Mark your calendars: Thursday, April 11, 11AM-1PM, Miller Center B-31
and/or http://media4.stcloudstate.edu/scsu
Miller Center B-31 is a classroom in the basement of Miller Center. Ask at HelpDesk for directions.
We invite the campus community to a presentation by three vendors of Classroom Response System (CRS), AKA “clickers”:
- Top Hat Monocle,
- Turning Technologies,
- iClikers
We need your feedback to select one of these vendors as the SCSU-supported classroom response system (i.e., “clickers”) provider on our campus.
The vendors were presented with a list of questions (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?p=281). Please email ims@stcloudstate.edu, if you have additional questions and/or come to the vendors’ presentation on Thursday, April 11, 11AM-1PM at Miler Center B-31.
You can also participate online by login as a guest in the following Adobe Connect session:
http://media4.stcloudstate.edu/scsu
For more information, follow us on
Twitter: @scsutechinstruc #clickers
IMS blog: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims
From: Perry Bratcher [mailto:bratcher@nku.edu]
Sent: Wednesday, November 06, 2013 9:01 AM
To: ‘lita-l@ala.org’
Cc: Michael Providenti; Michael Wells; Millie Mclemore; Perry Bratcher; Stephen Moon
Subject: [lita-l] RE: Classroom iPads
All – Thanks to each of you for your responses to my email regarding classroom use of iPads (see email at the bottom). Listed below are is a summary of the comments I received. I cut/pasted and have reconfigured these comments for this email, so some may be taken out of context. NOTE: My systems staff have adamantly opposed using the Microsoft Surface. We have a campus “tech bar” where student/staff can check out new devices for experimentation. My staff said that the Surface doesn’t work in our particular situation for a variety of reasons and they prefer the iPad tablet option (if we go the tablet route).
Before deciding on implementation of PCs vs. laptops vs. tablet for use in a classroom setting, one needs to consider the motivation for doing so. Space? Portability? Availability of apps? Is there a demand for using personal devices for research, etc? What type of portable device to use (iPad, Microsoft Surface, etc.)
Pros for using iPad/tablets:
- Keep a few in there to provide examples of how to search on mobile devices.
- The amount of apps and types of apps out there. Great education apps exist that do not exist elsewhere online or on other platforms (Android or Windows).
- The iPad is flexible and allows you to regain that floor space you lose with computers and give the user privacy.
- If setup correctly, the devices can be erased when they are returned so any private data is wiped.
- Users can download additional apps, even purchase apps if you allow them.
- They hold a charge much longer then any laptop or ChromeBook on the market.
- Apple sold 94% of its iPads into education – the reason being that it’s a great education and research tool.
- Another advantage that I can see boot up time. The iPad is instantly on and connected to the network. Perhaps this most applicable to last-minute library instruction or ad hoc group research? However, if I had the choice, I would equip a classroom with MacBook Air SSDs
- Understand how they need to be configured and the tools needed to do so. I created a kit for this not long ago for public libraries: http://www.macprofessionals.com/new-library-ipad-checkout-solution/ Thank you Chris Ross, Macprofessionals
- UVA has been using iPads for instruction for about 2 years. They have been very pleased with the results.
- Our electronic classroom is very small, so we purchased 30 iPads over a year ago to allow teaching in our larger meeting room. There are definitely distinct advantages: flexibility, mobility, lack of technical infrastructure needed (wires, ports, etc.), and the myriad possibilities of apps.
Cons for using iPad/tablets:
- Most mobile devices have not become “workhorse” devices as of yet, so much of the students’ research will still need to be done on a computer.
- We haven’t seen any advantage to having them either – but our librarians use them sporadically for instruction.
- Charging, syncing, configuring, Apple ID’s, erasing, cases, restrictions, printing, presenting, etc. For example if you want to present with these, you will need an Apple TV or an adapter. If you want to print you will need AirPrint supported printers or software. If you want to configure and erase you will need a Mac.
- The challenge I have found is trying to use an inherently personal device in the typical one shot classroom environment. There are lots of things you need to consider. How will they access the wireless? What about taking notes? What about apps that require login? And much more.
- Someone on staff is equipped and has the time to manage them.
- We have a pool of 30 loan laptops, recently we have supplemented this with 11 loan iPads. The iPads have generally been very popular but wouldn’t work as a substitute for laptops. As many have mentioned when it comes to getting real work done they are inferior to laptops and people have commented as such.
- As a complement to laptops though they are great – they are more portable and our nursing students love being able to carry them around and quickly access medical apps, take notes, check calculations etc. I definitely see them as being a valuable resource but if it’s an either/or proposition then I would go on the side of laptops.
- My personal opinion is that it’s not a bad idea as a supplement to existing systems, but I’d be wary of replacing more flexible with more limited ones, and am particularly wary of committing to one operating system/vendor (particularly one that tends to charge half-again to twice as much as their competitors with only limited advantages).
- In a classroom setting (e.g. instruction room) I see little advantage of tablets; their sole advantage from I can figure out is their portability. Why force people into a limited device if it is only going to be in one room anyway?
Good evening,
We are pleased to inform you that your classroom response system is chosen as final candidate for campus-wide adoption/support at St. Cloud State University. Should you be interested in pursuing this opportunity, we invite you to respond to the attached list of questions and to prepare a brief presentation for members of the selection committee and interested faculty/staff.
The deadline for responding to the questions is 12:00 pm (CST), Tuesday, April 9. This deadline will allow us to review the responses in time for the vendor presentations on Thursday, April 11, 11AM-1PM. The presentations will be held virtually via Adobe Connect: http://media4.stcloudstate.edu/scsu. Please let us know, if you need to test and familiarize yourself with the presentation platform.
The presentation should be no more than 10 minutes long, followed by 10 minutes for follow-up questions. We suggest that you focus on the highlights of your system, presuming a moderately knowledgeable audience. We may follow up via email or telephone call prior to making our final selection.
Thank you and looking forward to hearing from you soon.
Classroom Response System Taskforce:
Dr. Anthony Hansen
Dr. Michael Rentz
Dr. Joseph Melcher
Dr. Andrew Anda
Dr. Tracy Ore
Dr. Jack McKenna
Dr. Plamen Miltenoff
| Questions to vendor |
| 1. Is your system proprietary as far as the handheld device and the operating system software? |
| 2. Describe the scalability of your system, from small classes (20-30) to large auditorium classes. (500+). |
| 3. Is your system receiver/transmitter based, wi-fi based, or other? |
| 4. What is the usual process for students to register a “CRS”(or other device) for a course? List all of the possible ways a student could register their device. Could a campus offer this service rather than through your system? If so, how? |
| 5. Once a “CRS” is purchased can it be used for as long as the student is enrolled in classes? Could “CRS” purchases be made available through the campus bookstore? Once a student purchases a “clicker” are they able to transfer ownership when finished with it? |
| 6. Will your operating software integrate with other standard database formats? If so, list which ones. |
| 7. Describe the support levels you provide. If you offer maintenance agreements, describe what is covered. |
| 8. What is your company’s history in providing this type of technology? Provide a list of higher education clients. |
| 9. What measures does your company take to insure student data privacy? Is your system in compliance with FERPA and the Minnesota Data Practices Act? (https://www.revisor.leg.state.mn.us/statutes/?id=13&view=chapter) |
| 10. What personal data does your company collect on students and for what purpose? Is it shared or sold to others? How is it protected? |
| 11. Do any of your business partners collect personal information about students that use your technology? |
| 12. With what formats can test/quiz questions be imported/exported? |
| 13. List compatible operating systems (e.g., Windows, Macintosh, Palm, Android)? |
| 14. What are the total costs to students including device costs and periodic or one-time operation costs |
| 15. Describe your costs to the institution. |
| 16. Describe how your software integrates with PowerPoint or other presentation systems. |
| 17. State your level of integration with Desire2Learn (D2L)?
Does the integration require a server or other additional equipment the campus must purchase? |
| 18. How does your company address disability accommodation for your product? |
| 19. Does your software limit the number of answers per question in tests or quizzes? If so, what is the max question limit? |
| 20. Does your software provide for integrating multimedia files? If so, list the file format types supported. |
| 21. What has been your historic schedule for software releases and what pricing mechanism do you make available to your clients for upgrading? |
| 22. Describe your “CRS”(s). |
| 23. If applicable, what is the average life span of a battery in your device and what battery type does it take? |
| 24. Does your system automatically save upon shutdown? |
| 25. What is your company’s projection/vision for this technology in the near and far term. |
| 26. Does any of your software/apps require administrator permission to install? |
| 27. If your system is radio frequency based, what frequency spectrum does it operate in? If the system operate in the 2.4-2.5 ghz. spectrum, have you tested to insure that smart phones, wireless tablet’s and laptops and 2.4 ghz. wireless phones do not affect your system? If so, what are the results of those tests? |
| 28. What impact to the wireless network does the solution have? |
| 29. Can the audience response system be used spontaneously for polling? |
| 30. Can quiz questions and response distributions be imported and exported from and to plaintext or a portable format? (motivated by assessment & accreditation requirements). |
| 31. Is there a requirement that a portion of the course grade be based on the audience response system? |
—————-
Plamen Miltenoff, Ph.D., MLIS
Professor
204-J James W. Miller Center
Learning Resources and Technology Services
720 Fourth Avenue South
St. Cloud, MN 56301-4498
320-308-3072
pmiltenoff@stcloudstate.edu
http://web.stcloudstate.edu/pmiltenoff/faculty/
“I am not strange, I am just not normal.” Salvador Dali
what kind of clickers are you using?
what kind of clickers are you familiar with?
what qualities in clickers do you find useful, necessary, obligatory for your course[s]?
At the moment SCSU is still considering eInstruction http://www.einstruction.com/ as its default clicker system (clickers sold in the Bookstore)
However, faculty on campus are slowly adopting other systems:
– http://iresponseapp.com/features/
– http://www.turningtechnologies.com
– https://www.tophatmonocle.com/
– http://www.polleverywhere.com/
while each of these systems appeal differenetly to different faculty from different disciplines, having a standard, campus-wide clicker system has also strong advantages.
Polls and surveys tools for education
SCSU faculty asked for help with Kahoot.it Great tool. Especially the reward system, which most likely might engage students in the learning process. However, Kahoot is very “synchronous.” It assumes that the faculty is in a synchronous environment (F2F or online). At least the free version.
In 2012, six SCSU faculty members worked together and recommended “heavy duty” survey/polling options also known as Classroom Response Systems (CRS):
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=clickers
Among the considered vendors were Turning Technologies, which have both hardware and completely online option and integrate with D2L (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2013/09/10/crs-clickers-turning-technology-instructions/) and TopHatMonitor (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2013/04/10/clickers-documentation/), which is completely online, no hardware solution.
Here are additional free resources, as recommended for use in education:
http://www.educatorstechnology.com/2012/05/15-great-free-and-easy-survey-polls.html
1- Kwiqpoll (my note: seems out of business)
This is a simple poll making tool. It does not require any registration. Just visit the homepage and start creating you poll right away. You have the choice to provide multiple choice answers. You will also be provided with a generated URL to use when sharing your polls.
2- Flisti
This is another great simple poll tool. It is very easy to use and resembles Kwiqpoll in that it does not call for any sign up. Just head over to its main page and start working on your poll. You can add as many answers as you want to your poll. Again , you can embed your polls in your blog, wiki or website
3- Urtak (my note: dead – server not found message)
This tool allows users to create polls using yes or no multiple questions.
4- Vorbeo (my note: seems out of business)
This is another free and simple to use poll tool. Teachers can use it to create their own polls and customize them the way they want by adding colours, adjusting width and many more before sharing them on their blogs or websites.
5- Polldaddy
This is another popular polling service that allows users to create free polls and surveys containing up to ten questions.
6- Micropoll
Micropoll allows users to instantly create a poll using a set of questions and answers then one email address. It also provides embed codes to share polls online.
8- Obsurvey
This is a great utility for creating instant surveys. It is dead simple, just visit its main page , type in your questions and answers using their text editor and there you go.
9- Kwik Surveys
This is another great polling service. It allows users to design their own surveys, form, polls and feedback forms. It is free but it does require a sign up.
10- Polleverywhere
This is a great polling tool. It has different pricing plans and also has a free plan but very limited and allows for just 40 responses per poll.
12- Poll Junkie
This is a simple free service for creating instant polls. It lets users specify an expiry date for their polls and also opt for email notification to be notified each time there is an answer to the poll.
13- Yarp
This is another easy and simple poll creating tool. It basically allows users to create their own surveys or online invitations. It does not require any registration.
https://www.edsurge.com/news/2017-04-19-online-courses-shouldn-t-use-remote-proctoring-tools-here-s-why
when the option between taking a course online or in-person is provided, studies show students are more likely to stay in college.
Since the early days of online instruction, the response of many new instructors has been to figure out how to transfer elements of their face-to-face class into the online format. In response, education technology companies have been quick to create products that attempt to replicate in-person teaching. Some examples include learning management systems, lecture capture tools, and early online meeting systems.
online proctoring systems, such as ProctorU or Proctorio, replicate a practice that isn’t effective in-person. Exams are only good for a few things: managing faculty workload and assessing low level skill and content knowledge. What they aren’t good at is demonstrating student learning or mastery of a topic. As authors Rena Palloff and Keith Pratt discuss in their book “Assessing the Online Learner: Resources and Strategies for Faculty,” online exams typically measure skills that require memorization of facts, whereas learning objectives are often written around one’s ability to create, evaluate and analyze course material.
Authentic assessments, rather than multiple choice or other online exams, is one alternative that could be explored. For example, in a chemistry course, students could make a video themselves doing a set problems and explain the process. This would allow instructors to better understand students’ thinking and identify areas that they are struggling in. Another example could be in a psychology course, where students could curate and evaluate a set of resources on a given topic to demonstrate their ability to find, and critically analyze online information. (see Bryan Alexander‘s take on video assignments here: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=bryan+alexander+video+assignments
+++++++++++
more on online learning in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=online+learning
more on proctoring in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=proctor
Key Issues in Teaching and Learning
https://www.educause.edu/eli/initiatives/key-issues-in-teaching-and-learning
A roster of results since 2011 is here.

1. Academic Transformation
2. Accessibility and UDL
3. Faculty Development
4. Privacy and Security
5. Digital and Information Literacies
https://cdn.nmc.org/media/2017-nmc-strategic-brief-digital-literacy-in-higher-education-II.pdf
Three Models of Digital Literacy: Universal, Creative, Literacy Across Disciplines
United States digital literacy frameworks tend to focus on educational policy details and personal empowerment, the latter encouraging learners to become more effective students, better creators, smarter information consumers, and more influential members of their community.
National policies are vitally important in European digital literacy work, unsurprising for a continent well populated with nation-states and struggling to redefine itself, while still trying to grow economies in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent financial pressures
African digital literacy is more business-oriented.
Middle Eastern nations offer yet another variation, with a strong focus on media literacy. As with other regions, this can be a response to countries with strong state influence or control over local media. It can also represent a drive to produce more locally-sourced content, as opposed to consuming material from abroad, which may elicit criticism of neocolonialism or religious challenges.
p. 14 Digital literacy for Humanities: What does it mean to be digitally literate in history, literature, or philosophy? Creativity in these disciplines often involves textuality, given the large role writing plays in them, as, for example, in the Folger Shakespeare Library’s instructor’s guide. In the digital realm, this can include web-based writing through social media, along with the creation of multimedia projects through posters, presentations, and video. Information literacy remains a key part of digital literacy in the humanities. The digital humanities movement has not seen much connection with digital literacy, unfortunately, but their alignment seems likely, given the turn toward using digital technologies to explore humanities questions. That development could then foster a spread of other technologies and approaches to the rest of the humanities, including mapping, data visualization, text mining, web-based digital archives, and “distant reading” (working with very large bodies of texts). The digital humanities’ emphasis on making projects may also increase
Digital Literacy for Business: Digital literacy in this world is focused on manipulation of data, from spreadsheets to more advanced modeling software, leading up to degrees in management information systems. Management classes unsurprisingly focus on how to organize people working on and with digital tools.
Digital Literacy for Computer Science: Naturally, coding appears as a central competency within this discipline. Other aspects of the digital world feature prominently, including hardware and network architecture. Some courses housed within the computer science discipline offer a deeper examination of the impact of computing on society and politics, along with how to use digital tools. Media production plays a minor role here, beyond publications (posters, videos), as many institutions assign multimedia to other departments. Looking forward to a future when automation has become both more widespread and powerful, developing artificial intelligence projects will potentially play a role in computer science literacy.
6. Integrated Planning and Advising Systems for Student Success (iPASS)
7. Instructional Design
8. Online and Blended Learning
In traditional instruction, students’ first contact with new ideas happens in class, usually through direct instruction from the professor; after exposure to the basics, students are turned out of the classroom to tackle the most difficult tasks in learning — those that involve application, analysis, synthesis, and creativity — in their individual spaces. Flipped learning reverses this, by moving first contact with new concepts to the individual space and using the newly-expanded time in class for students to pursue difficult, higher-level tasks together, with the instructor as a guide.
Let’s take a look at some of the myths about flipped learning and try to find the facts.
Myth: Flipped learning is predicated on recording videos for students to watch before class.
Fact: Flipped learning does not require video. Although many real-life implementations of flipped learning use video, there’s nothing that says video must be used. In fact, one of the earliest instances of flipped learning — Eric Mazur’s peer instruction concept, used in Harvard physics classes — uses no video but rather an online text outfitted with social annotation software. And one of the most successful public instances of flipped learning, an edX course on numerical methods designed by Lorena Barba of George Washington University, uses precisely one video. Video is simply not necessary for flipped learning, and many alternatives to video can lead to effective flipped learning environments [http://rtalbert.org/flipped-learning-without-video/].
Myth: Flipped learning replaces face-to-face teaching.
Fact: Flipped learning optimizes face-to-face teaching. Flipped learning may (but does not always) replace lectures in class, but this is not to say that it replaces teaching. Teaching and “telling” are not the same thing.
Myth: Flipped learning has no evidence to back up its effectiveness.
Fact: Flipped learning research is growing at an exponential pace and has been since at least 2014. That research — 131 peer-reviewed articles in the first half of 2017 alone — includes results from primary, secondary, and postsecondary education in nearly every discipline, most showing significant improvements in student learning, motivation, and critical thinking skills.
Myth: Flipped learning is a fad.
Fact: Flipped learning has been with us in the form defined here for nearly 20 years.
Myth: People have been doing flipped learning for centuries.
Fact: Flipped learning is not just a rebranding of old techniques. The basic concept of students doing individually active work to encounter new ideas that are then built upon in class is almost as old as the university itself. So flipped learning is, in a real sense, a modern means of returning higher education to its roots. Even so, flipped learning is different from these time-honored techniques.
Myth: Students and professors prefer lecture over flipped learning.
Fact: Students and professors embrace flipped learning once they understand the benefits. It’s true that professors often enjoy their lectures, and students often enjoy being lectured to. But the question is not who “enjoys” what, but rather what helps students learn the best.They know what the research says about the effectiveness of active learning
Assertion: Flipped learning provides a platform for implementing active learning in a way that works powerfully for students.
9. Evaluating Technology-based Instructional Innovations

What is the total cost of my innovation, including both new spending and the use of existing resources?
What’s the unit I should measure that connects cost with a change in performance?
How might the expected change in student performance also support a more sustainable financial model?
The Exposure Approach: we don’t provide a way for participants to determine if they learned anything new or now have the confidence or competence to apply what they learned.
The Exemplar Approach: from ‘show and tell’ for adults to show, tell, do and learn.
The Tutorial Approach: Getting a group that can meet at the same time and place can be challenging. That is why many faculty report a preference for self-paced professional development.build in simple self-assessment checks. We can add prompts that invite people to engage in some sort of follow up activity with a colleague. We can also add an elective option for faculty in a tutorial to actually create or do something with what they learned and then submit it for direct or narrative feedback.
The Course Approach: a non-credit format, these have the benefits of a more structured and lengthy learning experience, even if they are just three to five-week short courses that meet online or in-person once every week or two.involve badges, portfolios, peer assessment, self-assessment, or one-on-one feedback from a facilitator
The Academy Approach: like the course approach, is one that tends to be a deeper and more extended experience. People might gather in a cohort over a year or longer.Assessment through coaching and mentoring, the use of portfolios, peer feedback and much more can be easily incorporated to add a rich assessment element to such longer-term professional development programs.
The Mentoring Approach: The mentors often don’t set specific learning goals with the mentee. Instead, it is often a set of structured meetings, but also someone to whom mentees can turn with questions and tips along the way.
The Coaching Approach: A mentor tends to be a broader type of relationship with a person.A coaching relationship tends to be more focused upon specific goals, tasks or outcomes.
The Peer Approach:This can be done on a 1:1 basis or in small groups, where those who are teaching the same courses are able to compare notes on curricula and teaching models. They might give each other feedback on how to teach certain concepts, how to write syllabi, how to handle certain teaching and learning challenges, and much more. Faculty might sit in on each other’s courses, observe, and give feedback afterward.
The Self-Directed Approach:a self-assessment strategy such as setting goals and creating simple checklists and rubrics to monitor our progress. Or, we invite feedback from colleagues, often in a narrative and/or informal format. We might also create a portfolio of our work, or engage in some sort of learning journal that documents our thoughts, experiments, experiences, and learning along the way.
The Buffet Approach:
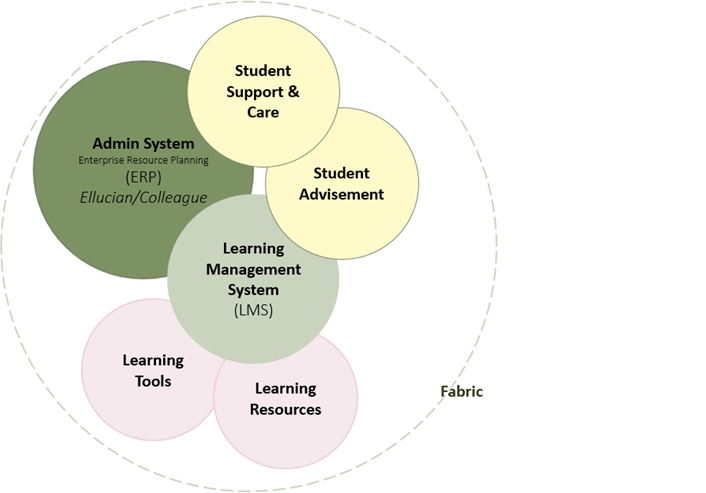
10. Open Education
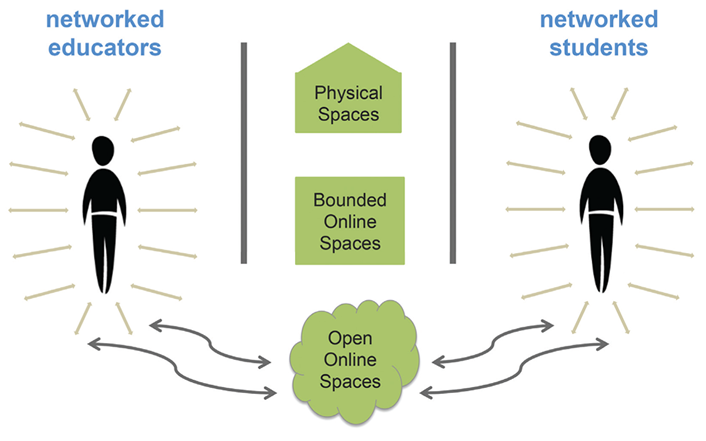
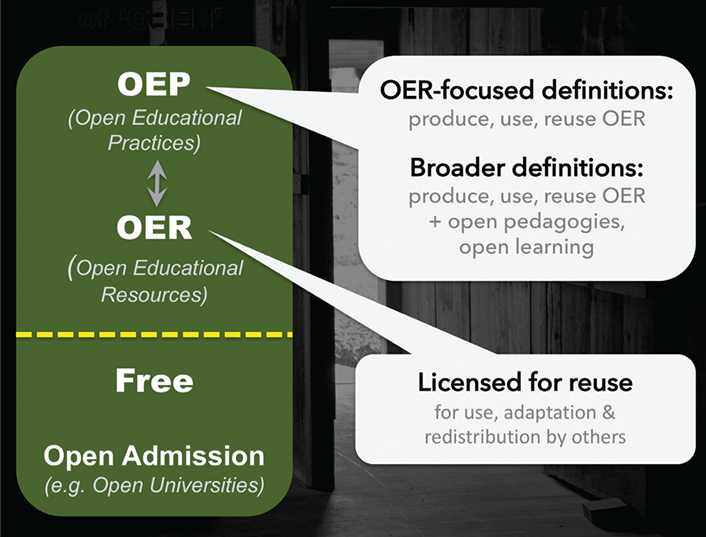

11. Learning Analytics
12. Adaptive Teaching and Learning
13. Working with Emerging Technology
In 2014, administrators at Central Piedmont Community College (CPCC) in Charlotte, North Carolina, began talks with members of the North Carolina State Board of Community Colleges and North Carolina Community College System (NCCCS) leadership about starting a CBE program.
Building on an existing project at CPCC for identifying the elements of a digital learning environment (DLE), which was itself influenced by the EDUCAUSE publication The Next Generation Digital Learning Environment: A Report on Research,1 the committee reached consensus on a DLE concept and a shared lexicon: the “Digital Learning Environment Operational Definitions,