Searching for "textbooks"
16 Startups Poised to Disrupt the Education Market
Colleges and universities are facing new competition for customers–students and their parents–from startups delivering similar goods (knowledge, credentials, prestige) more affordably and efficiently. Here’s a rundown of some of those startups.
Related story on the IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/01/12/cms-course-management-systemsoftware-alternatives/
In a new book, The End of College: Creating the Future of Learning and the University of Everywhere, author Kevin Carey distills a brave new world in which a myriad of lower-cost solutions–most in their infancy–threaten to upend the four-year, high-tuition business model by which colleges and universities have traditionally thrived.
1. Rafter
Using cloud-based e-textbooks and course materials, Rafter helps campus bookstores digitize their offerings and keep their prices low, allowing them to regain the market share they were losing to other stores and course-materials marketplaces.
2. Piazza
Piazza is an online study room where students can anonymously ask questions to teachers and other students. The best answers get pushed to the top through repeated user endorsement.
3. InsideTrack
As do the above two companies, InsideTrack sells its services to universities. It provides highly personalized coaching to students and it helps colleges assess whether their technology and processes are equipped to measure student progress. nsideTrack recently announced a partnership with Chegg, through which it will provide its coaching services directly to students.
4. USEED
If you attended a four-year school, then you know the feeling of receiving relentless requests for alumni donations. USEED is like Kickstarter for school fundraising:
5. Course Hero
One of Inc.‘s 30-Under-30 companies from 2013, Course Hero is an online source of study guides, class notes, past exams, flash cards, and tutoring services.
6. Quizlet
This is another site offering shared learning tools from students worldwide. Quizlet
according to Tony Wan’s superb story on EdSurge.
7. The Minerva Project
Other companies on this list provide services to schools or students. The Minerva Project is, literally, a new school.
8. Dev Bootcamp
In its own way, Dev Bootcamp is also a new school. Its program allows you to become a Web developer after a 19-week course costing under $14,000.
9. The UnCollege Movement
Founded by Thiel Fellow Dale Stephens (who took $100,000 from Peter Thiel to not go to college), The UnCollege Movement provides students with a 12-month Gap Year experience for $16,000.
10. Udacity
Founded by Stanford computer science professor Sebastian Thrun, Udacity creates online classes through which companies can train employees. AT&T, for example, paid Udacity $3 million to develop a series of courses, according to The Wall Street Journal.
11. Coursera
The tagline says it all: “Free online courses from top universities.” Indeed, Coursera’s partners include prestigious universities worldwide.
12. EdX
In a nonprofit joint venture, MIT and Harvard created their own organization offering free online courses from top universities. Several other schools now offer their courses through EdX, including Berkeley, Georgetown, and the University of Texas system.
13. Carnegie Mellon University’s Open Learning Initiative
CMU’s OLI is another example of a nonprofit startup founded by a school to ward off its own potential disruption.
14. Saylor.org
Founder Michael Saylor has been musing on how technology can scale education since he himself was an undergrad at MIT in the early ’80s. Anyone, anywhere, can take courses on Saylor.org for free.
15. Open Badges
Founded by Mozilla, Open Badges is an attempt to establish “a new online standard to recognize and verify learning.”
16. Accredible
Calling itself the “future of certificate management,” Accredible is the company that provides certification services for several of the online schools on this list, including Saylor.org and Udacity.
10 key takeaways about differences between classroom, blended, online and open learning
http://www.tonybates.ca/2015/02/21/10-key-takeaways-about-differences-between-classroom-blended-online-and-open-learning/
Tony Bates shares his thoughts on the difference
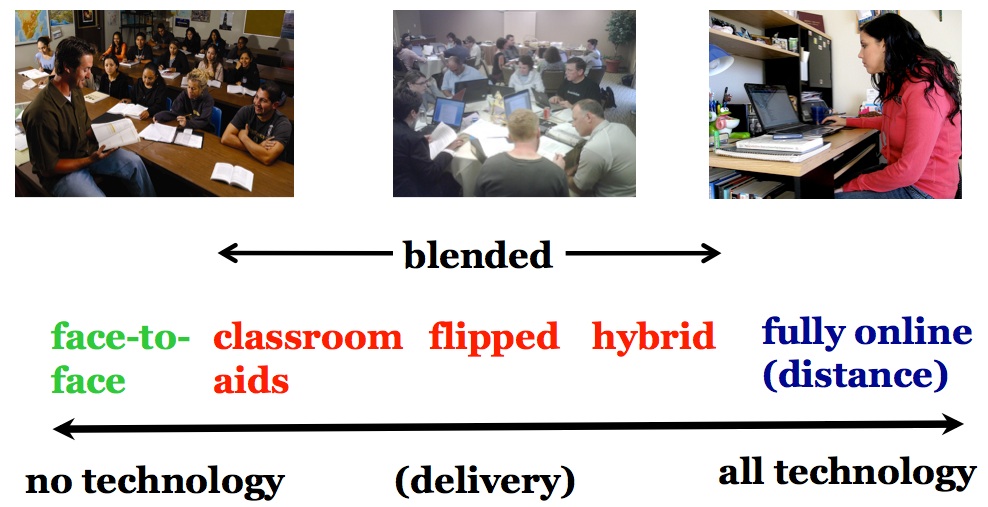
Chapter 10 of Tony Bates online open textbook, Teaching in a Digital Age:
– See more at: http://www.tonybates.ca/2015/02/21/10-key-takeaways-about-differences-between-classroom-blended-online-and-open-learning/#sthash.MOymkn9F.dpuf
More on F2F, blended/hybrid and online learning in this blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=blended
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=hybrid
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=online+learning
http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals/access/white-paper-social-media.pdf
#tfsocialmedia
Social media objectives:
- promotion
- collection management tool
- Outreach
- teaching and learning
Opportunities and challenges
- opportunity to build a sense of community between the library and its users
- the variability of skills across library staff for using social media effectively, striking the right tone between professional and personal, coordinating activities across the institution to avoid duplication
- maintaining visibility for the library brand and copyright issues relating to hosting library resources on social media sites
Policies and management:
- Librarians are divided on the benefits of introducing formalized social media policies and plans. About a third of libraries responding to the Taylor & Francis survey had a policy in place, but over 40% had no plans to introduce one
- Some believe that representing the library as a professional function with a
consistent tone is the priority, while others believe that a more human approach is important, with individual staff free to bring their own ideas and personalities to social media activities.
Effectiveness and assessment:
- difficult to prove return on effort and that the time required to do this was a major barrier to more comprehensive analysis of impact
- framework for evaluation, so it is likely that assessment against commonly agreed metrics will become an increasingly important part of social media activity within the library in the near future
Current Social Media Practices:
- In a study from the mid 2000s (Cantrell and Havens1 ), most library directors in the US when questioned about social media said they did not think that libraries had a role in social networking
- A more recent study from 2012 (Kai-Wah Chu and Du4) shows how use of social media by the library has now become mainstream. In this survey of libraries in Asia, North America and Europe, 71% were found to be using social media tools with a further 13% saying they planned to use them
Advantages of using social media
n Financially the costs of using social media are perceived to be low;
n It requires little training;
n It promotes library services and disseminates news quickly, delivering this information more directly to library users;
n It increases engagement and interactions with library users;
n It helps gather feedback to enhance user services;
n The promotion of library holdings via social media can help increase usage of content;
n It enhances communication both within the library and with other departments;
n It can be used for outreach activities through onward sharing, well beyond the institution itself, helping build connections and reputation more broadly
Social Media Objectives: graph on page 8 of the PDF document:
A To promote events
B To promote library services
C To promote resources/collections at the library
D To update on library refurbishments
E To promote new acquisitions
F To promote library guides, exhibition guides
G To connect with new students joining the university
H To engage with the academic community
I To connect with the wider community beyond the university e.g. the town in which the institution is based
J To connect with distance learners
K As a customer services tool- complaints, suggestions, enquiries, feedback
L To highlight subject specific information
M To connect with potential students
N As a teaching tool to promote information literacy, technology and writing tips (not library based)
O To promote courses
P As a research tool to locate official documents and studies
From UK-based focus group: “The library is a programme, not just a building.”
Channel preferences: Graph on page 10 of the PDF document
SOCIAL MEDIA USES Table on p 13 of the PDF document
Twitter n Distribute library news and information
n Provide customer service
n Build connections with researchers
n Build connections with other librarians and institutions
Facebook n Distribute library news and information
n More social and less formal than Twitter – share photographs and run competitions
n Arrange events including tracking RSVPs and sending event updates
n Engagement with students
Pinterest n Promote general library collections, digital and archive special collections and information literacy
n Set up of online repositories for students to pin researched references as part of
collaborative group work
n Display book titles to save time browsing and promote new titles
n Provide an arena for students and course leaders to pin reviewed and recommended reading
for a particular topic
n Develop communities with other online libraries
YouTube n Streaming film collections
n Instructional ‘how to’ videos teaching information literacy skills and how to use library
services and resources
There are also a number of other social media products that are being used by librarians that reflect regional
preferences and the need for the specific functions offered by niche applications.
Collection usage and discovery: Graph on p. 15
Teaching and learning
From US-based librarian interview: “The trend in education now is to create environments that foster collaborative learning. Faculty have ditched textbooks and course management systems in exchange for a Facebook page for their class, or a wiki, or a blog. These online environments are fun; students already know how to use them and are more motivated to comment, discuss and share in these environments than a dry CMS.”
Social media policies and management, p. 18
73% of respondents stating that they believed more roles dedicated to social media would appear in the library in the future.
Effectiveness of social media
From UK focus group: “We keep track of something particularly successful, then we redo the campaign 6 months later.”
From US focus group: “We have very few interactions with anyone on our Twitter feed.”
“Twitter is definitely the best platform, because we hashtag all of our posts with the keyword
of the publication, and so for the academic audience, once they click it’s going to pull up all
of the similar publications under that topic.
Promoting library social media channels
From UK focus group:
“We retweet each other to encourage new followers.” My note: Suggested by me regarding SCSU_Library for Twitter and Pinterest and SCSUTechinstruct but “considered” (in local lingo, slow death of the idea)
Blended Learning: Resource Roundup
http://www.edutopia.org/blended-learning-resources
4 Tips for Getting to Know the Blended Instructional Model
http://www.edutopia.org/blog/getting-to-know-blended-learning-victor-small
Tip #1: Kids Aren’t as Tech Savvy as You Think
Tip #2: Be Wary of Online Textbooks and Online Classes
Tip #3: PowerPoint is for Planning Lessons, Not Delivering Lectures
Tip #4: Get Your Students to Communicate with Each Other
10 technology hallmarks for every campus
http://www.ecampusnews.com/technologies/technology-hallmarks-campus-099
1. High-speed wireless broadband.
According to the Center for Digital Education’s recent “2013 Yearbook: Technology Innovation in Education,” over 80 percent of education institutions surveyed said that wireless broadband was their “top priority for IT investment.”
2. 24/7 IT support.
We have 24/7 support for emergencies and much of our staff, just like at a hospital, are on call. That’s not a perk for the campus, it’s a necessity.
3. The cloud.
The cloud can also: acquire and implement the latest software and application updates; streamline enrollment and admissions processes; and turn to subscriptions that are scalable and provide options, says Edudemic.
4. Digital textbooks.
Planning for digital textbooks means not only boosting mobile device capabilities on campus, but helping faculty learn to implement digital resources into their course.
5. 21st Century PD for faculty and admin.
From offering a MOOC on classroom management online solutions, to hosting a PD session on Twitter, campus admin should offer multiple options for PD delivery, just like how faculty should offer students multiple options for learning–there’s no better way to teach something than to model it first!
6. MOOCs.
[Read: “3 pros and 3 cons of MOOCs.”]
7. Online course management system.
From sending in-class emails to checking grades, course management systems, like Blackboard, offer faculty and students a fairly intuitive way to manage courses more efficiently.
8. Big Data…
Future-proofing universities are beginning to deploy storage solutions to help manage the unstructured data in physical, virtual and cloud environments. More modern storage solutions are also open source for a high learning curve but low cost.
9…security.
precautions can range from scanning existing databases on the university’s servers to determine where personal information is located and then, depending on the database, destroy the personal information or add more digital security; as well as put cybersecurity systems through a series of penetration tests to highlight security shortcomings.
[Read: “University data breach prompts ‘top-to-bottom’ IT review.”]
10. Social media done well.
of the major ways campuses use social media well is by serving up both “cake” and “broccoli,” or balancing the content that is important and good for the school (broccoli) and the content that is fun and delicious (cake). “If you share enough cake, your audience will consume the occasional broccoli,” she advises.
http://elearninginfographics.com/future-learning-tools-infographic/


