Searching for "retention"
https://www.dailyemerald.com/news/students-cheat-with-online-learning-service-professors-hope-to-identify-users/article_552d56f4-5a31-11eb-98ae-879264ec0299.html
Services like Chegg have become more accessible to students during unproctored exams in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic, causing what UO chemistry professor Shannon Boettcher believes is a “huge problem with academic dishonesty across the nation in the light of remote learning and COVID-19.”
he Digital Millennium Copyright Act’s notice and takedown process requires that service providers remove material that a copyright owner identifies on their website through a valid notice of copyright infringement or become subject to potential secondary liability for assisting with copyright infringement, according to Copyright Alliance.
Chegg Inc. has been sued twice in federal court for claims of copyright infringement, denying allegations in both instances.
Apart from its subscription services, Chegg rents and sells textbooks. The publishing company John Wiley & Sons Inc. filed a lawsuit against Chegg on Dec. 18, 2018, in Manhattan U.S. District Court, alleging that Chegg sold counterfeit versions of its textbooks.
+++++++++++
This $12 Billion Company Is Getting Rich Off Students Cheating Their Way Through Covid
https://www.forbes.com/sites/susanadams/2021/01/28/this-12-billion-company-is-getting-rich-off-students-cheating-their-way-through-covid
Chegg is based in Santa Clara, California, but the heart of its operation is in India, where it employs more than 70,000 experts with advanced math, science, technology and engineering degrees. The experts, who work freelance, are online 24/7, supplying step-by-step answers to questions posted by subscribers (sometimes answered in less than 15 minutes).
Chegg CEO Dan Rosensweig has profited handsomely. His holdings in Chegg plus after-tax proceeds from stock sales add up to $300 million. Rosensweig, who declined to speak to Forbes, has said that Chegg Study was “not built” for cheating. He describes it instead as the equivalent of an asynchronous, always-on tutor, ready to help students with detailed answers to problems. In a 2019 interview, he said higher education needs to adjust to the on-demand economy, the way Uber or Amazon have.
Throughout the pandemic, schools have spent millions on remote proctoring, a controversial practice in which colleges pay private companies like Honorlock and Examity to surveil students while they take tests.
Chegg Study was enjoying steady growth and little competition. Its only serious rival, privately held Course Hero, is a much smaller operation, valued at $1.1 billion, that generates most of its answers from students.
My note:
such proliferation would not have been possible, if the middle and upper administration has been more supportive of faculty when misconduct is detected. If the administration turns blind eye due to “enrollment” and “retention” priorities and curbs faculty reports regarding academic dishonesty, the industry naturally fills out the gap between a mere syllabus statement and inability to act upon it.
There is plenty of lipservice regarding “personalized learning,” but the reality is overworked faculty, who do not have the opportunity to spend sufficient time with students, less to educate them about plagiarism, cheating and similar “auxiliary” trends besides the content of the course.
+++++++++++
more on cheating in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=cheating
Faculty Members Fear Pandemic Will Weaken Their Ranks
By Megan Zahneis APRIL 09, 2020
https://www.chronicle.com/article/Faculty-Members-Fear-Pandemic/248476
Covid-19 is being described as both a crisis and an opportunity for higher education. But how “opportunity” is defined depends on where one stands in the academic hierarchy. While some hope the pandemic provides a chance to reverse troubling trends toward the adjunctification and casualization of academic labor, administrators may see it as a different sort of opportunity, to realign institutional priorities or exert greater authority over their faculties.
A statement by the Tenure for the Common Good group offers 20 recommendations for administrators, including that they “resist using the current crisis as an opportunity to exploit contingency further by hiring more contingent faculty into precarious positions.”
As faculty members are asked to take on greater teaching, advising, and administrative responsibilities, faculty development and retention “will be more important to institutional resilience — survival — than ever before,” Kiernan Mathews, executive director and principal investigator of the Harvard Graduate School of Education’s Collaborative on Academic Careers in Higher Education, wrote on Twitter.
To DePaola, the pandemic doesn’t pose new problems to academe as much as it magnifies existing ones. “Everything was held together with gum and paper clips, and coronavirus came and just sort of knocked it all down at once,” DePaola said. “I think none of the crises that this virus is causing are new. They’re just accelerated greatly. And the contradictions of the system are heightened all at once for people to see.”
++++++++++++++++
The Small World Network of College Classes: Implications for Epidemic Spread on a University Campus
https://osf.io/6kuet/
2020-04-11
Beginning in March 2020, many universities shifted to on-line instruction to slow the spread of the novel coronavirus, and many now face the difficult decision of whether and how to resume in-person instruction. This article uses complete transcript data from a medium-sized residential American university to map the two-node network that connects students and classes through course enrollments. We show that the enrollment networks of the university and its liberal arts college are “small-world” networks, characterized by high clustering and short average path lengths. In both networks, at least 98% of students are in the main component, and most students can reach each other in two steps. Removing very large courses slightly elongates path lengths, but does not disconnect these networks or eliminate all alternative paths between students. Although students from different majors tend to be clustered together, gateway courses and distributional requirements create cross-major integration. We close by discussing the implications of course networks for understanding potential epidemic spread of infection on university campuses.
+++++++++++++++
Gamifying PD is better for teacher engagement, participation
https://www.educationdive.com/news/gamifying-pd-is-better-for-teacher-engagement-participation/573191/
Allowing teachers to pursue their personal passions also creates a greater sense of job satisfaction, which may help with long-term retention.
Teachers also benefit from a variety of platforms through which they can pursue their advancement. Some teachers might prefer online options, such as webinars based on their interests and needs, while others could prefer working in small teacher-directed groups where they can collaborate with peers who have similar growth interests in person.
Professional development should also include a personal component that is relevant and effective. Data identifies teachers’ areas of weakness so administrators can work with them to set goals to make improvements.
+++++++++++++
more on gamification in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=gamification
please use this D2L discussion thread to log your thoughts regarding the readings below
https://stcloudstate.learn.minnstate.edu/d2l/le/4819732/discussions/threads/43535382/View
Instructional Design in Virtual Reality Experiences
reading this short article, what are the questions, VR poses to IDs (e.g. SCORM for things like learner picked up the correct tool.)
why do you think creating higher order thinking learning objectives for a virtual reality training
Instructional Design in VR Training
In this conversation between Monica Price and David Cleverdon, what is the most striking idea, you gathered?
Do you think Monica is right when she says that only “see and hear” is not that potent to let us learn?
Can you elaborate on Monica’s thoughts regrading the connection between simulation and retention (e.g. Imo’s group final project can argue that their project for new employees training is superior to the current training with the ability for the employee to repeat the simulation until they think, it is retained)
The Future of Instructional Design: Experience Design
A glimpse inside the role of instructional design for Immersive Learning
Allen claims that traditional ID does not translate to VR ID. Do you agree and why?
VR is supposed to be more engaging then 2D. Why?
Which of the six steps do you find important and why?
3 Instructional Design Strategies For Virtual Reality Learning
https://elearningindustry.com/instructional-design-strategies-virtual-reality-learning
which of the three instructional design strategies you find most appealing and why?
EDUCAUSE Academic Communities: Teaching and Learning + Student Success
https://events.educause.edu/webinar/2020/educause-academic-communities-teaching-and-learning-student-success
Tuesday, February 25, 2020, at 12:00 pm,
Miller Center, MC 205, the SCSU Professional Development Room
(how to get there? https://youtu.be/jjpLR3FnBLI )
You will receive an email from Canvas Catalog when you have been granted access to the event website. This site includes live event login details, program and speaker information, and technical requirements.
+++++++++++
My notes from the Adobe Connect webinar
Malcolm Brown (MB) and Kathe Pelletier (KP)
John Martin, UW-Madison: Interesting that “Student Success” = retention. I feel retention = org success.
Cindy Auclair: Cindy Auclair – ASU – Retention is important that goes hand in hand with well-being.
Kathy Fernandes, CSU Chico: Not sure how one would measure Becoming a Citizen? We do have public Debates, Town Hall, etc. to engage with community.
Lisa Durff: I thought of digital citizenship

Jim J – MiraCosta: “as a part of teaching and learning” is a real gray area –
Jim J – MiraCosta: We may measure all of these, but there is very little formality around “teaching and learning”
Lisa Durff: very few measure instructor satisfaction

student success after 2017 shifts from SS and technology to SS and other issues
digital transformation
why tech adoption doesn’t equal digital transformation. article from Forbes. MB: it is not for sale, cannot buy. not a product, but deep and coordinated shifts: culture, workforce, technology.

ask for EDUCAUSE Academic Communities PDF document
Malcolm Brown: 2019 Horizon Report https://library.educause.edu/resources/2019/4/2019-horizon-report
Malcolm Brown: Transforming Higher Ed blog https://er.educause.edu/columns/transforming-higher-ed
Malcolm Brown: EDUCAUSE Student Success https://library.educause.edu/topics/information-technology-management-and-leadership/student-success
https://www.educause.edu/research-and-publications/research/core-data-service
+++++++++++
more on Educause in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=educause
https://www.surveygizmo.com/s3/5155654/IT-Issues-2020?sguid=60122224
what i find most important:
Future IT Workforce: Deploying a broad array of modern recruitment, retention, and employment practices to develop a resilient IT talent pipeline for the institution
Digital Integrations: Ensuring system interoperability, scalability, and extensibility, as well as data integrity, security, standards, and governance, across multiple applications and platforms
Engaged Learning: Incorporating technologies that enable students to create content and engage in active learning in course curricula
Student Retention and Completion: Developing the capabilities and systems to incorporate artificial intelligence into student services to provide personalized, timely support
Administrative Simplification: Applying user-centered design, process improvement, and system reengineering to reduce redundant or unnecessary efforts and improve end-user experiences
Improved Enrollment: Using technology, data, and analytics to develop an inclusive and financially sustainable enrollment strategy to serve more and new learners by personalizing recruitment, enrollment, and learning experiences
Workforce of the Future: Using technology to develop curriculum, content, and learning experiences that prepare students for the evolving workforce
Holistic Student Success: Applying technology and data, including artificial intelligence, to understand and address the numerous contributors to student success, from finances to health and wellness to academic performance and degree planning (my note: this is what Christine Waisner, Mark Gill and Plamen Miltenoff are trying to do with their VR research)
Improved Teaching: Strengthening engagement among faculty, technologists, and researchers to achieve the true and expanding potential of technology to improve teaching
Student-Centric Higher Education: Creating a student-services ecosystem to support the entire student life cycle, from prospecting to enrollment, learning, job placement, alumni engagement, and continuing education
The Role of Librarians in Supporting ICT Literacy
Lesley Farmer May 9, 2019,
https://er.educause.edu/blogs/2019/5/the-role-of-librarians-in-supporting-ict-literacy
Academic librarians increasingly provide guidance to faculty and students for the integration of digital information into the learning experience.
TPACK: Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge
Many librarians have shied away from ICT literacy, concerned that they may be asked how to format a digital document or show students how to create a formula in a spreadsheet. These technical skills focus more on a specific tool than on the underlying nature of information.
librarians have begun to use an embedded model as a way to deepen their connection with instructors and offer more systematic collection development and instruction. That is, librarians focus more on their partnerships with course instructors than on a separate library entity.
If TPACK is applied to instruction within a course, theoretically several people could be contributing this knowledge to the course. A good exercise is for librarians to map their knowledge onto TPACK.
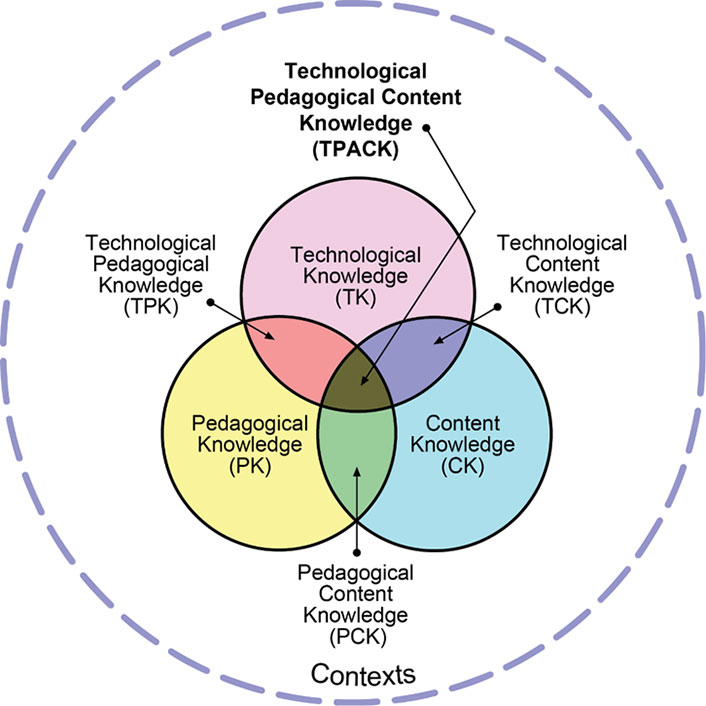
ICT reflects the learner side of a course. However, ICT literacy can be difficult to integrate because it does not constitute a core element of any academic domain. Whereas many academic disciplines deal with key resources in their field, such as vocabulary, critical thinking, and research methodologies, they tend not to address issues of information seeking or collaboration strategies, let alone technological tools for organizing and managing information.
Instructional design for online education provides an optimal opportunity for librarians to fully collaborate with instructors.
The outcomes can include identifying the level of ICT literacy needed to achieve those learning outcomes, a task that typically requires collaboration between the librarian and the program’s faculty member. Librarians can also help faculty identify appropriate resources that students need to build their knowledge and skills. As education administrators encourage faculty to use open educational resources (OERs) to save students money, librarians can facilitate locating and evaluating relevant resources. These OERs not only include digital textbooks but also learning objects such as simulations, case studies, tutorials, and videos.
Reading online text differs from reading print both physically and cognitively. For example, students scroll down rather than turn online pages. And online text often includes hyperlinks, which can lead to deeper coverage—as well as distraction or loss of continuity of thought. Also, most online text does not allow for marginalia that can help students reflect on the content. Teachers and students often do not realize that these differences can impact learning and retention. To address this issue, librarians can suggest resources to include in the course that provide guidance on reading online.
My note – why specialist like Tom Hergert and the entire IMS is crucial for the SCSU library and librarians and how neglecting the IMS role hurts the SCSU library –
Similarly, other types of media need to be evaluated, comprehended, and interpreted in light of their critical features or “grammar.” For example, camera angles can suggest a person’s status (as in looking up to someone), music can set the metaphorical tone of a movie, and color choices can be associated with specific genres (e.g., pastels for romances or children’s literature, dark hues for thrillers). Librarians can explain these media literacy concepts to students (and even faculty) or at least suggest including resources that describe these features
My note – on years-long repetition of the disconnect between SCSU ATT, SCSU library and IMS –
instructors need to make sure that students have the technical skills to produce these products. Although librarians might understand how media impacts the representation of knowledge, they aren’t necessarily technology specialists. However, instructors and librarians can collaborate with technology specialists to provide that expertise. While librarians can locate online resources—general ones such as Lynda.com or tool-specific guidance—technology specialists can quickly identify digital resources that teach technical skills (my note: in this case IMS). My note: we do not have IDs, another years-long reminder to middle and upper management. Many instructors and librarians have not had formal courses on instructional design, so collaborations can provide an authentic means to gain competency in this process.
My note: Tom and I for years have tried to make aware SCSU about this combo –
Instructors likely have high content knowledge (CK) and satisfactory technological content knowledge (TCK) and technological knowledge (TK) for personal use. But even though newer instructors acquire pedagogical knowledge (PK), pedagogical content knowledge (PCK), and technological pedagogical knowledge (TPK) early in their careers, veteran instructors may not have received this training. The same limitations can apply to librarians, but technology has become more central in their professional lives. Librarians usually have strong one-to-one instruction skills (an aspect of PK), but until recently they were less likely to have instructional design knowledge. ICT literacy constitutes part of their CK, at least for newly minted professionals. Instructional designers are strong in TK, PK, and TPK, and the level of their CK (and TCK and TPK) will depend on their academic background. And technology specialists have the corner on TK and TCK (and hopefully TPK if they are working in educational settings), but they may not have deep knowledge about ICT literacy.
Therefore, an ideal team for ICT literacy integration consists of the instructor, the librarian, the instructional designer, and the technology specialist. Each member can contribute expertise and cross-train the teammates. Eventually, the instructor can carry the load of ICT literacy, with the benefit of specific just-in-time support from the librarian and instructional designer.
My note: I have been working for more then six years as embedded librarian in the doctoral cohort and had made aware the current library administrator (without any response) about my work, as well as providing lengthy bibliography (e.g. https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/08/24/embedded-librarian-qualifications/ and have had meeting with the current SOE administrator and the library administrator (without any response).
I also have delivered discussions to other institutions (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/04/12/embedded-librarian-and-gamification-in-libraries/)
Librarians should seriously consider TPACK as a way to embed themselves into the classroom to incorporate information and ICT literacy.
+++++++++++++
more about academic library in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=academic+library
more on SAMR and TRACK models in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/05/17/transform-education-digital-tools/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/07/29/mn-esummit-2015/
Harper, A. (2019, April 2). Reducing teacher stress may require multiple strategies. Retrieved April 2, 2019, from Education Dive website: https://www.educationdive.com/news/reducing-teacher-stress-may-require-multiple-strategies/551604/?utm_source=Sailthru&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=Issue:%202019-04-02%20K-12%20Education%20Dive%20Newsletter%20%5Bissue:20185%5D&utm_term=Education%20Dive:%20K12
- In the face of mounting testing pressures, rapidly changing reform efforts and student circumstances over which teachers feel little control, more than half of teachers consider their jobs to be highly stressful, which is affecting teacher absenteeism rates, retention and student achievement, according to The Hechinger Report.
- There is a growing trend to address teachers’ mental health through stress-reduction and resiliency-building exercises. These include yoga and programs such as those offered by the Center for Resilience, Breathe for Change and mindfulness training offered through Cultivating Awareness and Resilience in Education. However, these efforts are mere triage and only offer short-term solutions, some experts say.
- Education leaders can offer longer-term solutions that address root issues by providing mentoring support in schools rather than bringing in outside experts, rolling out new initiatives in a more teacher-centered way, and involving teachers in discussions about what works best for students.
But principals also need to build relationships with teachers themselves to create a sense of trust and more open and honest lines of communication. Good teachers are hard to find and losing them to stress is not a good option. Finding ways to solve the issues that are causing them stress and helping them deal with the inevitable pressures along the way is well worth the effort in the long run.
+++++++++
more on stress
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=stress
5 Key Barriers to VR Adoption in Schools
March 31, 2019 @steve_bambury
https://www.virtualiteach.com/single-post/2019/03/31/5-Key-Barriers-to-VR-Adoption
- lack of understanding
- cost and ROI
- rate of change
- health and safety



- benefits for learning




How about Edgar Dale’s Cones of Learning? Well look at the highest level of retention rate and read what leads to this –

Study: Schools with principals from New Leaders program show higher student learning gains
K-8 students with the same principal, who was trained by the nonprofit, for at least three years get higher math and English language arts scores than those with other leaders.
Linda Jacobson
https://www.educationdive.com/news/study-schools-with-principals-from-new-leaders-program-show-higher-student/549011/
Principals trained and supported by New Leaders — a New York City-based nonprofit — are contributing to higher student achievement and staying in their jobs longer than those hired through other preparation programs, a new RAND Corp. study shows.
Students attending K-8 schools that have had a New Leaders principal for at least three years score at least 3% higher in math and roughly 2% higher in English language arts (ELA) than students with school leaders prepared in other ways.
The RAND researchers found that specific aspects of being a leader — specifically competencies related to instruction, and adult and team leadership — were more closely associated with increases in student achievement.
What New Leaders calls “cultural capital,” which includes skills related to “cultural leadership” and “operational leadership,” was more closely linked to retention.
A 2017 Stanford University study showed that academic growth among CPS students in grades 3-8 was increasing at a faster rate than in most districts in the nation.
++++++++++++
more of EDAD in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=edad












