Accessing Higher Ground – Accessible Media, Web and Technology Conference
Virtual Agenda November 14-16, 2018
++++++++++++++++++
Not So Fast: Implementing Accessibility Reviews in a University’s IT Software Review Process
- Crystal Tenan, IT Accessibility Coordinator, NC State University
- Bill Coker, Software Licensing Manager, NC State University
Summary
In this presentation, we will provide an overview of NC State’s IT Purchase Compliance process and focus on the accessibility review process. We will discuss the process of implementation, important considerations for working with the campus community and vendors, and the impact of the IT Purchase Compliance process on campus.
Abstract
Before a university purchases software, it should review the software to ensure it complies with university standards and follows Federal and State guidelines for security and accessibility. Without review, there is a higher risk that purchases put sensitive university data at risk, do not meet the needs of the campus population with disabilities, or require integration with enterprise level applications.
In a joint effort between the Office of Information Technology, the Office of General Counsel and the Purchasing Department, NC State University implemented a process to review purchases of software prior to issuing a purchase requisition.
In this presentation, we will provide an overview of NC State’s IT Purchase Compliance process and focus on the accessibility review process. We will discuss the process of implementation, important considerations for working with the campus community and vendors, and the impact of the IT Purchase Compliance process on campus.
Keypoints
- Participants will learn the importance of software reviews prior to purchasing.
- Participants will be exposed to an example format of how to structure a software review process.
- Participants will learn techniques for collaborating with various campus departments for software reviews.
(handouts available: ask me)
+++++++++
Math Accessibility in Word, Canvas, Conversion and More!
- Paul Brown, Vice President, Texthelp
- Rachel Kruzel, Assistive Technology & Accommodations Specialist, Augsburg University
Rachel Kruzel: Free and Low Cost Accessibility Tools (March 2018) https://vimeo.com/259224118
Link to Resources at Augsburg: http://www.augsburg.edu/class/groves/assistive-technology/
Session Details
- Length of Session: 1-hr
- Format: Lecture
- Expertise Level: Beginner
- Type of session: General Conference
Summary
This session will overview Texthelp’s exciting math accessibility program, EquatIO. Learn how students and professors easily insert math into Word, Canvas, and more as well as make STEM textbook conversion a much easier process. Augsburg’s Rachel Kruzel will provide an inside look into how EquatIO is making math accessible across her campus.
Abstract
EquatIO is Texthelp’s game-changing math software program that gives students and professors multiple means of producing, engaging with, and expressing math with ease. This session will overview how to easily insert math into Microsoft Word, Canvas, and other programs as well as how it can save valuable time and resources in STEM textbook conversion. The program’s core features including math-to-speech, speech-to-math, math prediction, math OCR capabilities and many other tools will be demonstrated, helping empower students in this traditionally challenging area. Attendees will not only learn the program, but also how they can gain free access to its premium features as well as assist their students in utilizing the freemium and premium tools.
Keypoints
- Math accessibility is here!
- EquatIO is a digital math solution for all students and staff.
- Save time and resources in STEM textbook conversion.
Disability Areas
All Areas, Cognitive/Learning, Vision
Topic Areas
Alternate Format, Assistive Technology, eBooks, Faculty Instruction/Accessible Course Design, Including Accessibility in Curriculum, Information Technology, Uncategorized, Web/Media Access
Speaker Bio(s)
Paul Brown
Paul Brown has been in education for 20 years as a teacher, technology coach, manager, and currently is a Vice President at Texthelp. Paul’s team oversees the successful implementation of the Read&Write and EquatIO product lines. Paul is a Cleveland Browns fan for life and asks for your pity ahead of time. He and his family live in Edina, MN.
Rachel Kruzel
Rachel Kruzel, ATP, is the Assistive Technology & Accommodations Specialist at Augsburg University in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and is a RESNA Certified Assistive Technology Practitioner (ATP). She has over 8 years of experience working in in the CLASS Office (Disability Resources) focusing on assistive technology, educational technology, transitioning from K-12 to higher education, academic accommodations implementation, and digital, electronic, and web accessibility. Rachel has presented both regionally and nationally on a variety of topics about assistive technology, as well as accessibility, transition, assistive technology tools such as the QIAT-PS and specific software program demonstrations and trainings, as well as general consultation with students, parents, schools, and organizations. She also provides consulting and direct consumer support through assistive technology consultation and the implementation process.
++++++++++++++++
“We don’t have enough staff assigned to making IT accessible!”
Summary
How often do we hear people say this or feel this way ourselves? In this session the speaker will engage with attendees on promising practices for making the most of limited resources toward a more accessible IT environment on campus.
Abstract
How often do we hear people say this or feel this way ourselves? In this session the speaker will engage with attendees on promising practices for making the most of limited resources toward a more accessible IT environment on campus. Topics will included but not be limited to convening a high level task force of key stakeholders on campus, developing policies and guidelines, offering training on accessibility within other training opportunities, presenting at regularly occurring meetings and special interest groups, developing partnerships, supporting a group of IT accessibility liaisons to extend the reach of central services, securing funds to proactively caption videos and remediate inaccessible documents (particularly those that are high impact/use), providing online resources for specific target groups, and purchasing accessibility tools for campus-wide use. The speaker will provide examples and the audience will contribute their own ideas, experiences, and lessons learned.
Keypoints
- Organizations promoting accessible IT on campuses are often under staffed.
- Promising practices have been developed at some schools for maximizing the impact of available resources.
- Promising practices have been developed at some schools for maximizing the impact of available resources.
Disability Areas
All Areas
Topic Areas
Administrative/Campus Policy, Information Technology, Uncategorized
Speaker Bio(s)
Sheryl Burgstahler
Dr. Sheryl Burgstahler founded and directs the DO-IT (Disabilities, Opportunities, Internetworking, and Technology) Center and the ATC (Access Technology Center) as part of her role as Director of Accessible Technology Services at the University of Washington (UW). These centers promote (1) the support the success of students with disabilities in postsecondary education and careers and (2) the development of facilities, IT, services, and learning activities that are welcoming and accessible to individuals with disabilities. The ATC focuses efforts at the UW; the DO-IT Center reaches national and international audiences with the support of federal, state, corporate, foundation, and private funds. Dr. Burgstahler is an affiliate professor in the UW College of Education. She developed and taught the Accessibility and Compliance in Online Education online course offered by Rutgers University and currently teaches graduate courses in applications of universal design in higher education at City University of New York and Saint Louis University.
(handouts available: ask me)
++++++++++++++++++
Evaluating and Repairing Word and PowerPoint Files
Summary
In this hands-on workshop, learn to evaluate and repair common accessibility issues in Microsoft Word and PowerPoint.
Abstract
Both Word and PowerPoint contain a very useful accessibility checker that can identify many potential accessibility issues within a document. However, like any automated checker, there are also many issues that it cannot detect–accessibility evaluation is always a combination of evaluation tools and manual checks.
During this workshop, participants will practice evaluating and repairing many common accessibility issues of Word and PowerPoint files. We will use practice files and a printable evaluation checklist to evaluate Word docs and Power Point slides.
Keypoints
- Learn to use the built-in Microsoft Office Accessibility Checker
- Identify accessibility issues that must be analyzed manually
- Practice evaluating and repairing the accessibility of Word and PowerPoint files
Disability Areas
All Areas
Topic Areas
Uncategorized, Web/Media Access
Speaker Bio(s)
Jonathan Whiting
o: Jonathan Whiting is the Director of Training at WebAIM, based at Utah State University. His main passion is helping others learn to make the web more accessible to people with disabilities. Jonathan is also currently involved in the GOALS Project, a program to assist institutions of Higher Education in improving their accessibility system-wide. With a Master’s Degree in Instructional Technology and over fifteen years of experience in the field of web accessibility, Jonathan has published dozens of articles, tutorials, and other instructional resources. He has traveled extensively to train thousands of web developers and other professionals who develop or maintain web content.
(handouts available: ask me)
+++++++++++++++++++++
Powerful Presentation Skills for the Accessibility Professional
- Christa Miller, Director of Inclusive Media Design, Virginia Tech
Summary
As subject matter experts in disabilities and accessibility, we are often called upon to provide training and professional development to others. However, it is uncommon for us to receive formal training in this area ourselves. Through discussion and small group activities, participants will explore and practice techniques for giving presentations
Abstract
As accessibility and disability professionals we are well equipped with the content knowledge needed to provide motivation, or justification on the what, why and how of accessibility. Unfortunately, we are often called upon to provide this to experts in a wide range of unrelated fields who do not intrinsically know what it means “to be accessible”. Not only is the audience challenging to reach, but the content challenges the audience on multiple levels. That being said, by using best practices for training adult learners, accessibility training can become a pleasure.
This session aims to provide techniques and practice on critical presentation skills for accessibility professionals including but not limited to: increasing audience engagement, developing powerful slides and visuals, checking your work for accessibility, and practicing before presenting.
Keypoints
- Presentations by accessibility professionals should exemplify best practice for accessibility
- Successful presentations are part performance and part technical know-how
- Accessibility presentations should contain more application and practice than background information
Disability Areas
All Areas
Topic Areas
Administrative/Campus Policy, Faculty Instruction/Accessible Course Design
Speaker Bio(s)
Christa Miller
Christa Miller is a proud Virginia Tech Hokie and is currently the Director of Inclusive Media Design. She first became interested in assistive technologies (AT) while earning her BS in Electrical Engineering. Her passion for accessible technology and universal design then led her to pursue her MS in Industrial Systems Engineering, concentrating in Human Factors Engineering.
Between 2006 and 2018, Christa has worked in many roles for Assistive Technologies, part of Technology-enhanced Learning and Online Strategies (TLOS). Notable among these was as the lead Braille Transcriber for Braille Services, an initiative to provide in-house production of Braille materials for the University for which she received the Excellence in Access and Inclusion Award in 2012. Her unique knowledge of the tools and technologies needed to produce Braille for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) courses has led her to consult with disability service providers from many other post-secondary institutions and share that knowledge at national conferences.
In her current role, Christa has enjoyed co-leading a several professional development programs aimed at providing Teaching Faculty, Instructors and Graduate Teaching Assistants with the knowledge, skills and confidence necessary to create inclusive learning environments.
(handouts available: ask me)
++++++++++++++++
IT Colleagues: from Accessibility Newbies into Accessibility Auditors
- Kristen Dabney, Assistive Technology Instruction Specialist, Tufts University
Summary
Tufts Student Accessibility Services office created accessibility testing guidelines designed to help IT professionals complete basic accessibility audits for digital products before they are purchased.
Abstract
As Tufts implemented its accessible procurement protocol, the need for a streamlined accessibility audit process became crucial. For a university to be proactive and evaluate product accessibility before purchase, a comprehensive auditing system must be in place. These audits (completed by our SAS-trained IT team) provide a more in-depth view than that described by a vendor’s VPAT. This simple to use guide enhanced campus-wide buy-in while also making forward progress on procurement audits. Attendees will learn the process used to initiate and develop these guidelines, the arguments successfully used to get the procurement process firmly in the IT office, the training process for IT auditors and best practices for sustainability beyond the initial training workshop. This session will conclude with a walk though of an example application using the guidelines developed by Tufts Student Accessibility Services office.
Keypoints
- Training guide for IT professionals new to testing accessibility
- Quick walk through Accessibility Audit process
- Accessibility Review Instructions + Vendor Accessibility Report Checklist (WCAG 2.1 standards)
Disability Areas
All Areas
Topic Areas
Administrative/Campus Policy, Assistive Technology, Information Technology, Uncategorized
Speaker Bio(s)
Kristen Dabney
Kristen Dabney graduated from Grinnell College with a degree in Physics, and later from University of Connecticut with a Postsecondary Disability Services Certification since the Physics degree wasn’t saying “I’m interested in accessibility” loud enough. She currently works as an Assistive Technology Instruction Specialist at Tufts University.
(handouts available: ask me)
+++++++++++++++++++
Social media and accessibility
- Gian Wild, Ms, AccessibilityOz
Summary
Gian Wild goes through the accessibility issues of each of the four main social media sites (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and LinkedIn) and discusses ways that you can make sure your social media content is accessible.
Abstract
Social media accessibility is an incredibly important tool in modern society. It is not just the young who access social media, with close to 30% of people over the age of 65 interacting on social networking sites, and 50% of people aged 50 – 64. As the percentage of recruiters who use LinkedIn is now 95%, social media is becoming an essential part of negotiating the current working environment. The main reason why social media is not accessible is that social networking sites and apps are almost continually refreshed. Facebook sometimes changes twice a day. This, coupled with a lack of a formal testing process, means that what may be accessible today may be literally gone tomorrow.
Keypoints
- Social media networks cannot be relied upon to be accessible
- A number of easy things you can do to make your social media more accessible
- The most improved and the most accessible social media networks of 2018
Disability Areas
All Areas
Topic Areas
Uncategorized, Web/Media Access
Speaker Bio(s)
Gian Wild
Gian works in the area of web accessibility: making sure web sites and mobile apps can be used by people with disabilities. She spent six years contributing to the international set of web accessibility guidelines used around the world and is also the CEO and Founder of AccessibilityOz. With offices in Australia and the United States, AccessibilityOz has been operating for five years. Its clients include the Department of Prime Minister and Cabinet, Gold Coast 2018 Commonwealth Games, Optus, Seek and Foxtel. A 2017 Australian of the Year award nominee, Gian splits her time between Australia the US. A regular speaker at conferences around the world, in 2015 she presented to the United Nations on the importance of web accessibility at the Conference of State Parties to the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities.
(handouts available: ask me)
+++++++++++++++++
I Was Wrong! Build Your Successful Accessibility Program by Learning from My Mistakes
Angela Hooker, Microsoft
Summary
Whether or not you’re new to the field, when you manage an accessibility program, you can fall into common traps–but there’s no need to! Learn from my observations and old mistakes! Get tips for running a successful program and avoiding poor management choices, poor policy, poor planning, and more that can hinder your program.
Abstract
So, you’re leading an accessibility program…how’s that working out?
If you’re a new accessibility program manager or a seasoned pro, you can still make rookie mistakes. I sure have, and that’s after over 16 years of running accessibility and user experience programs!
Has your laid back nature defeated your process-driven “evil twin”? Does your site’s written content defeat the accessibility features that your other team members created? Are you unsure why your developers still “don’t get it”? Do your leaders avoid you and conversations about accessibility, except to say that “It’s great!”? Or perhaps your web management direction–when it comes to overall content, design, and development choices–doesn’t quite support the needs of your audience, and you’re not sure where things are going wrong.
My experience from the corporate and government sectors will help you plan your program, whether it’s for a higher education, corporate, or government environment. Get on track with process, program management, setting proper expectations, and more to help you drive great user experiences and real accessibility across your organization.
Keypoints
- Learn the common mistakes in creating and sustaining an accessibility program and how to avoid them.
- Understand the importance of setting boundaries for accepting and establishing program responsibilities.
- Get tips to manage the overall content, design, development, and testing–which drive your program’s success.
Disability Areas
All Areas
Topic Areas
Uncategorized, Web/Media Access
Speaker Bio(s)
Angela Hooker
Angela Hooker is a Senior Accessibility Product Manager at Microsoft, where she’s built a center of expertise for accessibility, user experience, and universal design. She’s brought her web management, development, design, accessibility, and editorial and content management expertise to the government and private sector for over 20 years. Angela also advocates for role-based accessibility and believes that teaching people how to incorporate principles of accessibility in their everyday work creates a sustainable program and produces the most accessible user experiences. In addition to accessibility and universal design, she supports plain language and web standards. Angela speaks on and writes about accessibility, user experience, and plain language.
(handouts available: ask me)
+++++++++++++++++++++
Trending Tech Tools: What’s New, What’s Improved & What’s on the Horizon for Assistive Technology & Accessibility Tools
- Rachel Kruzel, Assistive Technology & Accommodations Specialist, Augsburg University
Summary
The field of Assistive Technology and Accessibility is constantly changing. Tech giants are making more frequent updates to their products. As a result, knowing the latest updates is essential. Assistive Technology and Accessibility software updates from major tech companies such as Texthelp, Sonocent, and Microsoft, as well as free and low cost tools to support students on campus will be featured and shown.
Abstract
Both the Assistive Technology and Accessibility fields are constantly changing. Software companies are soliciting user feedback continuously and deciding which suggestions are the most important to develop and update. These updates and developments are released every six to twelve weeks. Much of this AT is central for students to access courses and curriculum in an accessible way. This presentation will focus on the most recent updates from the major assistive technology companies who are making waves in the tech field. The latest releases from companies like Texthelp, Sonocent, Microsoft, as well as other tech giants will be shown. Free and low cost assistive technology tools that are on the cutting edge or are strong supports for students will be featured in this session as well. Participants will leave with updates to tools they are using to support students on their campuses and ideas on how to use these tools on campus to implement both Assistive Technology and Accessibility.
Keypoints
- Assistive technology companies are releasing product updates every six to twelve weeks on average.
- Latest updates and features to commonly used Assistive Technology tools in higher education will be shown.
- Both for-purchase and free/low cost assistive technology tools can be easily implemented to support students.
Disability Areas
All Areas
Topic Areas
Assistive Technology, Uncategorized
Speaker Bio(s)
Rachel Kruzel
Rachel Kruzel, ATP, is the Assistive Technology & Accommodations Specialist at Augsburg University in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and is a RESNA Certified Assistive Technology Practitioner (ATP). She has over 8 years of experience working in in the CLASS Office (Disability Resources) focusing on assistive technology, educational technology, transitioning from K-12 to higher education, academic accommodations implementation, and digital, electronic, and web accessibility. Rachel has presented both regionally and nationally on a variety of topics about assistive technology, as well as accessibility, transition, assistive technology tools such as the QIAT-PS and specific software program demonstrations and trainings, as well as general consultation with students, parents, schools, and organizations. She also provides consulting and direct consumer support through assistive technology consultation and the implementation process.
(handouts available: ask me)
++++++++++++++++
The Big Ten Academic Alliance’s Shared Approach to Procurement and Vendor Relations
- Bill Welsh, Rutgers University
- Charlie Collick, Director of IT Accessibility, Rutgers University
- Nate Evans, Manager, Digital Content & Accessibility, Michigan State University
Summary
Learn how the Big Ten Academic Alliance is working together to develop policies, processes and procedures for procurement of accessible IT as well as assisting each other with managing vendor relationships that can foster better product accessibility within the Big 10. Also, each presenter will share their own institutions practices in this area.
Abstract
The Big Ten Academic Alliance are working together through a CIO sponsored group called the Information Technology Accessibility Group to leverage their coalition in regards to the accessibility of IT products purchased. The presenters will provide insight into their current collaborative efforts and share the four goals that the ITAG/Procurement Working Group is developing to improve best practices and shared basic standards for accessibility in IT procurement processes. This partnership has identified the following four goals to address IT accessibility: 1.Education & Marketing 2. Shared Solicitation Requirements for IT purchases 3. Standardize Evaluation 4. Leverage the BTAA purchasing power to work with vendors to improve accessibility and develop shared repository of IT accessibility evaluations. Participants will discover methods of alignment, and see how shared approaches to vendor relationship management can leverage economy of scale and foster vendor commitment.
Keypoints
- Product accessibility best practices
- Establishing product accessibility repositories
- There are resources available in this arena for others to utilize and assist in developing
Disability Areas
All Areas
Topic Areas
Administrative/Campus Policy, Information Resources, Information Technology, Uncategorized
Speaker Bio(s)
Bill Welsh
Bill is the Associate VP of Rutgers Access and Disability Resources. He has worked at Rutgers since 2013. Previously, he worked at Penn State University (1999-2013) and Drexel University (1994-1999) as Director of Disability Services
Charlie Collick
Charlie is the Director of IT Accessibility at Rutgers University. He is responsible for the accessibility of all enterprise academic and administrative technology and digital content. He also serves as Director of Software Site Licensing where he is responsible for vetting all central funded technology purchases for the University and the distribution of the licenses to staff, faculty, and students. Charlie has been an employee of Rutgers OIT since 2008. Before serving in his current role, Charlie was the Acting Director of Teaching and Learning with Technology where he lead a team of instructional designers, education technologists, and LMS support staff. His professional experience includes accessibility, instructional design, instructional technology, functional management, organizational development, strategic planning, and technology procurement. His broad technical background spans general IT, applications and systems support, web design and development, and the delivery of related services.
Nate Evans
Nate works with students, faculty, staff, and administrators across the institution to help create more inclusive environments, and shape better digital experiences. He leads Michigan State University’s digital accessibility program, and the Digital Content & Accessibility team to provide central support and resources, and to measure digital accessibility improvement.
(handouts available: ask me)
+++++++++++++++++
Not Another Lecture-Style Presentation
- Brad Held, Accessible Technology Coordinator, University of Central Fl
Summary
Disability Professionals struggle to garner interest for their presentations or workshops. Just getting faculty or staff to register for their training doesn’t guarantee that the topics will be practiced. In this presentation, the presenter will share tips for designing a memorable educational experience that doesn’t involve a projector/clicker.
Abstract
As accessible technology experts, we often find it difficult to fill the seats at our presentations. This might be because of the topics we discussed are overwhelmingly complicated to understand, or because attendees do not believe enough students are affected by our subject matter. Regardless of the reason, the attendee doesn’t always leave with a lasting memory of how they can create access to their environment. What if we could take some of the visual elements of our technology and incorporate it with inclusive principles, then design an experience that is FUN? Based on the popular escape room game concept, you can challenge teams to be locked in a room full of barriers. Have them escape by identifying and removing the barriers within the room with more accessible approaches within the time allotted. UCF will share their design secrets for creating an escape room activity that will have your entire institution buzzing. The presentation will end with an interactive demonstration.
Keypoints
- How to create a different activity other than a lecture style presentation
- Designing a memorable experience involving accessibility.
- Incorporating accessible technology and inclusive principle.
Disability Areas
All Areas
Topic Areas
Other, Uncategorized
Speaker Bio(s)
Brad Held
Brad Held has been the Assistant Director – Accessible Technology for the Student Accessibility Services office at University of Central Florida (UCF) for the past four years. He earned his Bachelor’s degree in Applied Biotechnology at the University of Georgia in 2006. Prior to arriving at UCF, Brad worked in Assistive Technology for almost ten years: four years in a public school K-12 setting with Gwinnett County Public Schools in Georgia and five years in higher-education at The University of Georgia and The University of South Carolina. He is certified in Assistive Technology Applications. Aside from helping UCF students received academic supports, Brad also has a learning disability. Brad uses his personal experience to aid students in being active participants in the accommodation process.
++++++++++++++++++
Interactive 3d printed tactile campus maps
- Holly Lawson, Assistant Professor, Portland State University
- Shiri Azenkot, Assistant Professor, Cornell Tech
- Lei Shi, PhD Student, Cornell Tech
- Michael Cantino, Research Assistant, Portland State University
Summary
This presentation introduces the Markit and Talkit iOS software, which enables an individual to add text or audio annotations to a 3d printed model. Presenters share the use of this toolkit with 3d printed tactile maps.
Abstract
Recent advances in 3d printing technology have made tactile models more available to individuals who are visually impaired. With grant funding from the National Science Foundation, we have developed and field-tested iOS technology that empowers individuals to modify models by adding audio or text annotations. Using this technology, a modified model can provide voice output or display a description of a model component when it is touched by a user. In this session, we will introduce the 3d printing technology and its application with 3d printed tactile maps for use with individuals with visual impairments at Portland State University and Portland Community College.
Keypoints
- interactive 3d printed models can provide greater access to campus environments than traditional tactile maps
- interactive 3d printed maps can be customized to include wayfinding information most pertinent to the user
- the use of interactive 3d printed models is a cost effective solution for institutes of higher education
Disability Areas
Mobility, Vision
Topic Areas
Assistive Technology, Uncategorized
Speaker Bio(s)
Holly Lawson
Dr. Holly Lawson is an Assistant Professor at Portland State University and
the coordinator of the Visually Impaired Learner program. Since 1994, she has worked in the VIL field, beginning as a residential instructor for the Texas School for the Blind and Visually Impaired and then the Peace Corps in Morocco. Her master’s and PhD are from the University of Arizona where she held several positions in teaching and research. She came to PSU in 2014, having previously worked as an assistant professor and the coordinator for the Virginia Consortium of Teacher Preparation in Vision Impairment at George Mason University.
Shiri Azenkot
Dr. Shiri Azenkot is an Assistant Professor at the Jacobs Technion-Cornell Institute at Cornell Tech, Cornell University, and a field member in the Information Science Department. She is also an affiliate faculty member in the Computer Science Department at the Technion–Israel Institute of Technology. Currently, her research is funded by the NSF, AOL, Verizon, and Facebook. Before arriving at Cornell Tech, she was a PhD student in Computer Science & Engineering at the University of Washington, where she was advised by Richard Ladner and Jacob Wobbrock. Shiri has received the UW graduate medal (awarded to just one PhD candidate at the university each year), a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship, and an AT&T Labs Graduate Fellowship.
Lei Shi
Lei Shi is a fourth-year Ph.D. student at Cornell University and an AOL fellow at Cornell Tech, where he is advised by Shiri Azenkot. His research interests lie in the fields of accessibility, human-computer interaction, and design. Specifically, he explores how to combine 3D printing technologies and innovative design to help people. Previously, Lei got his bachelor degree in Electrical Engineering from Zhejiang University, with a double degree in Industrial Design.
Michael Cantino
Michael Cantino worked in K-12 special education for 11 years before coming to Portland Community College in 2017. During that time, he specialized in supporting students with behavioral challenges, Autism Spectrum Disorder, and students with visual impairments. Michael is a Library of Congress certified braille transcriber and is skilled in the production of tactile graphics and 3D models for visually impaired learners. At PCC, Michael provides a broad range of supports for students experiencing disabilities, with a focus on assistive technology, alternative formats, and in-class supports. In addition to his work at Portland Community College, Michael is also a Research Assistant at Portland State University where he is studying the use of interactive 3D models to support visually impaired learners.
(handouts available: ask me)
+++++++++++++++++++
The Power of PDF
Instructional designers, document developers, analysts QA
Naveesha and Sachun Gupta
++++++++++
more on UDL in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=udl
Key Issues in Teaching and Learning
https://www.educause.edu/eli/initiatives/key-issues-in-teaching-and-learning
A roster of results since 2011 is here.

1. Academic Transformation
2. Accessibility and UDL
3. Faculty Development
4. Privacy and Security
5. Digital and Information Literacies
https://cdn.nmc.org/media/2017-nmc-strategic-brief-digital-literacy-in-higher-education-II.pdf
Three Models of Digital Literacy: Universal, Creative, Literacy Across Disciplines
United States digital literacy frameworks tend to focus on educational policy details and personal empowerment, the latter encouraging learners to become more effective students, better creators, smarter information consumers, and more influential members of their community.
National policies are vitally important in European digital literacy work, unsurprising for a continent well populated with nation-states and struggling to redefine itself, while still trying to grow economies in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent financial pressures
African digital literacy is more business-oriented.
Middle Eastern nations offer yet another variation, with a strong focus on media literacy. As with other regions, this can be a response to countries with strong state influence or control over local media. It can also represent a drive to produce more locally-sourced content, as opposed to consuming material from abroad, which may elicit criticism of neocolonialism or religious challenges.
p. 14 Digital literacy for Humanities: What does it mean to be digitally literate in history, literature, or philosophy? Creativity in these disciplines often involves textuality, given the large role writing plays in them, as, for example, in the Folger Shakespeare Library’s instructor’s guide. In the digital realm, this can include web-based writing through social media, along with the creation of multimedia projects through posters, presentations, and video. Information literacy remains a key part of digital literacy in the humanities. The digital humanities movement has not seen much connection with digital literacy, unfortunately, but their alignment seems likely, given the turn toward using digital technologies to explore humanities questions. That development could then foster a spread of other technologies and approaches to the rest of the humanities, including mapping, data visualization, text mining, web-based digital archives, and “distant reading” (working with very large bodies of texts). The digital humanities’ emphasis on making projects may also increase
Digital Literacy for Business: Digital literacy in this world is focused on manipulation of data, from spreadsheets to more advanced modeling software, leading up to degrees in management information systems. Management classes unsurprisingly focus on how to organize people working on and with digital tools.
Digital Literacy for Computer Science: Naturally, coding appears as a central competency within this discipline. Other aspects of the digital world feature prominently, including hardware and network architecture. Some courses housed within the computer science discipline offer a deeper examination of the impact of computing on society and politics, along with how to use digital tools. Media production plays a minor role here, beyond publications (posters, videos), as many institutions assign multimedia to other departments. Looking forward to a future when automation has become both more widespread and powerful, developing artificial intelligence projects will potentially play a role in computer science literacy.
6. Integrated Planning and Advising Systems for Student Success (iPASS)
7. Instructional Design
8. Online and Blended Learning
In traditional instruction, students’ first contact with new ideas happens in class, usually through direct instruction from the professor; after exposure to the basics, students are turned out of the classroom to tackle the most difficult tasks in learning — those that involve application, analysis, synthesis, and creativity — in their individual spaces. Flipped learning reverses this, by moving first contact with new concepts to the individual space and using the newly-expanded time in class for students to pursue difficult, higher-level tasks together, with the instructor as a guide.
Let’s take a look at some of the myths about flipped learning and try to find the facts.
Myth: Flipped learning is predicated on recording videos for students to watch before class.
Fact: Flipped learning does not require video. Although many real-life implementations of flipped learning use video, there’s nothing that says video must be used. In fact, one of the earliest instances of flipped learning — Eric Mazur’s peer instruction concept, used in Harvard physics classes — uses no video but rather an online text outfitted with social annotation software. And one of the most successful public instances of flipped learning, an edX course on numerical methods designed by Lorena Barba of George Washington University, uses precisely one video. Video is simply not necessary for flipped learning, and many alternatives to video can lead to effective flipped learning environments [http://rtalbert.org/flipped-learning-without-video/].
Myth: Flipped learning replaces face-to-face teaching.
Fact: Flipped learning optimizes face-to-face teaching. Flipped learning may (but does not always) replace lectures in class, but this is not to say that it replaces teaching. Teaching and “telling” are not the same thing.
Myth: Flipped learning has no evidence to back up its effectiveness.
Fact: Flipped learning research is growing at an exponential pace and has been since at least 2014. That research — 131 peer-reviewed articles in the first half of 2017 alone — includes results from primary, secondary, and postsecondary education in nearly every discipline, most showing significant improvements in student learning, motivation, and critical thinking skills.
Myth: Flipped learning is a fad.
Fact: Flipped learning has been with us in the form defined here for nearly 20 years.
Myth: People have been doing flipped learning for centuries.
Fact: Flipped learning is not just a rebranding of old techniques. The basic concept of students doing individually active work to encounter new ideas that are then built upon in class is almost as old as the university itself. So flipped learning is, in a real sense, a modern means of returning higher education to its roots. Even so, flipped learning is different from these time-honored techniques.
Myth: Students and professors prefer lecture over flipped learning.
Fact: Students and professors embrace flipped learning once they understand the benefits. It’s true that professors often enjoy their lectures, and students often enjoy being lectured to. But the question is not who “enjoys” what, but rather what helps students learn the best.They know what the research says about the effectiveness of active learning
Assertion: Flipped learning provides a platform for implementing active learning in a way that works powerfully for students.
9. Evaluating Technology-based Instructional Innovations

What is the total cost of my innovation, including both new spending and the use of existing resources?
What’s the unit I should measure that connects cost with a change in performance?
How might the expected change in student performance also support a more sustainable financial model?
The Exposure Approach: we don’t provide a way for participants to determine if they learned anything new or now have the confidence or competence to apply what they learned.
The Exemplar Approach: from ‘show and tell’ for adults to show, tell, do and learn.
The Tutorial Approach: Getting a group that can meet at the same time and place can be challenging. That is why many faculty report a preference for self-paced professional development.build in simple self-assessment checks. We can add prompts that invite people to engage in some sort of follow up activity with a colleague. We can also add an elective option for faculty in a tutorial to actually create or do something with what they learned and then submit it for direct or narrative feedback.
The Course Approach: a non-credit format, these have the benefits of a more structured and lengthy learning experience, even if they are just three to five-week short courses that meet online or in-person once every week or two.involve badges, portfolios, peer assessment, self-assessment, or one-on-one feedback from a facilitator
The Academy Approach: like the course approach, is one that tends to be a deeper and more extended experience. People might gather in a cohort over a year or longer.Assessment through coaching and mentoring, the use of portfolios, peer feedback and much more can be easily incorporated to add a rich assessment element to such longer-term professional development programs.
The Mentoring Approach: The mentors often don’t set specific learning goals with the mentee. Instead, it is often a set of structured meetings, but also someone to whom mentees can turn with questions and tips along the way.
The Coaching Approach: A mentor tends to be a broader type of relationship with a person.A coaching relationship tends to be more focused upon specific goals, tasks or outcomes.
The Peer Approach:This can be done on a 1:1 basis or in small groups, where those who are teaching the same courses are able to compare notes on curricula and teaching models. They might give each other feedback on how to teach certain concepts, how to write syllabi, how to handle certain teaching and learning challenges, and much more. Faculty might sit in on each other’s courses, observe, and give feedback afterward.
The Self-Directed Approach:a self-assessment strategy such as setting goals and creating simple checklists and rubrics to monitor our progress. Or, we invite feedback from colleagues, often in a narrative and/or informal format. We might also create a portfolio of our work, or engage in some sort of learning journal that documents our thoughts, experiments, experiences, and learning along the way.
The Buffet Approach:
10. Open Education
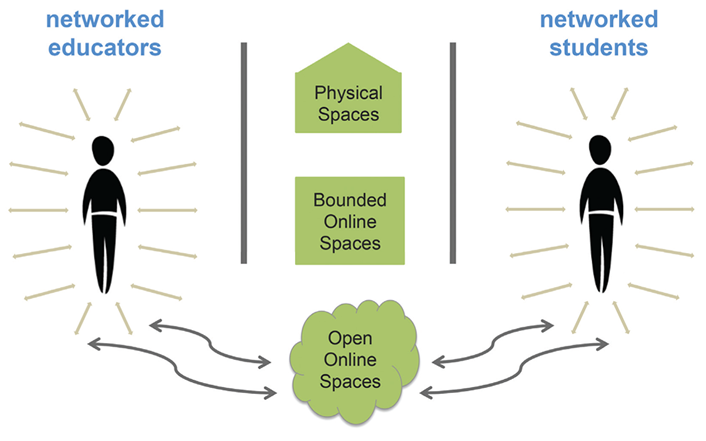
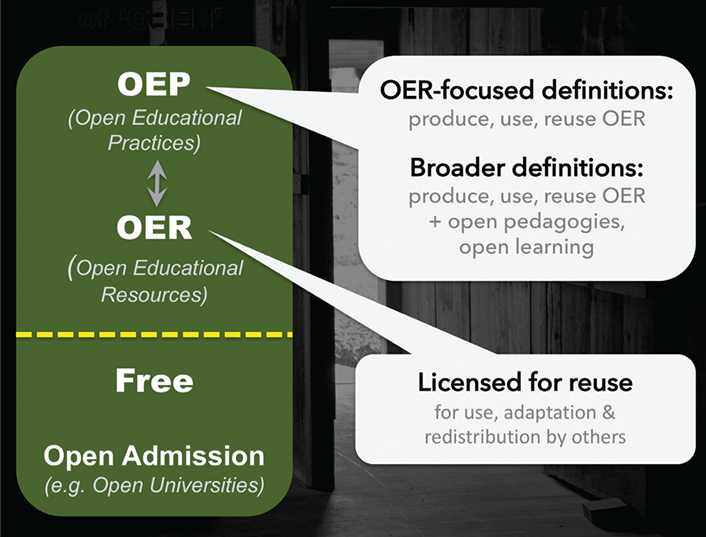

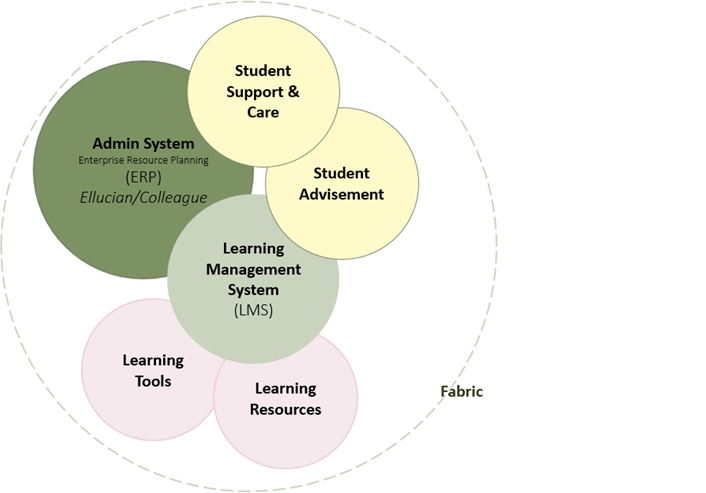
11. Learning Analytics
12. Adaptive Teaching and Learning
13. Working with Emerging Technology
In 2014, administrators at Central Piedmont Community College (CPCC) in Charlotte, North Carolina, began talks with members of the North Carolina State Board of Community Colleges and North Carolina Community College System (NCCCS) leadership about starting a CBE program.
Building on an existing project at CPCC for identifying the elements of a digital learning environment (DLE), which was itself influenced by the EDUCAUSE publication The Next Generation Digital Learning Environment: A Report on Research,1 the committee reached consensus on a DLE concept and a shared lexicon: the “Digital Learning Environment Operational Definitions,