Call for Papers
The Journal of Emerging Learning Design special issue: The Digital Humanities
Submissions due date
On/before November 14, 2016.
Editors
Jerry Alan Fails (Boise State University) and AJ Kelton (Montclair State University)
Introduction
The Journal of Emerging Learning Design is pleased to announce the Call for Papers for its first Special Issue: The Digital Humanities.
With roots reaching back as far as 1940, the term Digital Humanities came into wide usage in late 2012 and has slowly risen in popularity since then. A Google Scholar search for “digital humanities” yields just under 30 results during the year 2000 and over 4,700 during 2015. The increase in the number of published articles in 15 years is second only to the diversity of the research that is included.
About the ELDj
The Journal of Emerging Learning Design (ELDj) is an open access, peer-reviewed, online journal that provides a platform for academics and practitioners to explore emerging learning design theories, concepts, and issues and their implications at national and international levels.
An outgrowth of the annual Emerging Learning Design Conference, which makes its home at Montclair State University (MSU), the ELDj invites scholarly communication in the emerging learning design field and will present best practices in design and implementation by offering articles that present, propose, or review engaging and dynamic approaches to pedagogy and how technology can better enhance it.
More details can be found at http://eldj.montclair.edu/about/
About the Special Issue
The ELDj has purposefully kept the focus of the theme for this special issue broad. The intent is to continue to break down traditional academic silos and allow for an open dialogue and sharing with respect to what is considered the Digital Humanities. ELDj is intentionally taking a broad consideration for what is included in the digital humanities with the clear understanding that this issue, and the articles within, will contribute to this growing field and provide a groundwork for further reflection and research.
Timeline
Deadline for Submission: November 14, 2016
Notification of Acceptance: March 1st, 2017
Final Revised Submission: April 21, 2017
Publication: June 2, 2017
Publication and Presentation
The issue will be published prior to, and featured at, the 7th Annual Emerging Learning Design Conference (ELDc17) on June 2nd, 2017.
Based on when a submission is accepted, authors may be offered the opportunity to present their research at the 7th Annual Emerging Learning Design Conference in June, 2017. Presentations must be given in an appropriate presentation format for the conference: panel (full conference audience), workshop (120 minutes), concurrent (45 minutes), or Sparks! (5 minutes to full conference audience).
Submission Details
Manuscripts should be the appropriate length for the material being presented.
- Full paper manuscripts can vary from 2500-4500 words in addition to an abstract of 250 words and a works cited section of appropriate length.
- Briefs or Trends papers have a limit of 1000 words.
A description of each type of submission and guidelines can be found at http://eldj.montclair.edu/submission-guidelines/ ELDj uses a double-blind, peer-review process. Submissions should not have been published previously or be under consideration for publication elsewhere. Authors should review the above linked guidelines for important and relevant information.
Submissions should be sent to eldj@mail.montclair.edu: questions and information requests may be sent to the Editors at the same address.
++++++++++++++++++
more on digital humanities and publications for digital humanities in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=digital+humanities
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is the new Learning Styles
https://fillingthepail.substack.com/p/universal-design-for-learning-udl
UDL is a complicated way to teach. It involves giving multiple representations of the same information to students which they then choose from. Students also choose to work collaboratively or individually. And they decide how to demonstrate their learning through written work, a video, a poster or some other means.
UDL as a form of classroom differentiation. Differentiation – the process of giving different students in the same classroom different forms of instruction
a new paper by Dr. Guy A. Boysen of McKendree University in the U.S. Boysen claims that this lack of evidence is one of the five ways in which UDL parallels debunked learning styles theories.
Learning styles theories are still remarkably popular despite most serious researchers classing them as a ‘neuromyth’.
++++++++++++++++++++++
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=udl
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=learning+styles
Building a Learning Innovation Network
https://www.insidehighered.com/digital-learning/blogs/technology-and-learning/building-learning-innovation-network
a new interdisciplinary field of learning innovation emerging.
Learning innovation, as conceptualized as an interdisciplinary field, attempts to claim a space at the intersection of design, technology, learning science and analytics — all in the unique context of higher education.
professional associations, such as POD, ELI, UPCEA, (https://upcea.edu/) OLC (https://onlinelearningconsortium.org/), ASU GSV (https://www.asugsvsummit.com/) and SXSW Edu (https://www.sxswedu.com/) — among many other conferences and events put on by professional associations.
A professional community of practice differs from that of an interdisciplinary academic network. Professional communities of practice are connected through shared professional goals. Where best practices and shared experiences form the basis of membership in professional associations, academic networks are situated within marketplaces for ideas. Academic networks run on the generation of new ideas and scholarly exchange. These two network models are different.
+++++++++++
https://elearningindustry.com/learning-experience-design-instructional-design-difference
“Learning Experience Design™ is a synthesis of Instructional Design, educational pedagogy, neuroscience, social sciences, design thinking, and User Experience Design.”
The Process: ADDIE Vs. Design Thinking
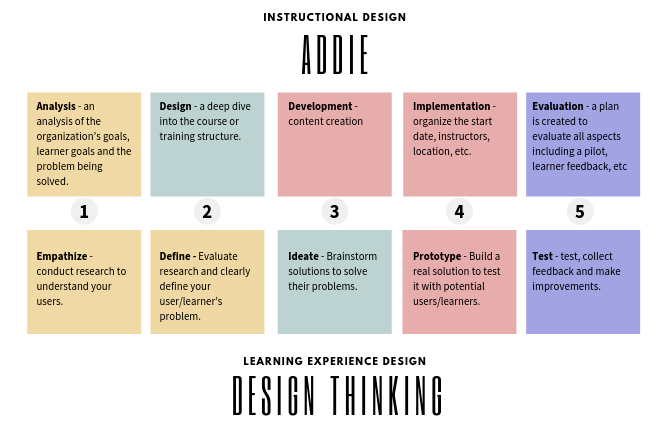
++++++++++++++
more on LX design in this iMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=learning+design
CAST’s 4th Annual UDL Symposium:Empowering Learners
http://www.cast.org/whats-new/events/2018/07/4th-annual-udl-symposium.html
This year’s UDL Symposium was an opportunity to come together as a community to explore the promise of Universal Design for Learning for empowering learners. By engaging in sessions designed to encourage critical conversations, problem-solving, and hands-on exploration, participants considered empowerment through a UDL lens. Participants left with a deeper understanding of the important role empowerment plays in learning and with concrete examples of ways to leverage UDL for these critical aims.We hope our participants left with the confidence and the motivation to apply their learning to their practice—and with a new network of colleagues to encourage and support their efforts.
Microlearning: The Emerging Instructional Design Strategy in Elearning
BY SYED AMJAD ALI NOVEMBER 8, 2017
Microlearning is a learning strategy that involves bite-sized learning nuggets (small and focused segments) designed to meet a specific learning outcome. To put it simply, the learning content is chunked to reduce learner’s cognitive overload making it easy for learners to absorb and recall.
An effective microlearning course:
- Provides deeper learning on a specific concept or a performance objective
- Is bite-sized, effectively chunked and easily digestible
- Designed for exact moment-of-need – Right information at right time
- Ideal for extended performance support providing a better mobile learning experience
- Focused on a single performance objective, concept or idea
- Is usually 4 to 5 minutes in length, or shorter
My note:
Adobe is trying to reshape an old theory: chunking
by calling it “microlearning”?
What do you think?
+++++++++++++++++
more on instructional design in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=instructional+design
An Open Repository of Learning Space Design
The cross-institutional FLEXspace team created a global forum for sharing examples of technology-enhanced learning environments and their impact on teaching and learning.
By Meg Lloyd 10/12/16
https://campustechnology.com/articles/2016/10/12/an-open-repository-of-learning-space-design.aspx
The Flexible Learning Environments eXchange (FLEXspace) a highly searchable, peer-reviewed repository of technology-enhanced learning spaces, freely available to the higher ed community.
FLEXspace uses the Artstor Shared Shelf platform to create its open education resource and share it with the higher education community.
A user begins by accessing the public facing FLEXspace website, which describes each project.
Ultimately, FLEXspace, used in conjunction with other resources like the Learning Space Rating System, will not only promote understanding of other institutions’ efforts, but also assist individual campus stakeholders in creating master learning space plans.
+++++++++++++++++++
more on learning spaces in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=learning+space
Online learning can work if universities just rethink the design of their courses
https://theconversation.com/online-learning-can-work-if-universities-just-rethink-the-design-of-their-courses-50848
Course design is key to improving student engagement
Training teachers in how to design their courses is key to re-engaging individual students and holding back the tide of dropouts.
- State your objective: Each lesson should have one concise, action-oriented learning objective to ensure your lesson design process is focused.
- Think as a private tutor: Learners today are inundated with media tailored to them and they expect learning to be tailored as well. So think about how the tools available, including new technologies, will help create meaningful learning moments for all your students.
- Storyboard before you build: Being able to see a complete lesson, especially one that integrates various mediums, is essential to creating a successful learning experience.
- Build towards high-order thinking: Technology in education can go beyond multiple-choice questions and document repositories. Don’t be afraid to integrate tools that let learners create and share.
- Remember you’re learning too: Reviewing learner results from a lesson shouldn’t just be about their score, but also evaluating how effectively the lesson was developed and executed so your teaching can adapt and learn as well.
