Apr
2018
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
1. Ask Yourself: Why VR or AR
AR and VR are mediums for the transmission of information, and many people will judge these mediums by the content that is produced within them. For educators seeking to gain buy-in from administrators and other colleagues it is critical for them to justify the reasons their content requires new reality media.
2. Just Dive In
Gartner Hype Cycle’s “slope of enlightenment”—meaning the technology is just entering public acceptance.
Given the newness of these mediums, it is no surprise that few curricular resources exist to support courses around VR and AR. Professional development sessions on new reality tools are almost non-existent, which means educators seeking to use virtual or augmented reality simply need to dive into the subjects.
3. Go Beyond Storytelling
Studies using VR demonstrate the ‘Proteus Effect’—taking on the psychology of inhabiting a different body and unconsciously changing our behavior to conform to it (learning empathy through VR)
4. Master the Machines
“The equipment matters. If there is a latency between the computer and the VR set that can cause a lot of problems,”
With VR equipment ranging from about $15 to $600 educators will have to check the budget or start writing grant proposals to gain access to the higher quality machines.
5. Understand Your Student’s Needs
described as a “quantum shift” in the way we interact, learn and experience.
+++++++++++++
more on VR and AR in schools in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+rality+education
According to the latest report from Babson Survey Research Group, nearly 6.5 million American undergraduates now take at least one course online
1. Listen to students and faculty. Every college, university, or online-learning provider has a different approach to online learning. At Indiana University, where more than 30 percent of students take at least one online course, the online education team has launched Next.IU, an innovative pilot program to solicit feedback from the campus community before making any major edtech decision. By soliciting direct feedback from students and faculty, institutions can avoid technical difficulties and secure support before rolling out the technology campus-wide.
2. Go mobile. Nine in 10 undergraduates own a smartphone, and the majority of online students complete some coursework on a mobile device. Tapping into the near-ubiquity of mobile computing on campus can help streamline the proctoring and verification process. Rather than having to log onto a desktop, students can use features like fingerprint scan and facial recognition that are already integrated into most smartphones to verify their identity directly from their mobile device.
For a growing number of students, mobile technology is the most accessible way to engage in online coursework, so mobile verification provides not only a set of advanced security tools, but also a way for universities to meet students where they are.
3. Learn from the data. Analytical approaches to online test security are still in the early stages. Schools may be more susceptible to online “heists” if they are of a certain size or administer exams in a certain way, but institutions need data to benchmark against their peers and identify pain points in their approach to proctoring.
In an initial pilot with 325,000 students, for instance, we found that cheating rose and fell with the seasons—falling from 6.62 percent to 5.49 percent from fall to spring, but rising to a new high of 6.65 percent during the summer.
++++++++++++
more on proctoring in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=proctoring
Over the past 10 years, new learning management systems (LMSs) have sprung on the scene to rival the Blackboards and Moodles of old. On the EdSurge Product Index alone, 56 products self-identify and fall into the LMS category. And with certain established companies like Pearson pulling out of the LMS ranks, where do you start?
As University of Central Florida’s Associate Vice President of Distributed Learning, Tom Cavanagh, wrote in an article for EDUCAUSE, “every institute has a unique set of instructional and infrastructure circumstances to consider when deciding on an LMS,” but at the same time, “all institutions face certain common requirements”—whether a small charter school, a private university or a large public school district.
#1: Is the platform straightforward and user-friendly?
#2: Who do we want to have access to this platform, and can we adjust what they can see?
#3: Can the instructor and student(s) talk to and communicate with each other easily?
“Students and faculty live a significant portion of their daily lives online in social media spaces,” writes University of Central Florida’s Tom Cavanagh in his article on the LMS selection process. “Are your students and faculty interested in these sorts of interplatform connections?”
#5: Does this platform plug in with all of the other platforms we have?
“Given the pace of change and the plethora of options with educational technology, it’s very difficult for any LMS vendor to keep up with stand-alone tools that will always outperform built-in tools,” explains Michael Truong, executive director of innovative teaching and technology at Azusa Pacific University. According to Truong, “no LMS will be able to compete directly with tools like Piazza (discussion forum), Socrative (quizzing), EdPuzzle (video annotation), etc.”
As a result, Truong says, “The best way to ‘prepare’ for future technological changes is to go with an LMS that plays well with external tools.”
#6: Is the price worth the product?
++++++++++++++++++
more on LMS in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=learning+management+systems
Who contributed to the code that we use every day?
by Jimmy Daly APril 19, 2013
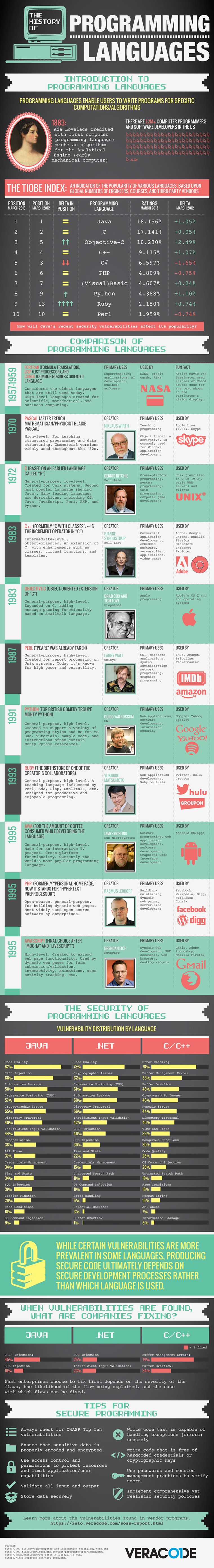
+++++++++++++++
more on coding in this IMS bog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=coding
Russia’s strongman president has many Americans convinced of his manipulative genius. He’s really just a gambler who won big.
JULIA IOFFE JANUARY/FEBRUARY 2018 ISSUE
https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2018/01/putins-game/546548/
(translated in Bulgarian http://librev.com/index.php/2013-03-30-08-56-39/prospects/europe/3371-igrata-na-putin-1
“They do plan,” said a senior Obama-administration official. “They’re not stupid at all. But the idea that they have this all perfectly planned and that Putin is an amazing chess player—that’s not quite it. He knows where he wants to end up, he plans the first few moves, and then he figures out the rest later. People ask if he plays chess or checkers. It’s neither: He plays blackjack. He has a higher acceptance of risk. Think about it. The election interference—that was pretty risky, what he did. If Hillary Clinton had won, there would’ve been hell to pay.”
Even the manner of the Russian attack was risky. The fact that the Russians didn’t really bother hiding their fingerprints is a testament to the change in Russia’s intent toward the U.S., Robert Hannigan, a former head of the Government Communications Headquarters, the British analogue to the National Security Agency, said at the Aspen Forum. “The brazen recklessness of it … the fact that they don’t seem to care that it’s attributed to them very publicly, is the biggest change.”
also: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/11/13/hacking-voting/
in German: http://www.sueddeutsche.de/medien/phishing-attacken-der-feind-liest-mit-1.3378411
+++++++++++
more on cybersecurity in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=cybersecurity
My note: nothing about education by this author. Here it is from our IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/01/12/blockchain-for-libraries/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/09/27/blockchain-credentialing-in-higher-ed/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/10/03/blockchain-credentialing/
Cybersecurity
Guardtime – This company is creating “keyless” signature systems using blockchain which is currently used to secure the health records of one million Estonian citizens.
REMME is a decentralized authentication system which aims to replace logins and passwords with SSL certificates stored on a blockchain.
Healthcare
Gem – This startup is working with the Centre for Disease Control to put disease outbreak data onto a blockchain which it says will increase the effectiveness of disaster relief and response.
SimplyVital Health – Has two health-related blockchain products in development, ConnectingCare which tracks the progress of patients after they leave the hospital, and Health Nexus, which aims to provide decentralized blockchain patient records.
MedRec – An MIT project involving blockchain electronic medical records designed to manage authentication, confidentiality and data sharing.
Financial services
ABRA – A cryptocurrency wallet which uses the Bitcoin blockchain to hold and track balances stored in different currencies.
Bank Hapoalim – A collaboration between the Israeli bank and Microsoft to create a blockchain system for managing bank guarantees.
Barclays – Barclays has launched a number of blockchain initiatives involving tracking financial transactions, compliance and combating fraud. It states that “Our belief …is that blockchain is a fundamental part of the new operating system for the planet.”
Maersk – The shipping and transport consortium has unveiled plans for a blockchain solution for streamlining marine insurance.
Aeternity – Allows the creation of smart contracts which become active when network consensus agrees that conditions have been met – allowing for automated payments to be made when parties agree that conditions have been met, for example.
Augur – Allows the creation of blockchain-based predictions markets for the trading of derivatives and other financial instruments in a decentralized ecosystem.
Manufacturing and industrial
Provenance – This project aims to provide a blockchain-based provenance record of transparency within supply chains.
Jiocoin – India’s biggest conglomerate, Reliance Industries, has said that it is developing a blockchain-based supply chain logistics platform along with its own cryptocurrency, Jiocoin.
Hijro – Previously known as Fluent, aims to create a blockchain framework for collaborating on prototyping and proof-of-concept.
SKUChain – Another blockchain system for allowing tracking and tracing of goods as they pass through a supply chain.
Blockverify – A blockchain platform which focuses on anti-counterfeit measures, with initial use cases in the diamond, pharmaceuticals and luxury goods markets.
Transactivgrid – A business-led community project based in Brooklyn allowing members to locally produce and cell energy, with the goal of reducing costs involved in energy distribution.
STORJ.io – Distributed and encrypted cloud storage, which allows users to share unused hard drive space.
Government
Dubai – Dubai has set sights on becoming the world’s first blockchain-powered state. In 2016 representatives of 30 government departments formed a committee dedicated to investigating opportunities across health records, shipping, business registration and preventing the spread of conflict diamonds.
Estonia – The Estonian government has partnered with Ericsson on an initiative involving creating a new data center to move public records onto the blockchain. 20
South Korea – Samsung is creating blockchain solutions for the South Korean government which will be put to use in public safety and transport applications.
Govcoin – The UK Department of Work and Pensions is investigating using blockchain technology to record and administer benefit payments.
Democracy.earth – This is an open-source project aiming to enable the creation of democratically structured organizations, and potentially even states or nations, using blockchain tools.
Followmyvote.com – Allows the creation of secure, transparent voting systems, reducing opportunities for voter fraud and increasing turnout through improved accessibility to democracy.
Charity
Bitgive – This service aims to provide greater transparency to charity donations and clearer links between giving and project outcomes. It is working with established charities including Save The Children, The Water Project and Medic Mobile.
Retail
OpenBazaar – OpenBazaar is an attempt to build a decentralized market where goods and services can be traded with no middle-man.
Loyyal – This is a blockchain-based universal loyalty framework, which aims to allow consumers to combine and trade loyalty rewards in new ways, and retailers to offer more sophisticated loyalty packages.
Blockpoint.io – Allows retailers to build payment systems around blockchain currencies such as Bitcoin, as well as blockchain derived gift cards and loyalty schemes.
Real Estate
Ubiquity – This startup is creating a blockchain-driven system for tracking the complicated legal process which creates friction and expense in real estate transfer.
Transport and Tourism
IBM Blockchain Solutions – IBM has said it will go public with a number of non-finance related blockchain initiatives with global partners in 2018. This video envisages how efficiencies could be driven in the vehicle leasing industry.
Arcade City – An application which aims to beat Uber at their own game by moving ride sharing and car hiring onto the blockchain.
La’Zooz – A community-owned platform for synchronizing empty seats with passengers in need of a lift in real-time.
Webjet – The online travel portal is developing a blockchain solution to allow stock of empty hotel rooms to be efficiently tracked and traded, with payment fairly routed to the network of middle-men sites involved in filling last-minute vacancies.
Media
Kodak – Kodak recently sent its stock soaring after announcing that it is developing a blockchain system for tracking intellectual property rights and payments to photographers.
Ujomusic – Founded by singer-songwriter Imogen Heap to record and track royalties for musicians, as well as allowing them to create a record of ownership of their work.
It is exciting to see all these developments. I am sure not all of these will make it into successful long-term ventures but if they indicate one thing, then it is the vast potential the blockchain technology is offering.
Bernard Marr is a best-selling author & keynote speaker on business, technology and big data. His new book is Data Strategy. To read his future posts simply join his network here.
by Serdar Abaci, Joshua Quick and Anastasia Morrone Monday, October 9, 2017
https://er.educause.edu/articles/2017/10/student-engagement-with-etexts-what-the-data-tell-us
Although cost savings is often cited as a key advantage of electronic textbooks (aka, e-textbooks or simply e-texts), e-texts also provide powerful markup and interaction tools. For these tools to improve student learning, however, their adoption is critically important.

The Indiana University e-texts program, which began in 2009, has four primary goals:
To date, student savings on textbooks amount to $21,673,338. However, we recognize that many students do not pay the full list price for paper textbooks when they purchase online, buy used copies, or recoup some of their costs when they resell their texts after the semester is over.
herefore, we divide the calculated savings by two and report that total as a more accurate representation of student savings. Consequently, we claim that students have saved about $11 million since IU’s e-texts program started in spring 2012.
In addition to printing through the e-text platform, students can purchase a print-on-demand (PoD) copy of an e-text for an additional fee.
One downside of e-texts is that students lease their textbook for a limited time instead of owning it. This lease generally lasts a semester or six months, and students lose their access afterwards. However, with IU’s e-text model, students get access to the textbook before the first day of class and maintain their access until they graduate from Indiana University. That is, students can go back to the e-texts after their course to review or reference the content in the book. This could be especially important if the e-text course is a prerequisite for another course.
+++++++++++++++++++
more on etext and ebooks in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=ebook