with the rest of the world. This includes both physical networks and the protocols you will use.
4. Cloud Platform
The cloud platform is the backbone of your IoT solution. If you are familiar with managing SaaS offerings, then you are well aware of everything that is entailed here. Your infrastructure will serve as the platform for these key areas:
Data Collection and Management
Your smart devices will stream information to the cloud. As you define the requirements of your solution, you need to have a good idea of the type and amount of data you’ll be collecting on a daily, monthly, and yearly basis.
Analytics
Analytics are one of they key components of any IoT solution. By analytics, I’m referring to the ability to crunch data, find patterns, perform forecasts, integrate machine learning, etc. It is the ability to find insights from your data and not the data alone that makes your solution valuable.
Cloud APIs
The Internet of Things is all about connecting devices and sharing data. This is usually done by exposing APIs at either the Cloud level or the device level. Cloud APIs allow your customers and partners to either interact with your devices or to exchange data. Remember that opening an API is not a technical decision, it’s a business decision.
Related post: The Business of APIs: What Product Managers Need to Plan For
5. Applications
This is the part of the stack that is most easily understood by Product teams and Executives. Your end-user applications are the part of the system that your customer will see and interact with. These applications will most likely be Web-based, and depending on your user needs, you might need separate apps for desktop, mobile, and even wearables.
The Bottom Line
As the Internet of Things continues to grow, the world will need an army of IoT-savvy Product Managers. And those Product Managers will need to understand each layer of the stack, and how they all fit together into a complete IoT solution.
++++++++++++++
more on Internet of Things in this blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=internet+of+things
Bibliography on Arduino use in education:
peer-reviewed
http://scsu.mn/2e8mdNh – permanent link to the SCSU online database search (Arduino + Education)
Almeida Cavalcante, M. (2013). Novas tecnologias no estudo de ondas sonoras. Caderno Brasileiro De Ensino De Física, 30(3), 579-613.
Almeida Cavalcante, M., Tavares Rodrigues, T. T., & Andrea Bueno, D. (2013). CONTROLE REMOTO: PRINCIPIO DE FUNCIONAMENTO (parte 1 de 2). Caderno Brasileiro De Ensino De Física, 30(3), 554-565.
Atkin, K. (2016). Construction of a simple low-cost teslameter and its use with arduino and MakerPlot software. Physics Education, 51(2), 1-1.
Galeriu, C., Edwards, S., & Esper, G. (2014). An arduino investigation of simple harmonic motion. Physics Teacher, 52(3), 157-159.
Galeriu, C., Letson, C., & Esper, G. (2015). An arduino investigation of the RC circuit. Physics Teacher, 53(5), 285-288.
Grinias, J. P., Whitfield, J. T., Guetschow, E. D., & Kennedy, R. T. (2016). An inexpensive, open-source USB arduino data acquisition device for chemical instrumentation. Journal of Chemical Education, 93(7), 1316-1319.
Kuan, W., Tseng, C., Chen, S., & Wong, C. (2016). Development of a computer-assisted instrumentation curriculum for physics students: Using LabVIEW and arduino platform. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 25(3), 427-438.
Kubínová, Š., & Šlégr, J. (2015). Physics demonstrations with the arduino board. Physics Education, 50(4), 472-474.
Kubínová, Š., & Šlégr, J. (2015). ChemDuino: Adapting arduino for low-cost chemical measurements in lecture and laboratory. Journal of Chemical Education, 92(10), 1751-1753.
Kubínova´, S., & S?le´gr, J. (2015). ChemDuino: Adapting arduino for low-cost chemical measurements in lecture and laboratory. Journal of Chemical Education, 92(10), 1751-1753.
López-Rodríguez, F. M., & Cuesta, F. (2016). Andruino-A1: Low-cost educational mobile robot based on android and arduino. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 81(1), 63-76.
McClain, R. L. (2014). Construction of a photometer as an instructional tool for electronics and instrumentation. Journal of Chemical Education, 91(5), 747-750.
Musik, P. (2010). Development of computer-based experiment in physics for charging and discharging of a capacitor. Annual International Conference on Computer Science Education: Innovation & Technology, , I111-I116.
Pagliuca, G., Arduino, L. S., Barca, L., & Burani, C. (2008). Fully transparent orthography, yet lexical reading aloud: The lexicality effect in italian. Language and Cognitive Processes, 23(3), 422-433.
Park, S., Kim, W., & Seo, S. (2015). Development of the educational arduino module using the helium gas airship. Modern Physics Letters B, 29(6), -1.
Pereira, A. M., Santos, A. C. F., & Amorim, H. S. (2016). Estatística de contagem com a plataforma arduino. Caderno Brasileiro De Ensino De Física, 38(4), 1-8.
Sulpizio, S., Arduino, L. S., Paizi, D., & Burani, C. (2013). Stress assignment in reading italian polysyllabic pseudowords. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 39(1), 51-68.
Teikari, P., Najjar, R. P., Malkki, H., Knoblauch, K., Dumortier, D., Gronfier, C., et al. (2012). An inexpensive arduino-based LED stimulator system for vision research. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 211(2), 227-236.
Walzik, M. P., Vollmar, V., Lachnit, T., Dietz, H., Haug, S., Bachmann, H., et al. (2015). A portable low-cost long-term live-cell imaging platform for biomedical research and education. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 64, 639-649.
Zachariadou, K., Yiasemides, K., & Trougkakos, N. (2012). A low-cost computer-controlled arduino-based educational laboratory system for teaching the fundamentals of photovoltaic cells. European Journal of Physics, 33(6), 1599-1610.
Zubrycki, I., & Granosik, G. (2014). Introducing modern robotics with ros and arduino, including case studies. Journal of Automation, Mobile Robotics & Intelligent Systems, 8(1), 69-75.
Пионкевич, В. А. (2016). ИНСТРУМЕНТЫ ДЛЯ ОБУЧЕНИЯ СОВРЕМЕННЫМ СРЕДСТВАМ ЦИФРОВЫХ СИСТЕМ АВТОМАТИЧЕСКОГО УПРАВЛЕНИЯ НЕТРАДИЦИОННЫМИ ИСТОЧНИКАМИ ЭЛЕКТРИЧЕСКОЙ ЭНЕРГИИ НА ОСНОВЕ МИКРОКОНТРОЛЛЕРОВ. Bulletin of Irkutsk State Technical University / Vestnik of Irkutsk State Technical University, (6), 136-145.
——————————-
popular literature:
http://playground.arduino.cc/Projects/Ideas
http://www.instructables.com/id/20-Unbelievable-Arduino-Projects/
20 Projects To Celebrate Arduino Day
https://www.quora.com/What-would-be-a-good-idea-for-an-Arduino-innovative-project
https://www.element14.com/community/groups/arduino/blog/2014/06/06/10-awesome-arduino-projects
+++++++++++++++++++
more on Arduino in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=arduino
Wednesday, October 19, 2016
1:00 p.m. – 2:30 p.m. (Eastern Time)
About the Webinar
As the cost of sensors and the connectivity necessary to support those sensors has decreased, this has given rise to a network of interconnected devices. This network is often described as the Internet of Things and it is providing a variety of information management challenges. For the library and publishing communities, the internet of things presents opportunities and challenges around data gathering, organization and processing of the tremendous amounts of data which the internet of things is generating. How will these data be incorporated into traditional publication, archiving and resource management systems? Additionally, how will the internet of things impact resource management within our community? In what ways will interconnected resources provide a better user experience for patrons and readers? This session will introduce concepts and potential implications of the internet of things on the information management community. It will also explore applications related to managing resources in a library environment that are being developed and implemented.
Education in the Internet of Things
Bryan Alexander, Consultant;
How will the Internet of Things shape education? We can explore this question by assessing current developments, looking for future trends in the first initial projects. In this talk I point to new concepts for classroom and campus spaces, examining attendant rises in data gathering and analysis. We address student life possibilities and curricular and professional niches. We conclude with notes on campus strategy, including privacy, network support, and futures-facing organizations.
What Does The Internet of Things Mean to a Museum?
Robert Weisberg, Senior Project Manager, Publications and Editorial Department; Metropolitan Museum of Art;
What does the Internet of Things mean to a museum? Museums have slowly been digitizing their collections for years, and have been replacing index cards with large (and costly, and labor-intensive) CMS’s long before that, but several factors have worked against adopting smart and scalable practices which could unleash data for the benefit of the institution, its collection, and its audiences. Challenges go beyond non-profit budgets in a very for-profit world and into the siloed behaviors learned from academia, practices borne of the uniqueness of museum collections, and the multi-faceted nature of modern museums which include not only curator, but conservators, educators, librarians, publishers, and increasing numbers of digital specialists. What have museums already done, what are they doing, and what are they preparing for, as big data becomes bigger and ever more-networked?
The Role of the Research Library in Unpacking The Internet of Things
Lauren di Monte, NCSU Libraries Fellow, Cyma Rubin Fellow, North Carolina State University
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a deceptively simple umbrella term for a range of socio-technical tools and processes that are shaping our social and economic worlds. Indeed, IoT represents a new infrastructural layer that has the power to impact decision-making processes, resources distribution plans, information access, and much more. Understanding what IoT is, how “things” get networked, as well as how IoT devices and tools are constructed and deployed, are important and emerging facets of information literacy. Research libraries are uniquely positioned to help students, researchers, and other information professionals unpack IoT and understand its place within our knowledge infrastructures and digital cultures. By developing and modeling the use of IoT devices for space and program assessment, by teaching patrons how to work with IoT hardware and software, and by developing methods and infrastructures to collect IoT devices and data, we can help our patrons unlock the potential of IoT and harness the power of networked knowledge.
Lauren Di Monte is a Libraries Fellow at NC State. In this role she develops programs that facilitate critical and creative engagements with technologies and develops projects to bring physical and traditional computing into scholarship across the disciplines. Her current research explores the histories and futures of STEM knowledge practices.
What does the internet of things mean for education?
Bryan Alexander: September 17, 2014
I’m not sure if the IoT will hit academic with the wave force of the Web in the 1990s, or become a minor tangent. What do schools have to do with Twittering refrigerators?
Here are a few possible intersections.
- Changing up the campus technology space. IT departments will face supporting more technology strata in a more complex ecosystem. Help desks and CIOs alike will have to consider supporting sensors, embedded chips, and new devices. Standards, storage, privacy, and other policy issues will ramify.
- Mutating the campus. We’ve already adjusted campus spaces by adding wireless coverage, enabling users and visitors to connect from nearly everywhere. What happens when benches are chipped, skateboards sport sensors, books carry RFID, and all sorts of new, mobile devices dot the quad? One British school offers an early example.
- New forms of teaching and learning. Some of these take preexisting forms and amplify them, like tagging animals in the wild or collecting data about urban centers. The IoT lets us gather more information more easily and perform more work upon it. Then we could also see really new ways of learning, like having students explore an environment (built or natural) by using embedded sensors, QR codes, and live datastreams from items and locations. Instructors can build treasure hunts through campuses, nature preserves, museums, or cities. Or even more creative enterprises.
- New forms of research. As with #3, but at a higher level. Researchers can gather and process data using networked swarms of devices. Plus academics studying and developing the IoT in computer science and other disciplines.
- An environmental transformation. People will increasingly come to campus with experiences of a truly interactive, data-rich world. They will expect a growing proportion of objects to be at least addressable, if not communicative. This population will become students, instructors, and support staff. They will have a different sense of the boundaries between physical and digital than we now have in 2014. Will this transformed community alter a school’s educational mission or operations?
MindTap Offers Users Free Access to Digital Portfolio Tool
By Sri Ravipati 08/03/16
https://campustechnology.com/articles/2016/08/03/mindtap-offers-users-free-access-to-digital-portfolio-tool.aspx
MindTap, an online learning platform from Cengage Learning, will be able to build digital portfolios of their work for free and keep them for life.
mobile app version is available on the Apple Store and Google Play.
++++++++++++++++
more on e-portfolio in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=electronic+portfolio
training session 10:30AM July 7
firefox is preferable to chrome and IE
in chrome, audio plays automatically. if students are using Chromes, need to have the audio file on the top, so students can stop it. NAPI is not supported by Google. So Softchalk must start local launch.
this is SO complex and SO many side steps that it will be a miracle to get the middle 50-60% of faculty into buying the SoftChalk idea.
local launch is client based and allows creating content without Internet connection
edit in Create Online allows creation on mobile devices such as tablet
have to have rights on the computer to install the local launch. Ha…
I am behind David, since my java is not up to date. i have to update now that. I wonder how many faculty will endure the initial process
Microsoft Edge is different the IE, but will act the same
SoftChalk is the same elitist ideas as LMS. It will require an extensive training of faculty, which they have no time and energy to invest in. The idea of Learning Objects will require years of compiling materials, sufficiently enough to be recycled by other faculty. In most disciplines, these learning objects will age by the time they reach the critical mass.
————-
training session 1PM July 6, 2016
David Evans from SoftChalk is doing the training session.
If we want to share with students, do they have to have a user account in softchalk?
Аnswer: No. The instructor can share the content by embedding the URL to the Softchalk content, but not allow students to participate in the creation
the answer defies the constructivist principles of learning
MnSCU site Educational Innovations -> MnSCU SoftChalk Pilot
http://www.asa.mnscu.edu/educationalinnovations/projects/SoftChalk_Cloud/educational-innovations-page.html
- Part 1: Trainer David Evans – SoftChalk’s cloud management (creating lessons, folders, sharing, uploading files and more) – 1 hour 5 min
https://mnscu.webex.com/mnscu/ldr.php?RCID=b15902c4eb57cfcbfc6559b4f2e4bcf7
- Part 2: – 21 min https://mnscu.webex.com/mnscu/ldr.php?RCID=2e0612ead1c04836ab614ebafe4607ed
- Lesley Blicker – MnSCU’s pilot project and web resources (7 min)
- Jon Werth – integrating SoftChalk with the D2L Brightspace gradebook, plus browsers to use or avoid
——————————–
MnSCU pilot. How to do the LT integration for the gradebook, including browsers constrains.
++++++++++++++++++++++
SoftChalk Session for CSAs and CTs
Java applet is essential, until HMTL5 is functional. IT and the System Office have things locked down and not much can be done. Java Application cannot be blocked.
http://asa.mnscu.edu/educationalinnovations/projects/SoftChalk_Cloud/educational-innovations-page.html
Integrating Softchalk Cloud w D2L. SCORM – don’t use it. Tool Provider.
SoftChalk (SC) can be used as an external link within D2L, internal integration only when used with the gradebook. The LTI link is ONLY needed if the instructor plans to use the gradebook. Otherwise, it’s a simple embed in content.
if recently installed Java 8.91, will not install the jar file and one have to go and manually delete it.
Browsers.
Firefox and IE will allow to launch the Java applet. Chrome and Safari will block it. it will require a local launch. The install will create an icon in the lower right corner.
I cannot believe such structure, in the times of drag and drop. Whoever came up w it, is DEFINITELY not a faculty and does not care about faculty time and effort.
the process is lengthy and cumbersome, not to mentioned repetitive. If this work is shifted toward faculty, i seriously doubt that the adoption rate will be in the double digits.
verdict: much ado about nothing: the work that faculty have to put toward such content versus the return on the Bloom’s taxonomy scale is so low that in my opinion is just squandering of efforts. If there is a LOR, where faculty can draw preset clusters of similar activities, I would be more willing to accept.
a license for SoftChalk Cloud is needed. Who is in charge of this? John and TLTR? Tom as faculty president?
++++++++++++++++++++++
more on Softchalk in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=softchalk
A Real-World Writing Project Integrating Mobile Technology and Team-Based Learning
http://douko.weebly.com/google-mapping-my-campus.html
More on Google Maps in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=google+maps
4 Great Curation Tools Created by Teachers for Teachers
http://www.educatorstechnology.com/2016/04/4-great-digital-curation-tools-created.html
April 28, 2016
Edshelf
Edshelf is ‘a socially curated discovery engine of websites, mobile apps, desktop programs, and electronic products for teaching and learning. You can search and filter for specific tools, create shelves of tools you use for various purposes, rate and review tools you’ve used, and receive a newsletter of tools recommended by other educators.
Graphite
a free service from nonprofit Common Sense Education designed to help preK-12 educators discover, use, and share the best apps, games, websites, and digital curricula for their students by providing unbiased, rigorous ratings and practical insights from our active community of teachers
Scoop.it
find out content related to your topics by ‘reviewing your suggestion lists and the topics from other curators
educlipper
social learning platform that allows teachers to curate and share educational content. Some of the interesting features it provides include: ‘Explore top quality education resources for K-12, create clips from the web, Drive, Dropbox, use your camera to capture awesome work that you create in and out of the classroom, create whiteboard recordings, create differentiated groups and share content with them, create Personal Learning Portfolios, create Class Portfolios as a teacher and share Assignments with students, provide quality feedback through video, audio, text, badges, or grades, collaborate with other users on eduClipboards for class projects or personal interests
Survey: What Gen Z Thinks About Ed Tech in College
A report on digital natives sheds light on their learning preferences.
Like the
millennials before them, Generation Z grew up as digital natives, with devices a fixture in the learning experience. According to the survey results, these students want “engaging, interactive learning experiences” and want to be “empowered to make their own decisions.” In addition, the students “expect technology to play an instrumental role in their educational experience.”
to cater to the digital appetites of tomorrow’s higher education learners, technology in education will need to play a bit of catch-up, states the New Media Consortium’s 2015
Course Apps report. According to NMC’s analysts, digital-textbook adoption was one of the leading trends helping to reinvent how higher education students learn. But publishers have not captured the innovations happening elsewhere in the digital marketplace.
The Generation Z report ranked the effectiveness of 11 education technology tools:
- Smartboards
- Do-It-Yourself Learning
- Digital Textbooks
- Websites with Study Materials
- Online Videos
- Game-Based Learning Systems
- Textbook
- Social Media
- Skype
- Podcasts
- DVD/Movies
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
more on Gen Z in this blog:
Generation Z bibliography
Research: Social media has negative impact on academic performance
By Denny Carter, Managing Editor
April 17th, 2013
study released by researchers at
The Miriam Hospital’s Centers for Behavioral and Preventive Medicine shows a link between social media use and poor academic performance
My note: weak arguments by the managing editor
- first: link to the Hospital Center, but not to the study; difficult to check the facts, which are discussed in the editorial.
- title talks about “social media,” but it is not about social media, it is about texting. danah boyd and Eszter Hargittai are apparently not household names in the house of the managing editor
- then the author jumps from one issue to another: mindfulness or contemplative computing, but h/she has no clue about these issues also.
the research, which claims that social media (which is not social media, but more like BYOD + texting) has a negative impact on academic performance is no different the research that shows very positive impact of learning with social media. It is NOT about social media, it is about how it is used (methodology).
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
More on contemplative computing in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=contemplative+computing
Also on the connection of mobile devices and sleep:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/04/09/sleep/
Our discussion:
++++++++++++++++++++++++
Main speaker: Ken Chapman
mapping what students are looking at the screen
intelligent agent: dancing hamster
immediate gratification – certification, this is practically badges
story builder – D2L tool
D2L dropbox – look previous assignments and submissions within dropbox
time savers: 1. miss an assignment deadline – use agent. My note: how does it roll over? how much time and effort to condition it after it is rolled over?
text expanders: create codes in the browsers to evoke repetitions (;runon)
“Daylight Experience” is the D2L new look and feel put on D2L. nice clean modern looking.
Mobile First, API Access, Assessments, Advanced CBE (competency-based education programs), Predictive Analytics (recommendation system to pick right course, red flags, Dashboards,
Content:
interactive publisher material. Dates and Feeds on Mobile, Curriculum Planning
Capture: my note – how does it fit with MediaSpace
ePortfolio my note – how does it fit TK-20
Repository – open content, publishers, how to bring easier into a course
Adaptive learning
D2L purchased a module. publisher packets, adaptive textbooks. D2L looks at it as an engine where faculty feeds the idea and the engine is making the links and structuring the ideas into content. It also the engine checks what learners already know and based on results finds knowledge gaps.
need well defined learning objective, good content and ways to assess the material.
Start with creating support course delivery, test preparation.
