E-textbook ad hoc team
purpose: draft a document for the provost to plan for charting the future goal 3.12 “develop a comprehensive strategy to increase awareness and development of e-textbooks and open educational resources (OERs)”
\\STCLOUDSTATE\HuskyNet\DeptFiles\LRS\ETextbooks
SCSU goal: to reduce the cost of textbooks as an affordable learning initiative. Amount of reduction is undetermined
my notes based on the material below:
- best, most applicable source for the purpose of this research: U of Alberta Committee’s notes on the learning environment:
http://www.governance.ualberta.ca/en/GeneralFacultiesCouncil/CommitteeontheLearningEnvironm/~/media/Governance/Documents/GO05/LEA/15-16/WEB/Item-4-eTextbook-Subcommittee-Report-CLE-TLAT.pdf
the Canadians are using (citing) Acker (Ohio) in their research. - best, most applicable source in terms of the logistics on e-texbooks creation and its pedagogical argumentation is this document from New Zealand: https://akoaotearoa.ac.nz/download/ng/file/group-7/guidelines-for-developing-interactive-etextbooks-on-net-tablets.pdf
- According to Bossaler et al (2014), it might be worth considering that SCSU (MnSCU?) must go first through implementing of e-text[books] in courses first by using publisher materials and then by using “in-house” produce. At this point, SCSU does NOT have an aligned policy of integrating e-texts in courses across campus. Lack of such experience might make a strategy for adoption of e-textbooks much more complex and difficult to implement
- stats are colored in green for convenience. Stats regarding the increase in textbook costs are re-printed from author to author: e.g. Acker (2011, p. 42). Murey and Perez (2011, p. 49 (bottom) – 50 (up)) reports stats from 2009 and projections for 2013 regarding etexbook adotion. Same authors, p. 50 second paragraph reports good stats regarding texbooks’ price increase : US$1122 per year for textbooks in 2010.
- Wimmer at al (2014) presents a lucid graphic of the structure of the publishing process (see bottom of this blog entry for citation and perm link).
- Wimmer at al (2014) discusses copyright and permissions, which is of interest for this research (p. 85)
- regarding in-house creation of e-textbooks, see (Distance education, e-learning, education and training, 2015). It very much follow the example of SUNY, which Keith was laying out: a team of faculty charged with creation the e-textbook for mass consumption.
Besides the SUNY model Keith is envisioning for MnSCU (comparable), there is the option of clustering OER sources: e.g. NASTA as per Horejsi (2013), CourseSmart. FlatWorld Knowledge (Murrey and Perez, 2011) etc. - Hamedi & Ezaleila (2015) present an entire etextbook program. Article has been ordered through ILL. Same with Joseph (2015).
- Open Educational Resources in Acker (2015, p. 44-47). Also in Murey and Perez (2011, p. 51).
Also in ICWL (Conference) (13th : 2014 : Tallinn, E., & Cao, Y. (2014): OpenDSA - Different models of pricing also in Acker (2015, p. 48). Keith touched on that
- students learn equally well from etextbooks as from paper ones: Taylor (2011)
- pedagogy
responses from colleagues:
Scott Robison, sarobison@mail.plymouth.edu: sparc-liboer@arl.org listserv
Jeff Gallant, Jeff.Gallant@usg.edu: David Ernst with the U and Ashley Miller from Ohio State U: dernst@umn.edu. Ashley’s is miller.6275@osu.edu.
definition e-textbook and
-
a dedicated device for reading electronic versions of printed books.
Definition of: e-book
my note: there is no good definition about e-textbook in terms of the complexity, which e-textbook on campus might involve.
Considering Wimmer et al (2014) account on their campus experience in publishing e-textbook, a textbook may involve an LMS (Canvas) and blog (WordPress). Per my proposal during the F2F meeting, and following Rachel’s suggestion about discrimination of the different types of e-textbooks, here is an outline of e-textbook definition:
*******************
working definition for e-textbook for the purposes of SCSU:
e-textbook is a compilation of textual, multimedia and interactive material, which can be viewed on various electronic devices. E-textbook can: 1. be purchased from a publisher; 2. compiled in HTML format on faculty or group web space; 3. compiled on the content module of LMS (BB, D2L, Canvas, Moodle, etc.) 4. compiled on LMS (BB, D2L, Canvas, Moodle, etc.) and including all interactive materials: e.g. hyperlinks to MediaSpace multimedia, quizzes, etc.; 5. compiled on special apps, such as iBook Author, eCub, Sigil.
*******************
(Electronic-BOOK) The electronic counterpart of a printed book, which can be viewed on a desktop computer, laptop, smartphone, tablet or e-book reader (e-reader). When traveling, a huge number of e-books can be stored in portable units, dramatically eliminating weight and volume compared to paper. Electronic bookmarks make referencing easier, and e-book readers may allow the user to annotate pages.
Although fiction and non-fiction books come in e-book formats, technical material is especially suited for e-book delivery because it can be searched. In addition, programming code examples can be copied, which is why CD-ROMs that contained examples or the entire text were often packaged inside technical paper books.
E-Book Formats
Wimmer, Morrow, & Weber: Collaboration in eTextbook Publishing
There are several e-book formats on the market, including EPUB, Mobipocket (PRC, MOBI), eReader (PDB), Kindle (AZW, KF8) and Apple iBook (EPUB variation). Many e-readers also accept generic formats, including Adobe PDF and plain text (TXT).
Oxford dictionary, an electronic book or e-book is “an electronic version of a printed book that can be read on a computer or handheld device designed specifically for this purpose.” An e-textbook is defined as an e-book used for instructional or educational purposes and often includes features such as bookmarking, searching, highlighting, and note-taking as well as built-in dictionaries and pronunciation guides, embedded video-clips, embedded hyperlinks, and animated graphics.
E-textbooks have moved from occasional usage to a mainstream technology on college campuses. According to the Association of American Publishers, sales of e-books hit over $90 million; this is up over 200% when compared to the same month the previous year. When the cost of textbooks and the availability of formats are considered, the use of an e-textbook in the classroom may be the reasonable choice.
—————–
The concepts of open access and open source support the idea of open textbooks, digital textbooks that are free (gratis) and easy to distribute, modify and update
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_textbook
Exploring Students’ E-Textbook Practices in Higher Education
Key Issues
Despite the advantages that e-textbooks pose, such as interactive features and accessibility on mobile devices, several barriers exist regarding implementation in higher education, namely non-standardization of the platform, limited use by students, and the unclear role of the instructor in adoption.
a survey questionnaire in 2012 that explored basic usage and attitudes regarding e-textbooks.
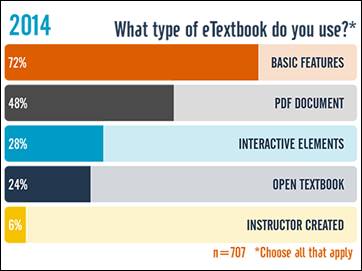
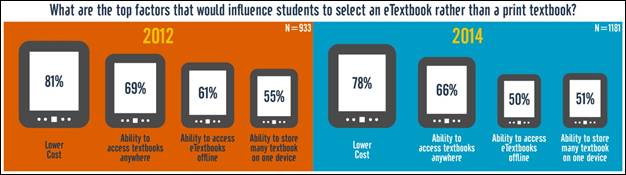
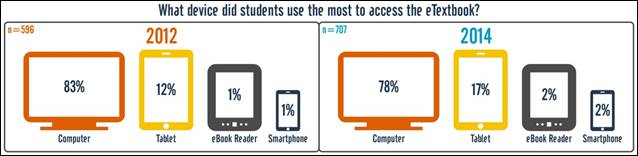
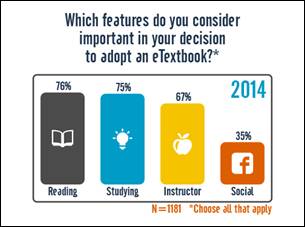

—————————–
Bossaller, J., & Kammer, J. (2014). Faculty Views on eTextbooks: A Narrative Study. College Teaching, 62(2), 68-75. doi:10.1080/87567555.2014.885877
Implementing eTexts into a Course:
- planning
- developing
- implementing
- delivering
This qualitative study gives insight into the experiences instructors have when working with publishers to integrate electronic content and technology into their courses.
Baek, E., & Monaghan, J. (2013). Journey to Textbook Affordability: An Investigation of Students’ Use of eTextbooks at Multiple Campuses. International Review Of Research In Open And Distance Learning, 14(3), 1-26.
http://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1017493
the Advisory Committee on Student Financial Assistance (2007) reported that textbook prices represent a significant barrier to students’ accessibility to textbooks. The report concluded that textbooks cost between $700-$1000 per year; textbook prices have risen much faster than other commodities; and that college aid fails to cover textbook expenses. Textbook costs are equivalent to 26% of tuition costs for an average four-year public university student and 72% of tuition costs for an average community college student. In fact, the California State Auditor (2008) reported that textbook costs grew more rapidly than student fees in academic year 2007–08.
++++++++++++
Wimmer, E. e., Morrow, A. a., & Weber, A. a. (2014). Collaboration in eTextbook Publishing: A Case Study.Collaborative Librarianship, 6(2), 82-86.
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dllf%26AN%3d108762075%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite

Distance education, e-learning, education and training. (2015). Clinical Chemistry & Laboratory Medicine, 53s557-s559. doi:10.1515/cclm-2015-5015
onto Youtube so that the user could access these via the internet.
CourseSmart. FlatWorld Knowledge,
Horejsi, M. (2014). Textbooks 2.0. Science Teacher, 81(3), 8. http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3daph%26AN%3d94603788%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
++++++++++++++
pedagogy
two Eastern Europeans (Moldova, Serbia) raise serious concerns about electronic textbooks
Španović, S. (2010). PEDAGOGICAL ASPECTS OF E-TEXTBOOKS. Odgojne znanosti. 12(2). 459-470.
Railean, E. (2015). https://prezi.com/sbidiadctrzo/beyond-textbook-digital-textbook-use-and-development/
http://www.governance.ualberta.ca/en/GeneralFacultiesCouncil/CommitteeontheLearningEnvironm/~/media/Governance/Documents/GO05/LEA/15-16/WEB/Item-4-eTextbook-Subcommittee-Report-CLE-TLAT.pdf :
- (Un)desirable features in etextbooks
- How etextbooks might affect course delivery
- Pilot projects that can help build institutional expertise
- Address how and where insights gained from pilot projects will be collected and
- made available
- People resources (e.g., instructional designers) that will be needed to assist
- instructors to use this technology
ICWL (Conference) (13th : 2014 : Tallinn, E., & Cao, Y. (2014). New horizons in web based learning: ICWL 2014 international workshops, SPeL, PRASAE, IWMPL, OBIE, and KMEL, FET, Tallinn, Estonia, August 14-17, 2014, revised selected papers. Cham: Springer.
++++++++++++++++++++
MnSCU will by as Content Authoring Tool – SoftChalk. Here is a promo from Softchalk (my bold):
NEW SoftChalk Create 10 and SoftChalk Cloud eBook publishing features will arrive on April 25th! Come check out the latest enhancements at our upcoming webinars!
Sleek Designer Headers and Callout Boxes – Add some new pizazz to your SoftChalk lessons!
Three New Quiz Types – Test your students’ understanding with Sentence Completion, Multiple Blanks and Feedback Questions.
Polished New QuizPopper and Activity displays – With an enhanced interface for instructors and students.
Accessibility enhancements – Make your lessons available to everyone with even more accessibility enhancements.
NEW SoftChalk Cloud eBook creation and publishing – Includes a totally re-vamped, easier eBook creation and management. New SoftChalk eReader apps available for free download in the iOS, Android, Chromebook and Windows app stores. (Cloud Only)
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
The future of textbooks looks like this
are any faculty really going digital? Which content distributors will thrive? What are the implementation concerns? And when will going digital really happen?
two massive surveys and reports by the National Association of College Stores (NACS) and the Independent College Bookstore Association (ICBA) in partnership with the Campus Computing Survey (CCS),

