Assessment Is an Enormous Waste of Time
https://www.chronicle.com/article/assessment-is-an-enormous-waste-of-time/
The assessment industry is not known for self-critical reflection. Assessors insist that faculty provide evidence that their teaching is effective, but they are dismissive of evidence that their own work is ineffective. They demand data, but they are indifferent to the quality of those data. So it’s not a surprise that the assessment project is built on an unexamined assumption: that learning, especially higher-order learning such as critical thinking, is central to the college experience.
the Lumina Foundation’s Degree Qualifications Profile “provides a qualitative set of important learning outcomes, not quantitative measures such as numbers of credits and grade-point averages, as the basis for awarding degrees.”
article in Change, Daniel Sullivan, president emeritus of St. Lawrence University and a senior fellow at the Association of American Colleges & Universities, and Kate McConnell, assistant vice president for research and assessment at the association, describe a project that looked at nearly 3,000 pieces of student work from 14 institutions. They used the critical-thinking and written-communication Value rubrics designed by the AAC&U to score the work. They discovered that most college-student work falls in the middle of the rubric’s four-point scale measuring skill attainment.
Richard Arum and Josipa Roska’s 2011 book, Academically Adrift, used data from the Collegiate Learning Assessment to show that a large percentage of students don’t improve their critical thinking or writing. A 2017 study by The Wall Street Journal used data from the CLA at dozens of public colleges and concluded that the evidence for learning between the first and senior years was so scant that they called it “discouraging.”
not suggesting that college is a waste of time or that there is no value in a college education. But before we spend scarce resources and time trying to assess and enhance student learning, shouldn’t we maybe check to be sure that learning is what actually happens in college?
+++++++++++++++
more on assessment in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=assessment
and critical thinking
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=critical+thinking
CALL FOR PAPERS AND PROPOSALS
iLRN 2021: 7th International Conference of the Immersive Learning Research Network
May 17 to June 10, 2021, on iLRN Virtual Campus, powered by Virbela
… and across the Metaverse!
Technically co-sponsored by the IEEE Education Society,
with proceedings to be submitted for inclusion in IEEE Xplore(r)
Conference theme: “TRANSCEND: Accelerating Learner Engagement in XR across Time, Place, and Imagination”
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
The 7th International Conference of the Immersive Learning Research Network (iLRN 2021) will be an innovative and interactive virtual gathering for a strengthening global network of researchers and practitioners collaborating to develop the scientific, technical, and applied potential of immersive learning. It is the premier scholarly event focusing on advances in the use of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), and other extended reality (XR) technologies to support learners across the full span of learning–from K-12 through higher education to work-based, informal, and lifelong learning contexts.
Following the success of iLRN 2020, our first fully online and in-VR conference, this year’s conference will once again be based on the iLRN Virtual Campus, powered by VirBELA, but with a range of activities taking place on various other XR simulation, gaming, and other platforms. Scholars and professionals working from informal and formal education settings as well as those representing diverse industry sectors are invited to participate in the conference, where they may share their research findings, experiences, and insights; network and establish partnerships to envision and shape the future of XR and immersive technologies for learning; and contribute to the emerging scholarly knowledge base on how these technologies can be used to create experiences that educate, engage, and excite learners.
Note: Last year’s iLRN conference drew over 3,600 attendees from across the globe, making the scheduling of sessions a challenge. This year’s conference activities will be spread over a four-week period so as to give attendees more opportunities to participate at times that are conducive to their local time zones.
##### TOPIC AREAS #####
XR and immersive learning in/for:
Serious Games • 3D Collaboration • eSports • AI & Machine Learning • Robotics • Digital Twins • Embodied Pedagogical Agents • Medical & Healthcare Education • Workforce & Industry • Cultural Heritage • Language Learning • K-12 STEM • Higher Ed & Workforce STEM • Museums & Libraries • Informal Learning • Community & Civic Engagement • Special Education • Geosciences • Data Visualization and Analytics • Assessment & Evaluation
##### SUBMISSION STREAMS & CATEGORIES #####
ACADEMIC STREAM (Refereed paper published in proceedings):
– Full (6-8 pages) paper for oral presentation
– Short paper (4-5 pages) for oral presentation
– Work-in-progress paper (2-3 pages) for poster presentation
– Doctoral colloquium paper (2-3 pages)
PRACTITIONER STREAM (Refereed paper published in proceedings):
– Oral presentation
– Poster presentation
– Guided virtual adventures
– Immersive learning project showcase
NONTRADITIONAL SESSION STREAM (1-2 page extended abstract describing session published in proceedings):
– Workshop
– Special session
– Panel session
##### SESSION TYPES & SESSION FORMATS #####
– Oral Presentation: Pre-recorded video + 60-minute live in-world discussion with
others presenting on similar/related topics (groupings of presenters into sessions determined by Program Committee)
– Poster Presentation: Live poster session in 3D virtual exhibition hall; pre-recorded video optional
– Doctoral Colloquium: 60-minute live in-world discussion with other doctoral researchers; pre-recorded video optional
– Guided Virtual Adventures: 60-minute small-group guided tours of to various social and collaborative XR/immersive environments and platforms
– Immersive Learning Project Showcase: WebXR space to assemble a collection of virtual artifacts, accessible to attendees throughout the conference
– Workshop: 1- or 2-hour live hands-on session
– Special Session: 30- or 60-minute live interactive session held in world; may optionally be linked to one or more papers
– Panel Session: 60-minute live in-world discussion with a self-formed group of 3-5 panelists (including a lead panelist who serves as a moderator)
Please see the conference website for templates and guidelines.
##### PROGRAM TRACKS #####
Papers and proposals may be submitted to one of 10 program tracks, the first nine of which correspond to the iLRN Houses of application, and the tenth of which is intended for papers making knowledge contributions to the learning sciences, computer science, and/or game studies that are not linked to any particular application area:
Track 1. Assessment and Evaluation (A&E)
Track 2. Early Childhood Development & Learning (ECDL)
Track 3. Galleries, Libraries, Archives, & Museums (GLAM)
Track 4. Inclusion, Diversity, Equity, Access, & Social Justice (IDEAS)
Track 5. K-12 STEM Education
Track 6. Language, Culture, & Heritage (LCH)
Track 7. Medical & Healthcare Education (MHE)
Track 8. Nature & Environmental Sciences (NES)
Track 9. Workforce Development & Industry Training (WDIT)
Track 10. Basic Research and Theory in Immersive Learning (not linked to any particular application area)
##### PAPER/PROPOSAL SUBMISSION & REVIEW #####
Papers for the Academic Stream and extended-abstract proposals for the Nontraditional Session Stream must be prepared in standard IEEE double-column US Letter format using Microsoft Word or LaTeX, and will be accepted only via the online submission system, accessible via the conference website (from which guidelines and templates are also available).
Proposals for the Practitioner Stream are to be submitted via an online form, also accessible from the conference website.
A blind peer-review process will be used to evaluate all submissions.
##### IMPORTANT DATES #####
– Main round submission deadline – all submission types welcome: 2021-01-15
– Notification of review outcomes from main submission round: 2021-04-01
– Late round submission deadline – Work-in-progress papers, practitioner presentations, and nontraditional sessions only: 2021-04-08
– Camera-ready papers for proceedings due – Full and short papers: 2021-04-15
– Presenter registration deadline – Full and short papers (also deadline for early-bird registration rates): 2021-04-15
– Notification of review outcomes from late submission round: 2021-04-19
– Camera-ready work-in-progress papers and nontraditional session extended abstracts for proceedings due; final practitioner abstracts for conference program due: 2021-05-03
– Presenter registration deadline – Work-in-progress papers, practitioner presentations, and nontraditional sessions: 2021-05-03
– Deadline for uploading presentation materials (videos, slides for oral presentations, posters for poster presentations): 2021-05-10
– Conference opening: 2021-05-17
– Conference closing: 2021-06-10
*Full and short papers can only be submitted in the main round.
##### PUBLICATION & INDEXING #####
All accepted and registered papers in the Academic Stream that are presented at iLRN 2021 and all extended abstracts describing the Nontraditional Sessions presented at the conference will be published in the conference proceedings and submitted to the IEEE Xplore(r) digital library.
Content loaded into Xplore is made available by IEEE to its abstracting and indexing partners, including Elsevier (Scopus, EiCompendex), Clarivate Analytics (CPCI–part of Web of Science) and others, for potential inclusion in their respective databases. In addition, the authors of selected papers may be invited to submit revised and expanded versions of their papers for possible publication in the IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies (2019 JCR Impact Factor: 2.714), the Journal of Universal Computer Science (2019 JCR Impact Factor: 0.91), or another Scopus and/or Web of Science-indexed journal, subject to the relevant journal’s regular editorial and peer-review policies and procedures.
##### CONTACT #####
More on Virbela in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virbela
Information Overload Helps Fake News Spread, and Social Media Knows It
Understanding how algorithm manipulators exploit our cognitive vulnerabilities empowers us to fight back
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/information-overload-helps-fake-news-spread-and-social-media-knows-it/
a minefield of cognitive biases.
People who behaved in accordance with them—for example, by staying away from the overgrown pond bank where someone said there was a viper—were more likely to survive than those who did not.
Compounding the problem is the proliferation of online information. Viewing and producing blogs, videos, tweets and other units of information called memes has become so cheap and easy that the information marketplace is inundated. My note: folksonomy in its worst.
At the University of Warwick in England and at Indiana University Bloomington’s Observatory on Social Media (OSoMe, pronounced “awesome”), our teams are using cognitive experiments, simulations, data mining and artificial intelligence to comprehend the cognitive vulnerabilities of social media users.
developing analytical and machine-learning aids to fight social media manipulation.
As Nobel Prize–winning economist and psychologist Herbert A. Simon noted, “What information consumes is rather obvious: it consumes the attention of its recipients.”
attention economy
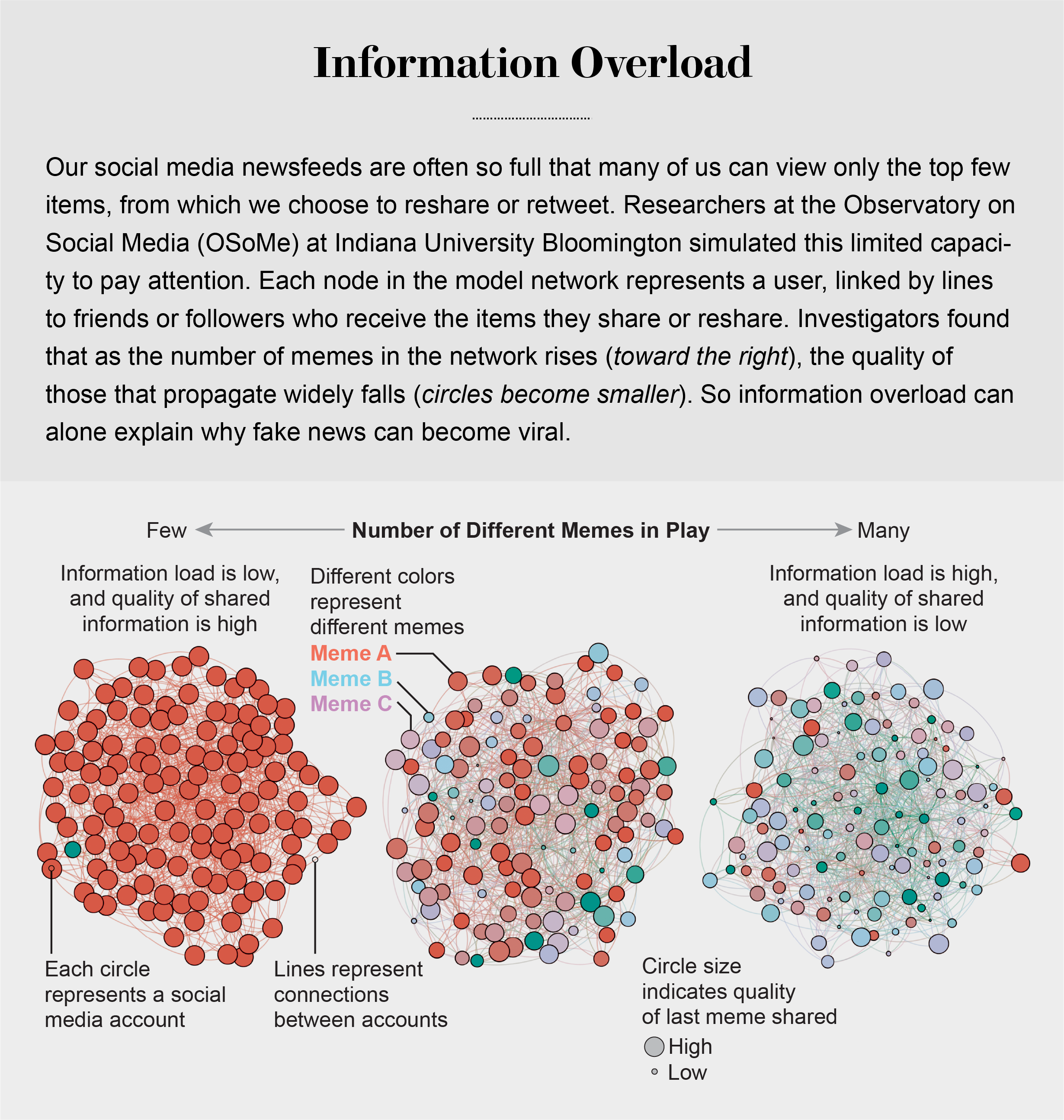
Our models revealed that even when we want to see and share high-quality information, our inability to view everything in our news feeds inevitably leads us to share things that are partly or completely untrue.
Frederic Bartlett
Cognitive biases greatly worsen the problem.
We now know that our minds do this all the time: they adjust our understanding of new information so that it fits in with what we already know. One consequence of this so-called confirmation bias is that people often seek out, recall and understand information that best confirms what they already believe.
This tendency is extremely difficult to correct.
Making matters worse, search engines and social media platforms provide personalized recommendations based on the vast amounts of data they have about users’ past preferences.
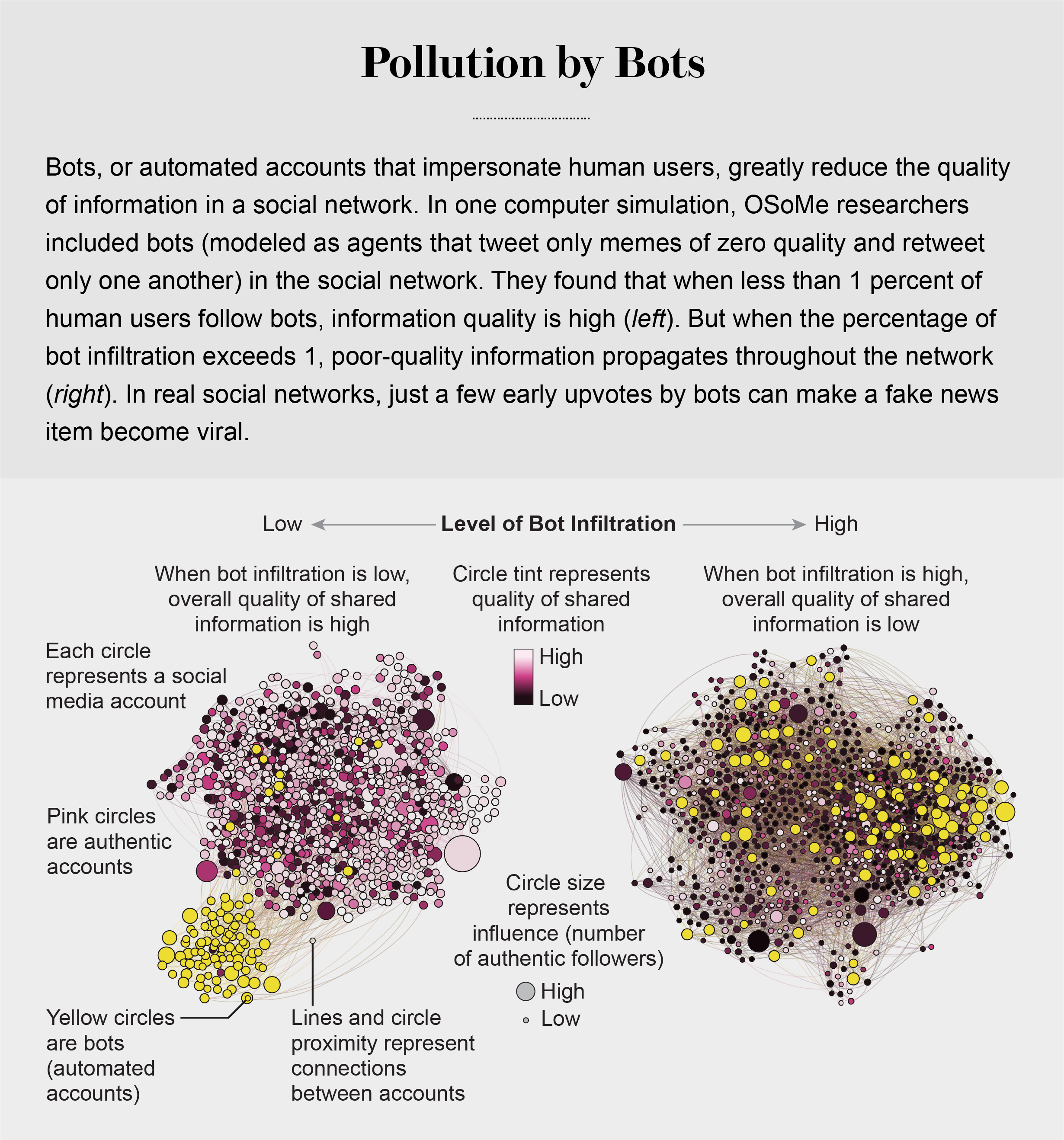
pollution by bots
Social Herding
social groups create a pressure toward conformity so powerful that it can overcome individual preferences, and by amplifying random early differences, it can cause segregated groups to diverge to extremes.
Social media follows a similar dynamic. We confuse popularity with quality and end up copying the behavior we observe.
information is transmitted via “complex contagion”: when we are repeatedly exposed to an idea, typically from many sources, we are more likely to adopt and reshare it.
In addition to showing us items that conform with our views, social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and Instagram place popular content at the top of our screens and show us how many people have liked and shared something. Few of us realize that these cues do not provide independent assessments of quality.
programmers who design the algorithms for ranking memes on social media assume that the “wisdom of crowds” will quickly identify high-quality items; they use popularity as a proxy for quality. My note: again, ill-conceived folksonomy.
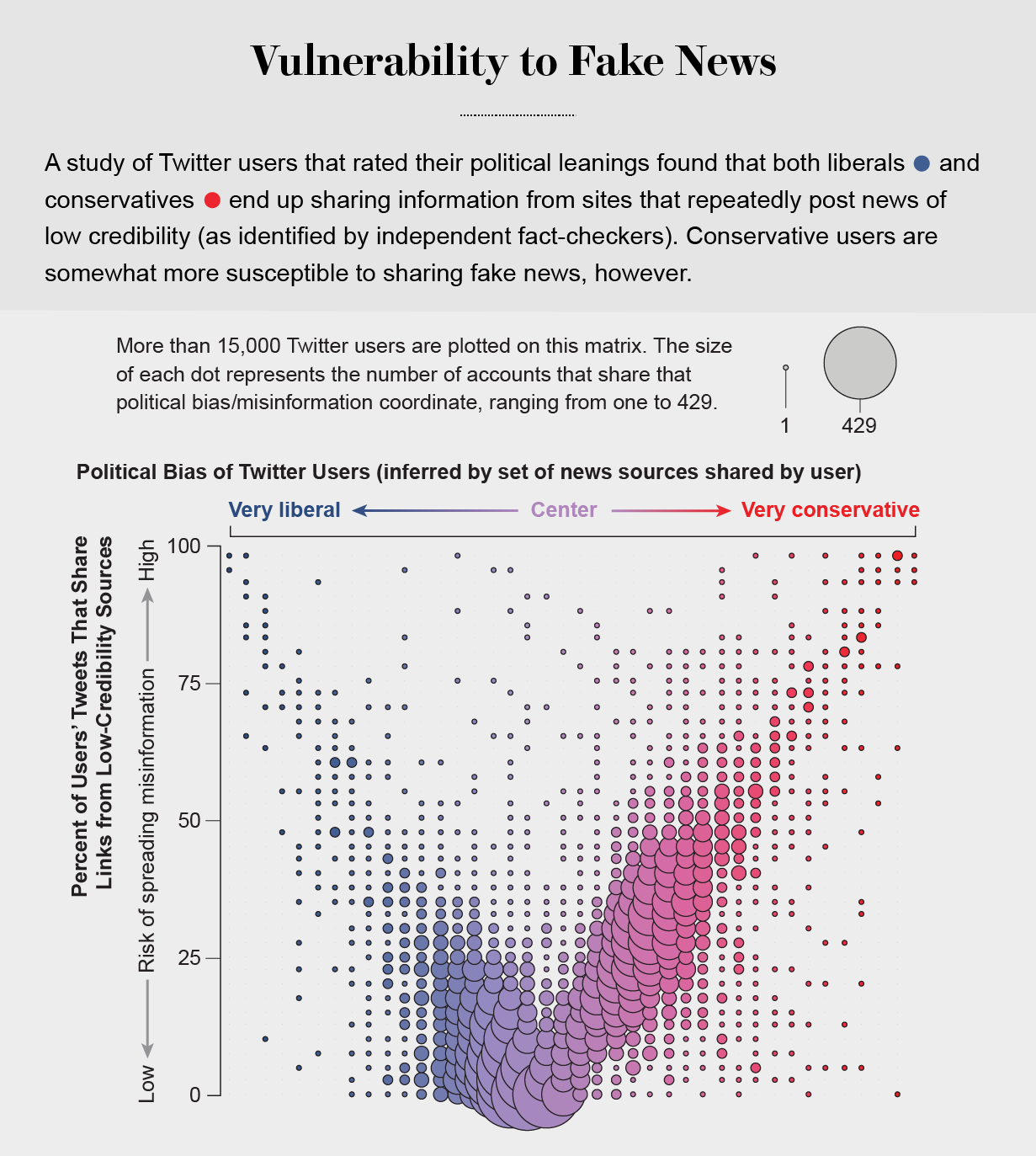
Echo Chambers
the political echo chambers on Twitter are so extreme that individual users’ political leanings can be predicted with high accuracy: you have the same opinions as the majority of your connections. This chambered structure efficiently spreads information within a community while insulating that community from other groups.
socially shared information not only bolsters our biases but also becomes more resilient to correction.
machine-learning algorithms to detect social bots. One of these, Botometer, is a public tool that extracts 1,200 features from a given Twitter account to characterize its profile, friends, social network structure, temporal activity patterns, language and other features. The program compares these characteristics with those of tens of thousands of previously identified bots to give the Twitter account a score for its likely use of automation.
Some manipulators play both sides of a divide through separate fake news sites and bots, driving political polarization or monetization by ads.
recently uncovered a network of inauthentic accounts on Twitter that were all coordinated by the same entity. Some pretended to be pro-Trump supporters of the Make America Great Again campaign, whereas others posed as Trump “resisters”; all asked for political donations.
a mobile app called Fakey that helps users learn how to spot misinformation. The game simulates a social media news feed, showing actual articles from low- and high-credibility sources. Users must decide what they can or should not share and what to fact-check. Analysis of data from Fakey confirms the prevalence of online social herding: users are more likely to share low-credibility articles when they believe that many other people have shared them.
Hoaxy, shows how any extant meme spreads through Twitter. In this visualization, nodes represent actual Twitter accounts, and links depict how retweets, quotes, mentions and replies propagate the meme from account to account.
Free communication is not free. By decreasing the cost of information, we have decreased its value and invited its adulteration.


