Apr
2016
Teacher Attrition/Retention
on a topic of teacher evaluation – Marzano, Danielson),
Richard Ingersoll,
David Chapman,
Jianping Shen, Barbara
Benham Tye, and
Erling Boe, Lynne Cook & Robert Sunderland.
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
on a topic of teacher evaluation – Marzano, Danielson),
Richard Ingersoll,
David Chapman,
Jianping Shen, Barbara
Benham Tye, and
Erling Boe, Lynne Cook & Robert Sunderland.
He’d give a lecture. Then, 20 minutes later, he’d follow up with a multiple-choice question from the material he had just covered. Handheld electronic “clicker” devices would record the students’ responses on his computer.
getting students to problem-solve. He gets them actively engaged with course material, working in smaller groups. The techniques have become known as an evidence-based, “active learning” style of teaching.
sees himself as a kind of cognitive coach rather than the classic “sage on the stage,” delivering knowledge. His lecturing, such as it is, is merely to prime the undergrads to grapple with the concepts and key questions on their own and try to figure out what’s important — or not.
+++++++++++++++++++++
More about training quizzes in this IMS blog
February 28, 2016 in Volume 6, Dr. Hope J. Hartman
the author explores the importance of understanding the multidimensional of cultural diversity and inclusion and how this understanding can be used by professors and instructors to more effectively develop varied instructional strategies which will allow them to teach with better cultural responsiveness. The author describes a variety of approaches she has used in highly diverse classrooms with undergraduate and graduate teacher education students.
Teaching with cultural responsiveness means applying strategies for culturally responsive teaching in my own courses. Teaching for cultural responsiveness means that students, pre and in-service teachers, should implement culturally responsive teaching strategies with their own preK-12 or higher education students.
Maturity
Both pre and in-service teachers are aware of culturally specific behavioral norms that result in discrepancies between the culture of many black students and the culture of the classroom. To address this gap, my students learn strategies for “culturally responsive social skills instruction” specifically designed for black adolescent males
Intelligence
Learning about this research helps students realize that even when they think that they are being responsive to cultural differences, they might be blinded by a cultural lens of invalid assumptions, causing them to lose sight of important cultural differences that can affect thinking and learning.
Cultural Identity
Everyone should realize that cultural stereotypes affecting identity go beyond race and ethnicity. For many people, their identity as adults is defined by their careers.
Gender identity/sexual orientation
Making LGBTQ resources and discussions a formal part of the curriculum helps to create a safe and accepting environment for the LGBTQ community, including not only people who identify as such, but also their parents, relatives, friends and teachers.
Special needs learners
http://ww2.kqed.org/mindshift/2016/03/16/7-qualities-that-promote-teacher-leadership-in-schools
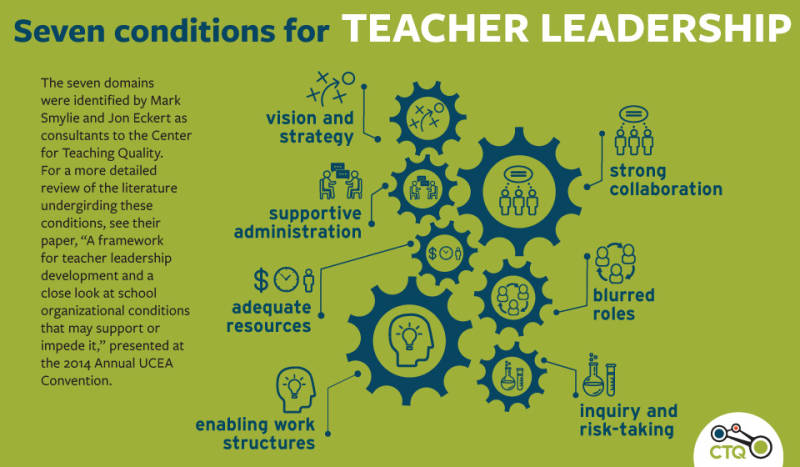
start with the teachers, not with the students
Participating teachers advance through a series of inquiry-based professional development modules. Teachers are awarded a digital badge for the successful completion of each 10-hour module. To accomplish this, they must complete the following steps: 1) study module content, 2) participate in a focused discussion with peers working on the same module, 3) create an original inquiry-based global lesson plan that incorporates new learning, 4) implement the original lesson plan in the classroom, 5) provide evidence of classroom implementation and 6) reflect on and revise the lesson created.
The final product of every module is a tested, global lesson plan that articulates learning objectives, activities, assessments, and resources for each stage of inquiry. Upon completion, teachers may publish finalized lessons in a resource library where they can be accessed by other educators. As designed, the HISD badging system will be a four-year, 16-badge approach that equates to 160 hours of professional learning for teachers.
five key features that taken together increase significantly the likelihood that the learning experience for a teacher will lead to results in the classroom for students — which, after all, is the point of professional development:
Training teachers to keep up technological change needs to be constant and if possible self directed so teachers can get the training they need to achieve the goals they want to achieve.
Training needs to be delivered by pedagogical experts who can give teachers hands on experience of using technology to learn.
Training examples need to be applied to the materials and content that teachers actually need and have to teach as part of their syllabus.
Training needs to be balanced with a critical eye so that teachers also understand the pitfalls, problems and limitations that accompany the use of technology.
Schools need to be wary edtech hardware vendors. The lifetime of most edtech hardware tends to be pretty short and like mobile phones, the new model can make previous models look tired and old fashioned very quickly.
Technology can’t be an add on or extra work. It has to be integrated into and help them with the material they have to cover in the classroom with their students.
Teachers need to be part of the selection and procurement process to ensure that they are getting the technology they want and need.
Tech support needs to be delivered in a way that serves and supports the teachers rather than the other way around. Teachers do need to be trained in how to articulate and describe teach problems with accuracy.
Before investing in classroom hardware schools need to make sure they have sufficient connectivity infrastructure to support the modes of use that teachers will apply with it.
Technology needs to be applied with an understanding of how it can enable a transformation in students’ pedagogical experience and teachers’ pedagogical practices.
In many cases teachers see the technology as a hindrance or unnecessary to achieving their aims and in some cases this may be correct.
In November 2015, the Open University released the latest edition of its ‘Innovating Pedagogy’ report, the fourth rendition of an annual educational technology and teaching techniques forecast. While the timelines and publishing interval may remind you of the Horizon Report, the methodology for gathering the trends is different.
The NMC Horizon Team uses a modified Delphi survey approach with a panel of experts.

Based upon a review of previous editions, the report tries to categorize pedagogical innovation into six overarching themes:
“What started as a small set of basic teaching methods (instruction, discovery, inquiry) has been extended to become a profusion of pedagogies and their interactions. So, to try to restore some order, we have examined the previous reports and identified six overarching themes: scale, connectivity, reflection, extension, embodiment, and personalisation.”
Follow these links to blog posts and EdITLib resources to further explore selected trends:
full article can be found here:
http://www.magnapubs.com/2016-teaching-professor-technology-conference/index.html
The Teaching Professor Technology Conference will include sessions on:
How to Register Online: http://www.magnapubs.com/2016-teaching-professor-technology-conference/ Email: support@magnapubs.com Phone: 800-433-0499 (US & Canada) or 608-246-3590 (Int’l)
http://www.teachthought.com/teaching/10-lessons-for-the-digital-teacher/
10 Lessons For The Digital Teacher
http://morethanatech.com/2015/07/21/21-top-presentation-tools-for-teachers/
As repeated by me for years, PPT should not be the one and only. Here are some choices. Please consider that IMS delivers workshops, one-on-one sessions and class sessions on the applications listed below:
| Tool | Windows | Mac | iPad | iPad App | Chromebook | Chromebook App | Android Tablet |
Android App |
| Animoto | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Bunkr | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Canva | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Clear Slide | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Creedoo | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| eMaze | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Flowvella | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Goanimate | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Google Slides | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Haiku Deck | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Impress | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Keynote | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| KnowledgeVision | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| MoveNote | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| PearDeck | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| PowerPoint | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| PowerPoint Online | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| PowToon | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Prezi | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Slidedog | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Visme | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
More on this topic at the IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=presentation&submit=Search