Recorded on February 25, 2016
Presenter
Dr. Cynthia Calongne
CTU Doctoral Program | ccalongne@ctuonline.edu
Twitter and Skype: @lyrlobo
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
My note: the US News and World Report is behind times on its reporting, unless this article has been held for a while by their editor: teenagers moved from Snapchat as quickly as they moved away from Facebook to Twitter and from Twitter to Snapchat. The generation, which is running US News and World Report is way too slow to notice the nomadic social media moves of the Millennials.
Here is the January 2016, exchange among faculty on the blend/online education listserv, which could’ve helped the author, Alexandra Pannoni line up with the times:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/01/11/social-network-highered/
The cited case from Nebraska, Katelyn Gilroy, a library media specialist, who is using Snapchat or school purposes, can undoubtedly have a niche in education, enticing students to learn about their library, reading, etc.
However, it is questionable to present the media specialist’s case from Nebraska as a blank statement; a case, which can be adopted nationwide. Ms. Pannoni fails to mention that since 15 years ago, when instant messaging was the “snapchat” of the times, U.S. students consider these applications their “virtual mall,” where they like to hang out, but are not keen to consider them for educational purposes. In the same fashion, U.S. students are somehow unique in considering Facebook, later Twitter, then Snapchat and now Kik, Yammer, Celly, or Elgg a domain reserved for their private, extracurricular activities.
More about use of social media in education in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=social+media+education&submit=Search
http://www.informationr.net/ir/18-3/colis/paperC41.html#.VuwOInpa2zA
Paul Scifleet
Charles Sturt University, School of Information Studies, Chalres Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW 2678, Australia
Maureen Henninger
Information & Knowledge Management Program, Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Technology, Sydney, Australia
Kathryn H. Albright
Charles Sturt University, School of Information Studies, Chalres Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW 2678, Australia
The view we bring to this study is one of documentary practice as the set of techniques, including processes for the selection, synthesis and interpretation of the material form of documents and their content, meaning and context, that librarianship brings to the organization and management of knowledge (Briet, 2006; Pédauque, 2003). Current emphases in social media research on ‘big data’ and quantitative analysis are distracting from the significant role social media have to play as a record of social significance that should be brought into public custody for future use.
In its multiple manifestations, social media are “a new kind of cultural artefact” (Lyman and Kahle, 1998, para 15), as was the World Wide Web when Brewster Kahle set up the Internet Archive, reasoning that “in future it may provide the raw material for a carefully indexed, searchable library” (Kahle, 1997, p. 82).
My note: what the German start promoting in the 60s as Alltagsgeschichte.
the possibility of selective acquisition and management of social media, as a document of specific events and topics, as an alternative to the Library of Congress’s whole-of-archive approach with Twitter.
http://2016libtechconference.sched.org/event/69f9/come-on-down-gaming-in-the-flipped-classroom#
gamification for the enthusiasm. credit course with buffet. the pper-to-peer is very important
gaming types
affordability; east to use; speed to create.
assessment. if you want heavy duty, SPSS kind of assessment, use polldaddy or polleverywhere.
Kahoot only Youtube, does not allow to upload own video or use Kaltura AKA Medispace, text versus multimedia
Kahoot is replacing Voicethread at K12, use the wave
Kahoot allows to share the quizzes and surveys
Kahoot is not about assessment, it is not about drilling knowledge, it is about conversation starter. why do we read an article? there is no shame in wrong answer.
the carrot: when they reach the 1000 points, they can leave the class
Kahoot music can be turned off, how short, the answers are limited like in Twitter
Quizlet
screenshot their final score and reach 80%
gravity is hard, scatter start with. auditory output
drill game
Teach Challenge.
1st day is Kahoot, second day is Team challange and test
embed across the curriculum
gaming toolkit for campus
what to take home: have students facing students from differnt library
+++++++++++++
Putting it all together: a holistic approach to utilizing your library’s user data for making informed web design decisions
In the age of Big Data, there is an abundance of free or cheap data sources available to libraries about their users’ behavior across the many components that make up their web presence. Data from vendors, data from Google Analytics or other third-party tracking software, and data from user testing are all things libraries have access to at little or no cost. However, just like many students can become overloaded when they do not know how to navigate the many information sources available to them, many libraries can become overloaded by the continuous stream of data pouring in from these sources. This session will aim to help librarians understand 1) what sorts of data their library already has (or easily could have) access to about how their users use their various web tools, 2) what that data can and cannot tell them, and 3) how to use the datasets they are collecting in a holistic manner to help them make design decisions. The presentation will feature examples from the presenters’ own experience of incorporating user data in decisions related to design the Bethel University Libraries’ web presence.
data tools: user testing, google analytics, click trakcer vendor data
questions:
is there a dashboard tool that can combine all these tools?
optimal workshop: reframe, but it is more about qualitative data.
how long does it take to build this? about two years in general, but in the last 6 months focused.
TCC 2016 cordially invites you to join a FREE special pre-conference webinar on competency-based education (CBE).
Unpack CBE
During this session, Diane Singer from Bandman University, and Susan Manning from the University of Wisconsin at Stout, discuss the meaning and processes behind CBE, with a specific eye to how the assessment and recognition of competencies benefit various stakeholders, including business and industry.
Date & time:
March 16, 2:00 PM Hawaii; 6:00 PM Mountain; 8:00 PM Eastern
March 17, 9:00 AM Tokyo & Seoul; 11:00 AM Sydney, Feb. 26
Other timezones:
http://bit.ly/tcc16precon2-unpackCBE
Full information:
http://2016.tcconlineconference.org/unpacking-cbe/
RSVP for this FREE session!
If you wish to participate, please RSVP. A reminder will be sent a few days prior along with instructions to sign-in.
http://bit.ly/tcc2016precon2-rsvp
The 21st Annual TCC Worldwide Online Conference: April 19-21, 2016
TCC, Technology, Colleges and Community, is a worldwide online conference attended by university and college personnel including faculty, academic support staff, counselors, student services personnel, students, and administrators.
More on competency-based learning in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=competency+based+learning&submit=Search
+++++++++++++++++
webinar archived recording:
http://2016.tcconlineconference.org/make-the-future/
Recorded on February 25, 2016
Dr. Cynthia Calongne
CTU Doctoral Program | ccalongne@ctuonline.edu
Twitter and Skype: @lyrlobo
http://www.educatorstechnology.com/2016/02/blooms-digital-taxonomy-cheat-sheet-for-teachers.html
| Resources for Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy |
| iPad Apps | Android Apps | Web Tools | |
| Creating | |||
| Evaluating |
|
||
| Analyzing | |||
| Applying | |||
| Understanding | |||
| Remembering |
Follow the discussion on the LinkedIn ISTE discussion group:
https://www.linkedin.com/groups/2811/2811-6107212405878566913
Similar visual representation in this IMS blog entry:
on January 2, 2015
https://www.quicksprout.com/2015/01/02/what-are-the-best-times-to-post-on-social-media/

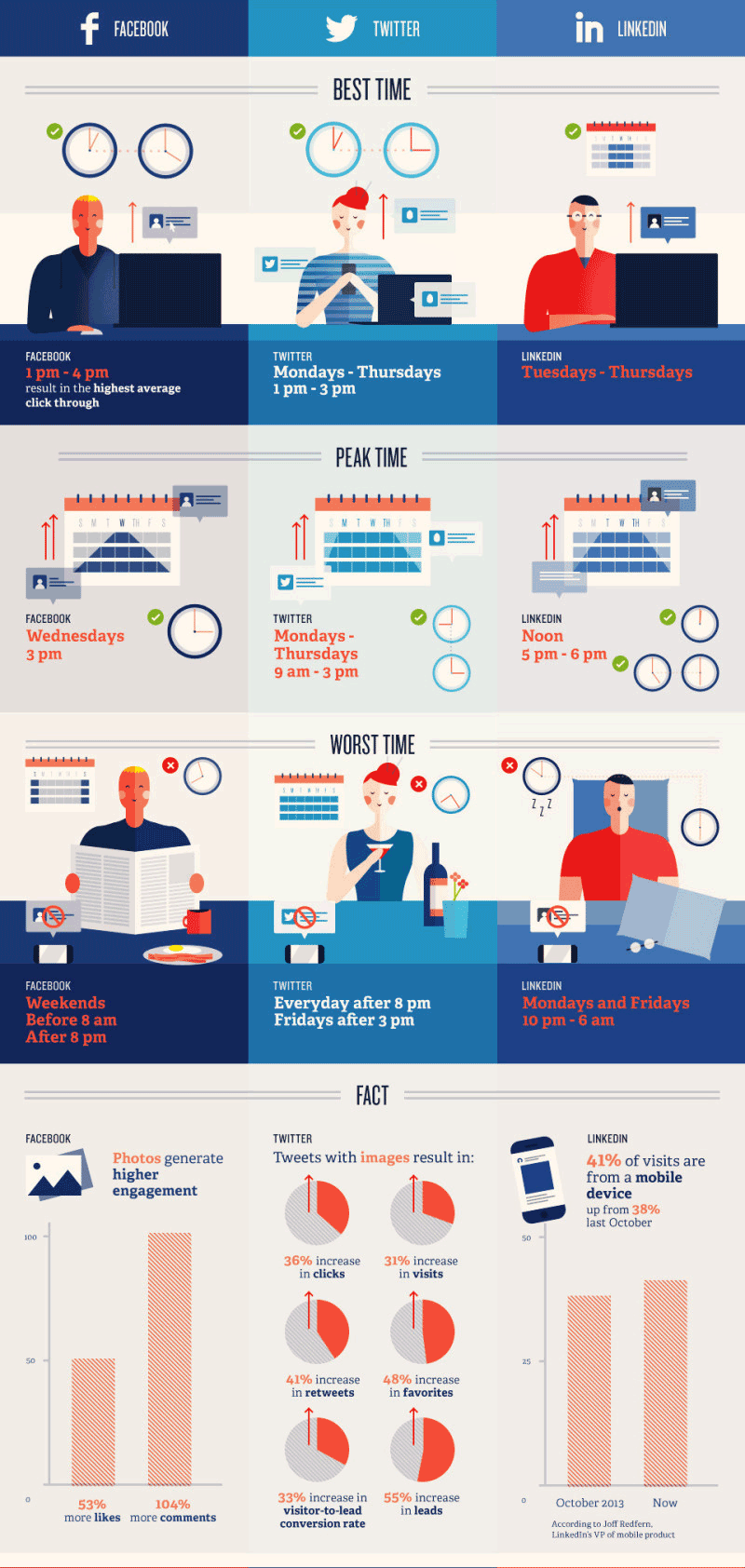
probably the most detailed break down:
https://blog.bufferapp.com/best-time-to-tweet-post-to-facebook-send-emails-publish-blogposts
and several others:
http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/best-times-post-pin-tweet-social-media-infographic
April 3, 2014
https://www.addthis.com/blog/2014/04/03/whens-the-best-day-and-time-to-post-on-social-media
this one talks about the use of Hootsuite and likes, might be worth looking at it:
http://www.socialmediatoday.com/content/best-times-post-social-media-infographic
per SCSU faculty request, please have compiled literature (books and peer-reviewed articles) on:
Here some names who are well regarded in the community of online learning as specialists in online discussions:
the most recent peer-reviewed literature on keywords: “engag*” + “student*” + “online” = 13K+ titles for the period 2010-2016:
and about 20 articles from the link above with the general search:
Record: 1
A Digital Badging Dataset Focused on Performance, Engagement and Behavior-Related Variables from Observations in Web-Based University Courses By: McDaniel, Rudy; Fanfarelli, Joseph R.. British Journal of Educational Technology, v46 n5 p937-941 Sep 2015. (EJ1071635)
Database:
ERIC
Record: 2
A Student-Centered Guest Lecturing: A Constructivism Approach to Promote Student Engagement By: Li, Lei; Guo, Rong. Journal of Instructional Pedagogies, v15 Oct 2015. (EJ1060070)
Full Text from ERIC
Database:
ERIC
Record: 3
Creating Effective Student Engagement in Online Courses: What Do Students Find Engaging? By: Dixson, Marcia D.. Journal of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, v10 n2 p1-13 Jun 2010. (EJ890707)
Full Text from ERIC
Database:
ERIC
Record: 4
Effects From Student Engagement Online. ASHE Higher Education Report. Nov2014, Vol. 40 Issue 6, p67-73. 7p. DOI: 10.1002/aehe.20018.
Database:
EBSCO MegaFILE
Record: 5
Engaging Students in Online Courses By: Jacobs, Pearl. Research in Higher Education Journal, v26 Oct 2014. (EJ1055325)
Full Text from ERIC
Database:
ERIC
Record: 6
Engaging Students via Social Media: Is It Worth the Effort? By: Mostafa, Rania B.. Journal of Marketing Education, v37 n3 p144-159 Dec 2015. (EJ1080980)
Database:
ERIC
Record: 7
Engaging Students with Social Media By: Bal, Anjali S.; Grewal, Dhruv; Mills, Adam. Journal of Marketing Education, v37 n3 p190-203 Dec 2015. (EJ1081047)
Database:
ERIC
Record: 8
HOW TO BETTER ENGAGE ONLINE STUDENTS WITH ONLINE STRATEGIES. By: BRITT, DR. MARGARET. College Student Journal. Fall2015, Vol. 49 Issue 3, p399-404. 6p.
Database:
EBSCO MegaFILE
Record: 9
Instructor scaffolding for interaction and students’ academic engagement in online learning: Mediating role of perceived online class goal structures. By: Cho, Moon-Heum; Cho, YoonJung. Internet & Higher Education. Apr2014, Vol. 21, p25-30. 6p. DOI: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2013.10.008.
Database:
EBSCO MegaFILE
Record: 10
Measuring Student Engagement in an Online Program By: Bigatel, Paula; Williams, Vicki. Online Journal of Distance Learning Administration, v18 n2 Sum 2015. (EJ1065381)
Database:
ERIC
Record: 11
Measuring Student Engagement in the Online Course: The Online Student Engagement Scale (OSE) By: Dixson, Marcia D.. Online Learning, v19 n4 Sep 2015. (EJ1079585)
Full Text from ERIC
Database:
ERIC
Record: 12
On-Line Course Development: Engaging and Retaining Students By: Bruster, Benita G.. SRATE Journal, v24 n2 p1-7 Sum 2015. (EJ1083122)
Full Text from ERIC
Database:
ERIC
Record: 13
Promoting Online Students’ Engagement and Learning in Science and Sustainability Preservice Teacher Education By: Tomas, Louisa; Lasen, Michelle; Field, Ellen. Australian Journal of Teacher Education, v40 n11 Article 5 Nov 2015. (EJ1083370)
Full Text from ERIC
Database:
ERIC
Record: 14
Strengthening student engagement: what do students want in online courses? By: Chakraborty, Misha; Nafukho, Fredrick Muyia. European Journal of Training & Development. 2014, Vol. 38 Issue 9, p782-802. 21p. DOI: 10.1108/EJTD-11-2013-0123.
Database:
EBSCO MegaFILE
Record: 15
Student Engagement in Online Learning: What Works and Why. ASHE Higher Education Report. Nov2014, Vol. 40 Issue 6, p1-14. 14p. DOI: 10.1002/aehe.20018.
Database:
EBSCO MegaFILE
Record: 16
Student Perceptions of Twitters’ Effectiveness for Assessment in a Large Enrollment Online Course By: Rohr, Linda; Costello, Jane. Online Learning, v19 n4 Sep 2015. (EJ1079590)
Full Text from ERIC
Database:
ERIC
Record: 17
Techniques for Student Engagement Online. ASHE Higher Education Report. Nov2014, Vol. 40 Issue 6, p37-66. 30p. DOI: 10.1002/aehe.20018.
Database:
EBSCO MegaFILE
Record: 18
The civic-social media disconnect: exploring perceptions of social media for engagement in the daily life of college students. By: Mihailidis, Paul. Information, Communication & Society. Oct2014, Vol. 17 Issue 9, p1059-1071. 13p. DOI: 10.1080/1369118X.2013.877054.
Database:
EBSCO MegaFILE
Record: 19
The Online University Classroom: One Perspective for Effective Student Engagement and Teaching in an Online Environment By: Carr, Marsha. Journal of Effective Teaching, v14 n1 p99-110 2014. (EJ1060450)
Full Text from ERIC
Database:
ERIC
Record: 20
The Perils of a Lack of Student Engagement: Reflections of a “Lonely, Brave, and Rather Exposed” Online Instructor By: Stott, Philip. British Journal of Educational Technology, v47 n1 p51-64 Jan 2016. (EJ1086712)
Database:
ERIC
Record: 21
The VIRI (Virtual, Interactive, Real-Time, Instructor-Led) Classroom: The Impact of Blended Synchronous Online Courses on Student Performance, Engagement, and Satisfaction By: Francescucci, Anthony; Foster, Mary. Canadian Journal of Higher Education, v43 n3 p78-91 2013. (EJ1018277)
Full Text from ERIC
Database:
ERIC
======================================================
More on “Classroom Discussion and Students Participation” in this IMS blog entry:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/01/29/classroom-discussion-and-students-participation/
More on Digital Humanities in this blog:
====================================================
1 credit, summer 2016
Technology forecast for education: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/01/27/4710/
Course Description
This synchronous online course will introduce school administrators to the multitude and complexity of educational technology issues. Through group discussions and exercises, the course will focus on the development of knowledge, skills and depositions to effective professional practice in educational leadership. The goal of the course is to develop knowledge and understanding of appropriate application of technology in the teaching and learning process and in the management of educational programs.
Information and experience in the course will include review of the latest trends in technology. Familiarity to acquisition of expertise will be sought in understand and use of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0, as well as social media, multimedia and interactivity and how it affects school life as well as the role of the educational leader. Specific attention will be paid to the importance and ability to develop and maintain policies, which reflect the ever-changing world of technology. Auxiliary, but no less important issues such as legal issues, copyright issues, ethics and other forms of digital citizenship will be discussed.
Course Objectives:
Upon successful completion of this course the student will:
| Course Objective | Knowledge | Skill | Disposition | Impact |
| 1. Demonstrate knowledge and the use of related technologies appropriate to the management of a school # | o | o | ||
| 2. Demonstrate knowledge and the use of related technologies appropriate to the instructional program of a school # | o | o | ||
| 3. Demonstrate knowledge and the use of various types of related technologies for supporting the instructional program of the school # | o | o | ||
| 4. Demonstrate knowledge of planning and management procedures and policies for the appropriate use of technological resources to serve the mission of the school # | o | o | ||
| 5. Demonstrate knowledge of common computer and related technological applications # | o | o | ||
| 6. Identify gender & diversity issues related to technology in education | o | o | o | |
| 7. Demonstrate knowledge of adaptive technology devices for individuals with special needs | o | o | o | o |
| 8. Demonstrate skill in the use of technology for materials preparation, presentations, record keeping, computation, communication, information / data collection and management, and the effective use of the Internet | o | o | o | |
| 9. Demonstrate an understanding of legal issues, including copyright issues, related to educational technology | o | o | ||
| 10. Demonstrate an understanding of the importance of ethical practice in the use of technology | o | o | ||
| 11. Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of administrative policies and procedures that promote appropriate utilization of technology by school personnel | o | o | o | |
| 12. Demonstrate familiarity with appropriate professional standards related to educational leadership and technology | o | o | o | o |
| 13. Demonstrate an understanding of the digital age learning culture, digital citizenship in particular | o | o |
National Educational Technology Standards for Administrators.
http://www.iste.org/standards/ISTE-standards/standards-for-administrators
Demonstrate familiarity with appropriate professional standards related to educational leadership and technology
http://www.ccsso.org/Documents/2015/ProfessionalStandardsforEducationalLeaders2015forNPBEAFINAL.pdf
Resources On Line
IMS Technology blog: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/
Twitter: #edtech ; #edtechchat ; #edtechUK; @Edtech_K12
Facebook: #edtech ; #edleadership
Pinterest #edtech; #edleadership ; #edtechleadership
Agency for Instructional Technology http://www.ait.net
Center for Technology and Teacher Education http://www.teacherlink.org
Center for Children and Technology http://www.edc.org/CCT/
T.H.E. Journal (Technology Horizons in Education Online Journal) http://www.thejournal.com
Cybertimes Navigator (New York Times) http://www.nytimes.com/navigator
International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE) http://cnets.iste.org/
Technology Standards for School Administrators (TSSA) http://cnets.iste.org/tssa
ISTE curriculum and Content Area Standards http://Cnets.iste.org/currstands/
Preparing Tomorrow’s Teachers to use Technology (PT3) http://www.pt3.org
Assistive Technology information: http://www.abilityhub.com http://www.enablemart.com
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
1 credit, Summer 2016
Course Description
This course seeks hands-on experience in integration of educational technology into the classroom. Students will learn to select opportunities for application [or not] of technology in education. The course will provide a hands-on experience for educational leaders to understand the application of technology in the curriculum process. Topics of consideration include instructional design, media and formats, devices, telecommunications and social interactivity. The course will provide an opportunity to apply technology knowledge and experience in hands-on exercises for curriculum management as well as monitoring student achievement progress. Further discussions and practical approach will include modern, effective and efficient ways of communications among parents, students, faculty and administration. The course offered in synchronous online mode and F2F mode.
Objectives/Outcomes
Upon successful completion of this course the student will:
Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
http://www.udlcenter.org/aboutudl/whatisudl
The ISTE National Educational Technology Standards (NETS•T) and
Performance Indicators for Teachers
https://www.kent.edu/sites/default/files/file/ISTEstandards.pdf
1 credit, Summer 2016
Course Description
Course Description
This class will support teacher leaders and school administrators in reviewing and systematizing the fast aspects of modern electronic technologies. Based on a foundational better understanding of how technologies work, future educational leaders will develop skills and practice the application of ideas, tactics and methods for better integration of technologies in the teaching and learning process as well as the creation of better policies and procedures.
The course is designed to bring research and analytical skills and build structure in the process of resolving technology issues, which educational leaders face in modern schools, including hardware and software problems, networks and computers, curriculum and teaching and learning methods.
The course will offer discussions as well as practical solutions such as social media (e.g. Twitter) for professional development, online tools for teacher evaluation, online tools for collaboration and creativity, immediate and future trends, which already impact education and educational leadership.
The course offered in synchronous online mode and F2F mode.
Objectives/Outcomes
Class ED 610 Introduction to Curriculum and Instruction Summer 2018
Instructor: Hsuehi(Martin) Lo
short link to this session: http://bit.ly/edad829
for online participation, please use the following Zoom or Adobe Connect session (your instructor will direct you which one:
My name is Plamen Miltenoff and I will be leading your digital literacy instruction today: Here is more about me: http://web.stcloudstate.edu/pmiltenoff/faculty/ and more about the issues we will be discussing today: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/
As well as my email address for further contacts: pmiltenoff@stcloudstate.edu
Here is a preliminary plan. We will not follow it strictly; it is just an idea about the topics we would like to cover. Shall there be points of interest, please feel free to contribute prior and during the session.
Keeping in mind the ED 610 Learning Goals and Objectives, namely:
lets review our search and research skills:
https://www.semanticscholar.org/
+++++++++++++
PICO framework to structure a question:
Population, Patient, Problem
Intervention
Comparison
Outcome

What is a DOI? A Digital Object Identifier (DOI) is assigned to electronic journal articles (and selected other online content) to specifically and permanently identify and access that article. Most of the standard academic citation formats now require the inclusion of DOIs within a citation when available.
How to find a DOI: Most current academic journal articles include a DOI (usually listed on the first page of the article). Most library databases list a DOI with the record for recent academic journal articles. Most non-academic articles (including magazine and newspaper articles) as well as many older academic journal articles do not have a DOI. Crossref.org provides a DOI Lookup service that will search for a DOI based on citation information (author’s last name, journal name, article title, etc.).
How to access an article via a DOI: Use the CSU Stanislaus Library DOI Look-up for options provided by the library, including access to the full-text via the publisher’s site or a library database service when available. Other, general DOI look-up systems (CrossRef & DOI.org) usually link to the article’s “homepage” on the publisher’s site (which usually include a free abstract but full-text access is restricted to subscribers).
shall more info be needed and or “proper” session with a reference librarian be requested. http://stcloud.lib.mnscu.edu/subjects/guide.php?subject=EDAD-D
-Strategies for conducting advanced searches (setting up filters and search criteria)
Filters
+++++++++++++++++
Search criteria
++++++++++++++++
Social media and its importance for the topic research and the dissertation research:
Small business owners use social media primarily as a marketing and search engine optimization tool. However, more and more small businesses are using social media to get answers for business related questions. Specific industry related articles, and statistics are found useful for small business owners in 80% of the cases.
https://www.linkedin.com/today/post/article/20140331225132-25026422-small-business-owners-turning-to-social-media
Altmetrics: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/10/23/altmetrics-library-lily-troia/
Other sources for information:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/01/27/research-how-to/
Blogs – use tags
learn how to use Zotero and/or Refworks in Microsoft Word

and/or
Refworks and/or Mendeley in Google Docs 
Login into ProQuest Refworks AddOn for Google Doc:
Zotero, Mendeley, Refworks
Evernote, Diigo
If Twitter, Facebook or LinkedIn, use hashtags
—————-
Plamen Miltenoff, Ph.D., MLIS
Professor
320-308-3072
pmiltenoff@stcloudstate.edu
http://web.stcloudstate.edu/pmiltenoff/faculty/
pedagogues under a minute: http://www.pinterest.com/pin/178173728981990450/