Resources on Kinesiology and Virtual, Augmented and Mixed Reality:
Home – VR Health Institute
Lee, S.-H., Yeh, S.-C., Chan, R.-C., Chen, S., Yang, G., & Zheng, L.-R. (2016). Motor Ingredients Derived from a Wearable Sensor-Based Virtual Reality System for Frozen Shoulder Rehabilitation. BioMed Research International, 2016, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7075464
Dvorkin, A. Y., Shahar, M., & Weiss, P. L. (2006). Reaching within Video-Capture Virtual Reality: Using Virtual Reality as a Motor Control Paradigm. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 9(2), 133–136. https://doi.org/10.1089/cpb.2006.9.133
Zeng, N., Pope, Z., Lee, J. E., & Gao, Z. (2018). Virtual Reality Exercise for Anxiety and Depression: A Preliminary Review of Current Research in an Emerging Field.
Journal of Clinical Medicine,
7(3), 1-N.PAG.
https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7030042
Kramer, M., Honold, M., Hohl, K., Bockholt, U., Rettig, A., Elbel, M., & Dehner, C. (2009). Reliability of a new virtual reality test to measure cervicocephalic kinaesthesia.
Journal of Electromyography & Kinesiology,
19(5), e353–e361.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2008.05.005
How AR and VR Can Make Students Laugh and Cry Out Loud—and Embed Them in Their Learning
https://www.edsurge.com/news/2018-08-28-how-ar-and-vr-can-make-students-laugh-and-cry-out-loud-and-embed-them-in-their-learning
40 virtual reality headsets with haptic handsets for them to manipulate in the VR/AR space, and I connected them to content from New York Times VR and WITHIN. The content placed students in settings such as on the ground in a refugee crisis or in the midst of the Millions March in New York City.
At the beginning of every class, they would go into this virtual space and engage with the content instead of just reading it. They’d respond to me about what it was like to be immersed in the experience.
The content from the WITHIN app provided one of the more visceral experiences for students.
At the end of the course, for example, students met with a shark tank-type group—investors from the community, business, and industry folks—and pitched them business ideas that would utilize VR to provide a solution to problems that were local, regional, national or even global in scope.
Were you able to measure this success?
The way that I measured it was completion. How many of my students actually got through my class successfully? It was over 85%. My research from the two classes where I used VR and this approach shows students were engaged, and ultimately more successful in my classes.
zSpace https://info.zspace.com/2018-vived-allied-health-promo
Also:
Intro To Haptic Technology
Haptics provide a critical role in making our devices more interactive.
https://www.iotforall.com/intro-to-haptic-technology-tachammer-haptic-actuator/
1. Eccentric Rotating Mass (ERM)
2. Linear Resonant Actuator (LRA)
Apple Taptic Engine
3. Piezoelectric Actuators
4. Forced Impact (Accelerated Ram)
+++++++++++
more on VR in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+reality
5 ways virtual reality is being used in education right now
October 17th, 2016
Stansbury, M. (2016, October 17). 5 ways virtual reality is being used in education right now. Retrieved January 26, 2017, from
http://www.eschoolnews.com/2016/10/17/5-ways-virtual-reality-used-education-right-now/
A
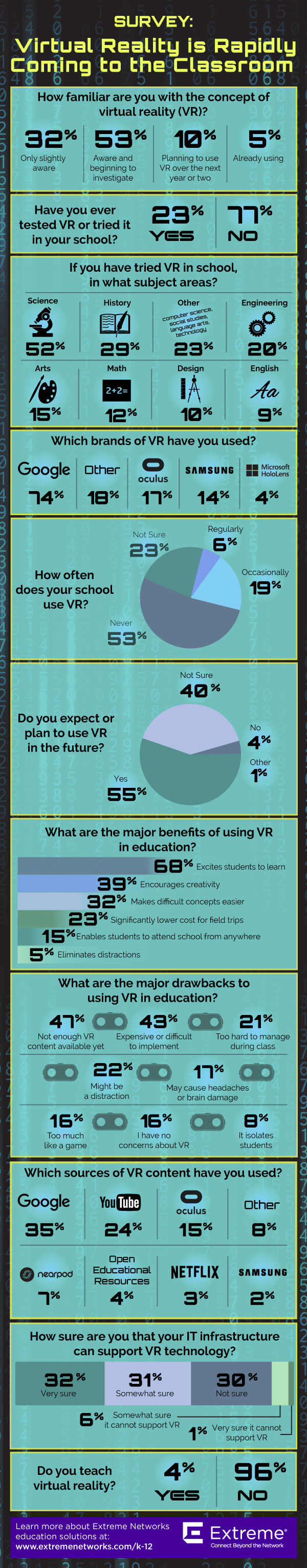
new survey from Extreme Networks aimed to answer this question by polling nearly 350 schools within higher ed and K-12. According to the results, 23 percent of respondents have tested VR, while 77 percent have not (40 percent of schools polled still aren’t sure if they’ll use the technology in the future). Meaning that although virtual reality has an important and growing role in education, it may take several years to get all institutions on board.
The survey notes that one challenge to implementation is that nearly two-thirds of schools are “somewhat or not sure” their IT infrastructure can currently support VR technology.
Respondents also had concerns about the lack of VR content available, as well as a lack of student resources, with 43 percent of respondents saying that VR is too expensive or difficult to implement. However, one respondent is taking this approach to providing VR to students at low or no cost: “We are putting out a call for old smartphone donations in our [community for those] who no longer need them. With the donations, we’re making sets of Google Cardboard and phones to create traveling VR stations for classes in all of our buildings.”
1. For new research: According to the Wall Street Journal, Professor Jeremy Bailenson, founding director of the Virtual Reality Human Interaction Lab at Stanford University, is using a state-of-the-art “haptic” floor of aeronautic metal that vibrates and moves to stimulate the physical world for research on how VR has the potential to change the way users feel and behave. For example, spending time flying around the world like Superman in virtual reality has been shown to increase participants’ altruistic actions outside of the lab. There may also be implications for confronting racism, sexism, and aiding in
empathy and humanitarian efforts, says Bailenson. (see more in about
empathy and VR in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/11/18/immersive-journalism/)
2. For coding and 3D design:
a class on virtual reality that gives students the opportunity to design their own interactive world, work with 3D audio and experiment with immersive technology through a combination of hands-on learning and case studies. Also, the University of Georgia is offering similar classes where students design and explore applications for VR.
3. For anatomy and dissection:
4. For engagement: A whopping 68 percent of survey respondents said the major benefit of using VR in education is to excite students about the subject matter. 39 percent said it’s great for encouraging creativity.
##########################
July 26th, 2016
Sixty percent of surveyed teachers said they would like virtual reality to become a part of their students’ learning experience, according to the study from Samsung Electronics America, Inc. and GfK.
#####################
Virtual reality helping Calif. students overcome learning barriers | eSchool News. (2016, June). Retrieved January 26, 2017, from
http://www.eschoolnews.com/2016/06/21/virtual-reality-helping-calif-students-overcome-learning-barriers/
+++++++++++++++++++++++
more on VR in education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+reality
Save
Save
5 ways virtual reality is being used in education right now
By Meris Stansbury
1. For new research: using a state-of-the-art “haptic” floor of aeronautic metal that vibrates and moves to stimulate the physical world for research on how VR has the potential to change the way users feel and behave. There may also be implications for confronting racism, sexism, and aiding in
empathy and humanitarian efforts, says Bailenson.
2. For coding and 3D design:
According to Bob Nilsson, director of Vertical Solutions Marketing for Extreme Networking, the University of Maryland, College Park, now offers a class on virtual reality that gives students the opportunity to design their own interactive world, work with 3D audio and experiment with immersive technology through a combination of hands-on learning and case studies. Also, the University of Georgia is offering similar classes where students design and explore applications for VR. Conrad Tucker, an assistant professor of engineering at Pennsylvania State University, has received funding to build a virtual engineering lab where students hold, rotate, and fit together virtual parts as they would with their real hands.
3. For anatomy and dissection: Said one Extreme Networks survey respondent, “Our students have been developing a VR model of a cow’s anatomy for dissection and study. You have the ability to drill down to the circulatory system, brain, muscle, skeleton, etc. Our applied tech program is using VR in conjunction with Autocad for models of projects they design.”
4. For engagement: A whopping 68 percent of survey respondents said the major benefit of using VR in education is to excite students about the subject matter. 39 percent said it’s great for encouraging creativity.
5. For field trips: Google has eliminated restrictions on Expeditions, their VR field trips program. Google Expeditions was cited in the survey as one of the most popular sources of VR content, but with the complaint that it was a restricted program.

comment:
·
Virtual reality may have its place, but until traditional education moves away from their 20th century teaching methodology and replaces it with educationally innovative, 21st century learning methodology, within a blended and flipped learning environment, virtual reality is currently, much ado about nothing.
Unless any new application is educationally innovative and directly and measurably contributes to effective, efficient, consistent, affordable, relevant advanced student success outcomes for ALL students, future innovations must wait for current innovations to be implemented.
This process of appriate choice and appropriate implemention must start at the top and be beta tested for measured student success before its rolled out system wide.
+++++++++++++++
more on VR in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+reality
Save
