Embedded Librarianship in Online Courses
Embedded Librarianship in Online Courses
more on embedded librarianship in this iMS blog
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
Since the Open University was founded in 1984, more than 250,000 students have enrolled in courses. The Open University offers courses of study at the bachelor’s and master’s degree levels in cultural studies, education science, law, management, psychology, science and technology. Five of its master’s degree programs were top-ranked in 2017
4CID ID Model https://edutechwiki.unige.ch/en/4C-ID
http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/hrd/learning/id/4c_id.html
++++++++++
more on open education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=open+education
According to the latest report from Babson Survey Research Group, nearly 6.5 million American undergraduates now take at least one course online
1. Listen to students and faculty. Every college, university, or online-learning provider has a different approach to online learning. At Indiana University, where more than 30 percent of students take at least one online course, the online education team has launched Next.IU, an innovative pilot program to solicit feedback from the campus community before making any major edtech decision. By soliciting direct feedback from students and faculty, institutions can avoid technical difficulties and secure support before rolling out the technology campus-wide.
2. Go mobile. Nine in 10 undergraduates own a smartphone, and the majority of online students complete some coursework on a mobile device. Tapping into the near-ubiquity of mobile computing on campus can help streamline the proctoring and verification process. Rather than having to log onto a desktop, students can use features like fingerprint scan and facial recognition that are already integrated into most smartphones to verify their identity directly from their mobile device.
For a growing number of students, mobile technology is the most accessible way to engage in online coursework, so mobile verification provides not only a set of advanced security tools, but also a way for universities to meet students where they are.
3. Learn from the data. Analytical approaches to online test security are still in the early stages. Schools may be more susceptible to online “heists” if they are of a certain size or administer exams in a certain way, but institutions need data to benchmark against their peers and identify pain points in their approach to proctoring.
In an initial pilot with 325,000 students, for instance, we found that cheating rose and fell with the seasons—falling from 6.62 percent to 5.49 percent from fall to spring, but rising to a new high of 6.65 percent during the summer.
++++++++++++
more on proctoring in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=proctoring
http://www.tonybates.ca/2015/02/21/10-key-takeaways-about-differences-between-classroom-blended-online-and-open-learning/
Tony Bates shares his thoughts on the difference
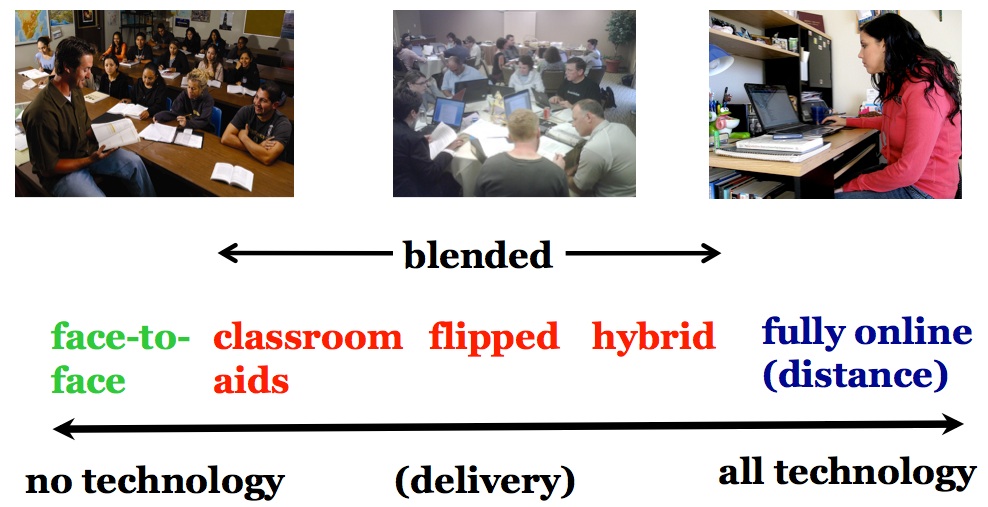
Chapter 10 of Tony Bates online open textbook, Teaching in a Digital Age:
More on F2F, blended/hybrid and online learning in this blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=blended