https://www.edsurge.com/news/2019-12-24-the-answer-for-schools-is-not-more-technology-it-s-teachers-and-human-connection
A business-minded person may think a large class with 50 students, one adult and 50 screens makes fiscal sense, and is therefore an “innovative” idea.A business person may also think that because focus groups of children demonstrate that kids like and enjoy a tech product, that it is educationally sound. Education shouldn’t be viewed as simply a “market,” and children are certainly not “widgets.”
Technology can and should be used with fidelity in schools, but we must balance technology use with developmental psychology, the psychology of addiction and educational psychology. We need educational technology that puts highly trained teachers at the center of product design and implementation. It is human interaction that truly engages children and inspires them.
How to Give Your Students Better Feedback With Technology ADVICE GUIDE
y Holly Fiock and Heather Garcia
https://www.chronicle.com/interactives/20191108-Advice-Feedback
students continue to report dissatisfaction with the feedback they get on assignments and tests — calling it vague, discouraging, and/or late.
The use of technology in the classroom (both in face-to-face and online environments)
- Rubrics: online scoring guides to evaluate students’ work.
- Annotations: notes or comments added digitally to essays and other assignments.
- Audio: a sound file of your voice giving feedback on students’ work.
- Video: a recorded file of you offering feedback either as a “talking head,” a screencast, or a mix of both.
- Peer review: online systems in which students review one another’s work.
Two main types of feedback — formative and summative — work together in that process but have different purposes. Formative feedback occurs during the learning process and is used to monitor progress. Summative feedback happens at the end of a lesson or a unit and is used to evaluate the achievement of the learning outcomes.
Good feedback should be: Frequent, Specific, Balanced, Timely
guide on inclusive teaching, frequent, low-stakes assessments are an inclusive teaching practice.
Time-Saving Approaches: rubrics and peer-reviews.
When to Use Audio or Video Tools for Feedback: personalize your feedback, convey nuance, demonstrate a process, avoid miscommunication
Faculty interest in classroom innovation is on the rise. Professors are trying all sorts of new techniques to improve the first few minutes of class, to make their teaching more engaging, to hold better class discussions. Buzzwords like active learning, authentic assessment, technology integration, and case-based learning are more and more a part of faculty discussions.
Don’t assume technology will solve every problem.
Avoid making long videos
Video and audio feedback doesn’t have to be perfect.
There is such a thing as too much information.
Have a plan.
++++++++++
more on feedback in education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=feedback
AI and Mixed Reality Drive Educational Gaming into ‘Boom Phase’
By Dian Schaffhauser 09/16/19
https://campustechnology.com/articles/2019/09/16/ai-and-mixed-reality-drive-educational-gaming-into-boom-phase.aspx
Artificial intelligence and mixed reality have driven demand in learning games around the world, according to a new report by Metaari. A five-year forecast has predicted that educational gaming will reach $24 billion by 2024, with a compound annual growth rate of 33 percent and a quadrupling of revenues. Metaari is an analyst firm that tracks advanced learning technology.
https://www.edsurge.com/news/2018-01-16-ready-player-one-science-fiction-s-vision-for-the-future-of-education
Whenever I’m doing a virtual-reality demonstration, I ask for 40 minutes to an hour to get all of the students set up with their headsets, oriented in the virtual space, and then the learning can actually begin. It is not just something where you can throw headsets in a classroom and expect everyone to immediately start the learning objectives that you’re aiming for. You do need to do a little of that work explaining how the technology functions and making sure that everyone has the vision requirements, the hearing requirements, the physical requirements.
+++++++++++
more on Ready Player One in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=ready+player+one
https://www.edsurge.com/news/2019-01-23-how-much-artificial-intelligence-should-there-be-in-the-classroom
a two-day conference about artificial intelligence in education organized by a company called Squirrel AI.
he believes that having AI-driven tutors or instructors will help them each get the individual approach they need.
the Chinese government has declared a national goal of surpassing the U.S. in AI technology by the year 2030, so there is almost a Sputnik-like push for the tech going on right now in China.
+_+++++++++++++++++
more on AI in education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=Artificial+Intelligence+and+education
The Role of Librarians in Supporting ICT Literacy
Lesley Farmer May 9, 2019,
https://er.educause.edu/blogs/2019/5/the-role-of-librarians-in-supporting-ict-literacy
Academic librarians increasingly provide guidance to faculty and students for the integration of digital information into the learning experience.
TPACK: Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge
Many librarians have shied away from ICT literacy, concerned that they may be asked how to format a digital document or show students how to create a formula in a spreadsheet. These technical skills focus more on a specific tool than on the underlying nature of information.
librarians have begun to use an embedded model as a way to deepen their connection with instructors and offer more systematic collection development and instruction. That is, librarians focus more on their partnerships with course instructors than on a separate library entity.
If TPACK is applied to instruction within a course, theoretically several people could be contributing this knowledge to the course. A good exercise is for librarians to map their knowledge onto TPACK.
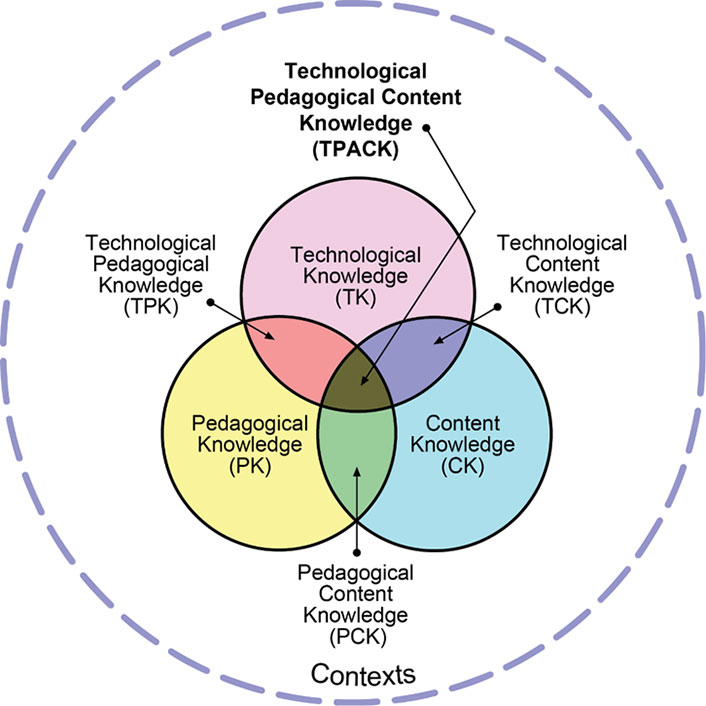
ICT reflects the learner side of a course. However, ICT literacy can be difficult to integrate because it does not constitute a core element of any academic domain. Whereas many academic disciplines deal with key resources in their field, such as vocabulary, critical thinking, and research methodologies, they tend not to address issues of information seeking or collaboration strategies, let alone technological tools for organizing and managing information.
Instructional design for online education provides an optimal opportunity for librarians to fully collaborate with instructors.
The outcomes can include identifying the level of ICT literacy needed to achieve those learning outcomes, a task that typically requires collaboration between the librarian and the program’s faculty member. Librarians can also help faculty identify appropriate resources that students need to build their knowledge and skills. As education administrators encourage faculty to use open educational resources (OERs) to save students money, librarians can facilitate locating and evaluating relevant resources. These OERs not only include digital textbooks but also learning objects such as simulations, case studies, tutorials, and videos.
Reading online text differs from reading print both physically and cognitively. For example, students scroll down rather than turn online pages. And online text often includes hyperlinks, which can lead to deeper coverage—as well as distraction or loss of continuity of thought. Also, most online text does not allow for marginalia that can help students reflect on the content. Teachers and students often do not realize that these differences can impact learning and retention. To address this issue, librarians can suggest resources to include in the course that provide guidance on reading online.
My note – why specialist like Tom Hergert and the entire IMS is crucial for the SCSU library and librarians and how neglecting the IMS role hurts the SCSU library –
Similarly, other types of media need to be evaluated, comprehended, and interpreted in light of their critical features or “grammar.” For example, camera angles can suggest a person’s status (as in looking up to someone), music can set the metaphorical tone of a movie, and color choices can be associated with specific genres (e.g., pastels for romances or children’s literature, dark hues for thrillers). Librarians can explain these media literacy concepts to students (and even faculty) or at least suggest including resources that describe these features
My note – on years-long repetition of the disconnect between SCSU ATT, SCSU library and IMS –
instructors need to make sure that students have the technical skills to produce these products. Although librarians might understand how media impacts the representation of knowledge, they aren’t necessarily technology specialists. However, instructors and librarians can collaborate with technology specialists to provide that expertise. While librarians can locate online resources—general ones such as Lynda.com or tool-specific guidance—technology specialists can quickly identify digital resources that teach technical skills (my note: in this case IMS). My note: we do not have IDs, another years-long reminder to middle and upper management. Many instructors and librarians have not had formal courses on instructional design, so collaborations can provide an authentic means to gain competency in this process.
My note: Tom and I for years have tried to make aware SCSU about this combo –
Instructors likely have high content knowledge (CK) and satisfactory technological content knowledge (TCK) and technological knowledge (TK) for personal use. But even though newer instructors acquire pedagogical knowledge (PK), pedagogical content knowledge (PCK), and technological pedagogical knowledge (TPK) early in their careers, veteran instructors may not have received this training. The same limitations can apply to librarians, but technology has become more central in their professional lives. Librarians usually have strong one-to-one instruction skills (an aspect of PK), but until recently they were less likely to have instructional design knowledge. ICT literacy constitutes part of their CK, at least for newly minted professionals. Instructional designers are strong in TK, PK, and TPK, and the level of their CK (and TCK and TPK) will depend on their academic background. And technology specialists have the corner on TK and TCK (and hopefully TPK if they are working in educational settings), but they may not have deep knowledge about ICT literacy.
Therefore, an ideal team for ICT literacy integration consists of the instructor, the librarian, the instructional designer, and the technology specialist. Each member can contribute expertise and cross-train the teammates. Eventually, the instructor can carry the load of ICT literacy, with the benefit of specific just-in-time support from the librarian and instructional designer.
My note: I have been working for more then six years as embedded librarian in the doctoral cohort and had made aware the current library administrator (without any response) about my work, as well as providing lengthy bibliography (e.g. https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/08/24/embedded-librarian-qualifications/ and have had meeting with the current SOE administrator and the library administrator (without any response).
I also have delivered discussions to other institutions (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/04/12/embedded-librarian-and-gamification-in-libraries/)
Librarians should seriously consider TPACK as a way to embed themselves into the classroom to incorporate information and ICT literacy.
+++++++++++++
more about academic library in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=academic+library
more on SAMR and TRACK models in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/05/17/transform-education-digital-tools/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/07/29/mn-esummit-2015/
Research from the Center for Higher Education CIO Studies (CHECS) has been transferred to EDUCAUSE, including a report on the role of the Chief Academic Technology Officer and its differences and similarities to other higher ed IT tech executives.
https://library.educause.edu/resources/2019/1/the-center-for-higher-education-cio-studies-reports-2003-2018 Friday, January 18, 2019
The Center for Higher Education CIO Studies (CHECS) was a nonprofit organization founded by Dr. Wayne A. Brown, dedicated to the education and development of technology leaders in higher education. CHECS produced the CIO Study, the Technology Leadership (TL) Study, the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) Study and the Higher Education Chief Academic Technology Officer Study.
The Chief Information Officer (CIO) study provides information about higher education CIOs’ attributes, education, experience and effectiveness. The CIO study was conducted from 2003 to 2018. Find all the CIO reports here.
The Technology Leadership (TL) study surveyed those in the next organizational layer down from the CIO. The TL study examines the demographics of the TL, where they have worked, and the activities they are undertaking to prepare themselves to become CIOs. The TL study was study was conducted from 2009 to 2018. Find all the TL reports here.
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) study examines the demographics of the higher education CISO, the career route they have taken to their role, and the activities and attributes needed for a CISO according to the CISO and the CIO. The CISO study was study was conducted from 2014 to 2017. Find all the CISO reports here.
The Higher Education Chief Academic Technology Officer Study, 2018 canvassed CIOs, known CATOs and academic technology leaders, as well as deans and provosts to understand changes happening across institutions of higher education in academic technology.
K–12 Teachers Use Augmented and Virtual Reality Platforms to Teach Biology
Immersive technology allows students to explore the world firsthand on a molecular level.
Eli Zimmerman
https://edtechmagazine.com/k12/article/2019/03/k-12-teachers-use-augmented-and-virtual-reality-platforms-teach-biology-perfcon
t universities and medical schools, students are already using AR and VR
Originally, AR and VR lesson plans revolved around the virtual field trip.with the HTC Vive, for example, can take a detailed, 3D-rendered journey.
In May 2018, Google announced a partnership with Labster, a virtual lab simulator, to develop immersive high school and college biology and anatomy courses.
by Intel last year, Middle Township High School in New Jersey embraced the idea of using Oculus Rift headsets to examine virtual frogs. In California, a new bill introduced in the state legislature would swap out real animals in schools for virtual replacements to teach biology more humanely.
