Tag: research
female birds had unique songs
Few people knew female birds had unique songs—until women started studying them
A rise in studies on female bird behavior shows how gender equity can spark change in research
Library Instruction STEM 199
Library Instruction delivered by Plamen Miltenoff, pmiltenoff@stcloudstate.eduDr. Chris Kvaal, |
Short link to this tutorial: http://bit.ly/scsustem199 |
My name is Plamen Miltenoff (https://web.stcloudstate.edu/pmiltenoff/faculty/) and I am the InforMedia Specialist with the SCSU Library (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/free-tech-instruction/).
+++++++++++++++++++++++
LIBRARY INSTRUCTION – Information, Digital and Media Literacy
- How (where from) do you receive your news? Do you think you are able to distinguish real news from fake news?
- Last year, researchers at Oxford University found that 70 countries had political disinformation campaigns over two years.
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2020/01/20/bots-and-disinformation/ - according to Pew Research Center, 68 percent of American adults get their news from social media—platforms where opinion is often presented as fact.
results of the international test revealed that only 14 percent of U.S. students were able to reliably distinguish between fact and opinion.
- Last year, researchers at Oxford University found that 70 countries had political disinformation campaigns over two years.
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2020/01/16/fake-news-prevention/
News and Media Literacy (and the lack of) is not very different from Information Literacy
An “information literate” student is able to “locate, evaluate, and effectively use information from diverse sources.” See more About Information Literacy.
How does information literacy help me?
Every day we have questions that need answers. Where do we go? Whom can we trust? How can we find information to help ourselves? How can we help our family and friends? How can we learn about the world and be a better citizen? How can we make our voice heard?
| The content of the tutorial is based on the Information Literacy Competency Standards for Higher Education as approved by the Board of Directors of the Association of College and Research Libraries (ACRL). |  |
The standards are:
Standard 1. The information literate student determines the nature and extent of the
information needed
Standard 2. The information literate student accesses needed information effectively
and efficiently
Standard 3. The information literate student evaluates information and its sources
critically and incorporates selected information into his or her knowledge
base and value system
Standard 4. The information literate student, individually or as a member of a group,
uses information effectively to accomplish a specific purpose
Standard 5. The information literate student understands many of the economic, legal,
and social issues surrounding the use of information and accesses and uses
information ethically and legally
Project Information Literacy
A national, longitudinal research study based in the University of Washington’s iSchool, compiling data on college students habits to seek and use information.
+++++++++++++++++++++++
- Developing Your Research Topic/Question
Research always starts with a question. But the success of your research also depends on how you formulate that question. If your topic is too broad or too narrow, you may have trouble finding information when you search. When developing your question/topic, consider the following:
- Is my question one that is likely to have been researched and for which data have been published? Believe it or not, not every topic has been researched and/or published in the literature.
- Be flexible. Consider broadening or narrowing the topic if you are getting a limited number or an overwhelming number of results when you search. In nursing it can be helpful to narrow by thinking about a specific population (gender, age, disease or condition, etc.), intervention, or outcome.
- Discuss your topic with your professor and be willing to alter your topic according to the guidance you receive.
- Getting Ready for Research
Library Resources vs. the Internet
How (where from) do you receive information about your professional interests?
Advantages/disadvantages of using Web Resources
Evaluating Web Resources
- Google or similar; Yahoo, Bing
- Google Scholar
- Reddit, Digg, Quora
- Wikipedia
- Become a member of professional organizations and use their online information
- Use the SCSU library page to online databases
- Building Your List of Keywords

-
- Why Keyword Searching?
Why not just type in a phrase or sentence like you do in Google or Yahoo!?- Because most electronic databases store and retrieve information differently than Internet search engines.
- A databases searches fields within a collection of records. These fields include the information commonly found in a citation plus an abstract (if available) and subject headings. Search engines search web content which is typically the full text of sources.
- Why Keyword Searching?
-
- The bottom line: you get better results in a database by using effective keyword search strategies.
- To develop an effective search strategy, you need to:
- determine the key concepts in your topic and
- develop a good list of keyword synonyms.
-
- Why use synonyms?
Because there is more than one way to express a concept or idea. You don’t know if the article you’re looking for uses the same expression for a key concept that you are using. - Consider: Will an author use:
- Hypertension or High Blood Pressure?
- Teach or Instruct?
- Therapy or Treatment?
- Why use synonyms?
Don’t get “keyword lock!” Be willing to try a different term as a keyword. If you are having trouble thinking of synonyms, check a thesaurus, dictionary, or reference book for ideas.
Keyword worksheet
- Library Resources
How to find the SCSU Library Website
SCSU online databases
-
- SCSU Library Web page
- Basic Research Skills
Locating and Defining a Database
Database Searching Overview:
You can search using the SCSU library online dbases by choosing:
Simple search
Advanced search
- Identifying a Scholarly Source
- Boolean operators
- Databases:
CINAHL, MEDLINE, PubMed, Health Source: Consumer Edition, Health Source: Nursing/Academic Edition
Psychology:
PsychINFO
General Science
ScienceDirect
Arts & Humanities Citation Index
- How do you evaluate a source of information to determine if it is appropriate for academic/scholarly use. There is no set “checklist” to complete but below are some criteria to consider when you are evaluating a source.
- ACCURACY
- Does the author cite reliable sources?
- How does the information compare with that in other works on the topic?
- Can you determine if the information has gone through peer-review?
- Are there factual, spelling, typographical, or grammatical errors?
- AUDIENCE
- Who do you think the authors are trying to reach?
- Is the language, vocabulary, style and tone appropriate for intended audience?
- What are the audience demographics? (age, educational level, etc.)
- Are the authors targeting a particular group or segment of society?
- AUTHORITY
- Who wrote the information found in the article or on the site?
- What are the author’s credentials/qualifications for this particular topic?
- Is the author affiliated with a particular organization or institution?
- What does that affiliation suggest about the author?
- ACCURACY
-
- CURRENCY
-
-
- Is the content current?
- Does the date of the information directly affect the accuracy or usefulness of the information?
-
-
- OBJECTIVITY/BIAS
-
-
- What is the author’s or website’s point of view?
- Is the point of view subtle or explicit?
- Is the information presented as fact or opinion?
- If opinion, is the opinion supported by credible data or informed argument?
- Is the information one-sided?
- Are alternate views represented?
- Does the point of view affect how you view the information?
-
-
- PURPOSE
- What is the author’s purpose or objective, to explain, provide new information or news, entertain, persuade or sell?
- Does the purpose affect how you view the information presented?
- PURPOSE
- InterLibrary Loan
- Copyright and Fair Use
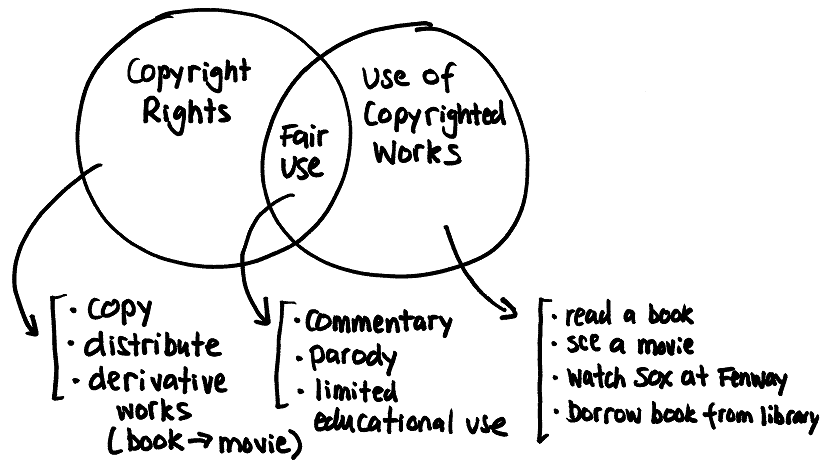
(https://sites.google.com/site/cuin3313/resources/copyright-fair-use-what-is-it-why-should-i-care)
Author Rights and Publishing & Finding Author Instructions for Publishing in Scholarly Journals
-
- Plagiarism, academic honesty
- Writing Tips
- Dissemination of Research
+++++++++++
Plamen Miltenoff, Ph.D., MLIS
Professor
320-308-3072
pmiltenoff@stcloudstate.edu
http://web.stcloudstate.edu/pmiltenoff/faculty/
schedule a meeting: https://doodle.com/digitalliteracy
find my office: https://youtu.be/QAng6b_FJqs
ISTeSSH2020
International Conference on ICT enhanced Social Sciences and Humanities 2020
- a three-day virtual conference,
- free to attend,
- the attractive topic and nice program with 17 papers presentations and a panel discussion,
- 2 workshops and 1 training,
- an ICT quiz with 500 euros prize award for the winner,
Dates of the conference: June 29th – July 1st, 2020

 Jeff Clovins, Clavirate Analytics
Jeff Clovins, Clavirate Analytics
Wednesday, June 1
Challenges to Social Sciences and Humanities
Best practices: Two Web-browser-based methods for stimuluspresentation in behavioral experiments with high-resolution timingrequirementsPablo Garaizar1&Ulf-Dietrich
(PDF) Best practices: Two Web-browser-based methods for stimulus presentation in behavioral experiments with high-resolution timing requirements. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328012311_Best_practices_Two_Web-browser-based_methods_for_stimulus_presentation_in_behavioral_experiments_with_high-resolution_timing_requirements [accessed Jul 01 2020].
SCSU EDAD Scopus vs Academia vs ResearchGate
https://youtu.be/4_gGIuZhMnw
media literacy guide
The Global Critical Media Literacy Educators’ Resource Guide
http://gcml.org/the-global-critical-media-literacy-educators-resource-guide/
- Introduction
- About the GCMLP
- Contacts for GCMLP Publication
- Methods of Media Manipulation
- Breaking the Corporate News Frame: Project Censored’s Networked News Commons
- Validated Independent News Story Assignment
- How to Find, Evaluate, and Summarize Validated Independent News Stories
- Validated Independent News Story Grading Rubric
- Validated Independent News Story Grading Criteria
- Student Guide For Evaluating Web Sources
- ‘Becoming the Media:’ Experiential Learning through Media Criticism and Political Activism During National Presidential Elections
- ACME Classroom Activities: Challenging Big Media and News Censorship
- Digging Deeper: Politico-Corporate Media Manipulation, Critical Thinking, and Democracy
- Service Learning: The SUNY Buffalo State and Project Censored Partnership
- Commodifying the Public Sphere Through Advertising and Commercial Media
- Group Advertisement Assignment
- Junk Food News Assignment
- News Abuse Assignment
- Meme Assignment
- Solutions Video Project
- Video Summary Assignment
- Ethics Alerts: Applied Learning Opportunity in Higher Education
- Ethics Alert Assignment
- Critical Analysis of Gender Stereotypes on Television Assignment
- Critical Analysis of Race, Ethnicity, and Class Stereotypes in Entertainment
- 18 Fun and Easy Classroom Activities for Media Education
- Five Ways to Flex Your Media Literacy Muscles
- List of Independent and Corporate News and News Criticism Outlets
- GCMLP Biographies and Participating Institutions
- GCMLP Event on Your Campus Instructions
- Sacred Heart University Graduate Program
- Media Education for a Digital Generation Book Flyer
Regular Pages: https://www.dropbox.com/s/jp5isqrn6ijv9lx/ACMEbookFINAL101215.pdf?dl=0
Spreads: https://www.dropbox.com/s/enya4iyyxahg8ik/ACMEbookFINAL101215SPREADS.pdf?dl=0
+++++++++++++
more on media literacy in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=media+literacy
qualitative method research
Qualitative Method Research
quote
Data treatment and analysis
Because the questionnaire data comprised both Likert scales and open questions, they were analyzed quantitatively and qualitatively. Textual data (open responses) were qualitatively analyzed by coding: each segment (e.g. a group of words) was assigned to a semantic reference category, as systematically and rigorously as possible. For example, “Using an iPad in class really motivates me to learn” was assigned to the category “positive impact on motivation.” The qualitative analysis was performed using an adapted version of the approaches developed by L’Écuyer (1990) and Huberman and Miles (1991, 1994). Thus, we adopted a content analysis approach using QDAMiner software, which is widely used in qualitative research (see Fielding, 2012; Karsenti, Komis, Depover, & Collin, 2011). For the quantitative analysis, we used SPSS 22.0 software to conduct descriptive and inferential statistics. We also conducted inferential statistics to further explore the iPad’s role in teaching and learning, along with its motivational effect. The results will be presented in a subsequent report (Fievez, & Karsenti, 2013)
Fievez, A., & Karsenti, T. (2013). The iPad in Education: uses, benefits and challenges. A survey of 6057 students and 302 teachers in Quebec, Canada (p. 51). Canada Research Chair in Technologies in Education. Retrieved from https://www.academia.edu/5366978/The_iPad_in_Education_uses_benefits_and_challenges._A_survey_of_6057_students_and_302_teachers_in_Quebec_Canada
unquote
The reason was the advent of computing power in the second half of the 20th century, which allowed exact sciences to claim “scientific” and “data-based” results.
One of the statistical package, SPSS, is today widely known and considered a magnificent tools to bring solid statistically-based argumentation, which further perpetuates the superiority of quantitative over qualitative method.
Florian Kohlbacher
http://www.qualitative-research.net/index.php/fqs/article/view/75/153
excellent guide to the structure of a qualitative research
Abbyy Fine Reader, https://www.abbyy.com/en-us/finereader/
OmniPage, http://www.nuance.com/for-individuals/by-product/omnipage/index.htm
Readirus http://www.irislink.com/EN-US/c1462/Readiris-16-for-Windows—OCR-Software.aspx
The text from the articles is processed either through NVIVO or related programs (see bottom of this blog entry). As the authors propose: ” This is immediately useful for literature review and proposal writing, and continues through the research design, data gathering, and analysis stages— where NVivo’s flexibility for many different sources of data (including audio, video, graphic, and text) are well known—of writing for publication” (p. 353).
– RQDA (the small one): http://rqda.r-forge.r-project.org/ (see on youtube the tutorials of Metin Caliskan); one active developper.
– GATE (the large one): http://gate.ac.uk/ | https://gate.ac.uk/download/
text mining: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Text_mining
Text mining, also referred to as text data mining, roughly equivalent to text analytics, is the process of deriving high-quality information from text. High-quality information is typically derived through the devising of patterns and trends through means such as statistical pattern learning. Text mining usually involves the process of structuring the input text (usually parsing, along with the addition of some derived linguistic features and the removal of others, and subsequent insertion into a database), deriving patterns within the structured data, and finally evaluation and interpretation of the output.
https://ischool.syr.edu/infospace/2013/04/23/what-is-text-mining/
Qualitative data is descriptive data that cannot be measured in numbers and often includes qualities of appearance like color, texture, and textual description. Quantitative data is numerical, structured data that can be measured. However, there is often slippage between qualitative and quantitative categories. For example, a photograph might traditionally be considered “qualitative data” but when you break it down to the level of pixels, which can be measured.
word of caution, text mining doesn’t generate new facts and is not an end, in and of itself. The process is most useful when the data it generates can be further analyzed by a domain expert, who can bring additional knowledge for a more complete picture. Still, text mining creates new relationships and hypotheses for experts to explore further.
quick and easy:
intermediate:
advanced:
http://tidytextmining.com/
Introduction to GATE Developer https://youtu.be/o5uhMF15vsA
use of RapidMiner:
https://rapidminer.com/pricing/
– ATLAS.TI
– QDA Miner: http://provalisresearch.com/products/qualitative-data-analysis-software/
There is also a free version called QDA Miner Lite with limited functionalities: http://provalisresearch.com/products/qualitative-data-analysis-software/freeware/
– MAXQDA
– NVivo
– SPSS Text Analytics
– Kwalitan
– Transana (include video transcribing capability)
– XSight
– Nud*ist https://www.qsrinternational.com/
(Cited from: https://www.researchgate.net/post/Are_there_any_open-source_alternatives_to_Nvivo [accessed Apr 1, 2017].
– IBM Watson Conversation
– IBM Watson Text to Speech
– Google Translate API
– MeTA
– LingPipe
– NLP4J
– Timbl
– Colibri Core
– CRF++
– Frog
– Ucto
– CRFsuite
Sociological Research Online, vol. 3, no. 3, <http://www.socresonline.org.uk/3/3/4.html>
Pros and Cons of Computer Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software
more on quantitative research:
literature on quantitative research:
| St. Cloud State University MC Main Collection – 2nd floor | AZ195 .B66 2015 |
academic search engines
Educational Technology and Mobile Learning educatorstechnology.com · Dec 23, 2016
https://www.pinterest.com/pin/71072500350222752/
10 Great Academic Search Engines for Research Students
https://scholar.google.com/ | https://eric.ed.gov/ | http://www.virtuallrc.com/ | http://www.citeulike.org/ | http://jurn.org/ | http://academic.research.microsoft.com/ | https://www.loc.gov/ | https://www.refseek.com/ | http://www.sciencedirect.com/ | https://www.academia.edu/ | https://www.researchgate.net/
+++++++++++++++++
more about research in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=research
limitations and delimitations in research
Shortly:
Limitations are influences that the researcher cannot control. They are the shortcomings, conditions or influences that cannot be controlled by the researcher that place restrictions on your methodology and conclusions. Any limitations that might influence the results should be mentioned.
Delimitations are choices made by the researcher which should be mentioned. They describe the boundaries that you have set for the study.
Assumptions are accepted as true, or at least plausible, by researchers and peers who will read your dissertation or thesis.
More:
https://www.bcps.org/offices/lis/researchcourse/develop_writing_methodology_limitations.html
http://dissertationrecipes.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/04/AssumptionslimitationsdelimitationsX.pdf
Dissertation Guidelines
http://www.regent.edu/acad/schedu/pdfs/residency/su09/dissertation_guidelines.pdf
++++++++++++++
more on dissertation research in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=dissertation+research
research how to
also: http://bit.ly/edad829
Are Q&A startups a threat to Google?

++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
– The Internet
– Google Scholar https://scholar.google.com/
- web sites (Web 1.0)
– blogs, listservs etc (Web 2.0)
– social media
– YouTube https://www.youtube.com/ and similar
– e.g. SCSU streaming : http://www.stcloudstate.edu/library/research/video.aspx
– Q&A plaforms such as Quora https://www.quora.com/, AskScience https://www.reddit.com/r/askscience/, Medium, PeerPong and similar
– Reddit https://www.reddit.com/, Digg http://digg.com/ , StackExchange http://stackexchange.com/ , Mahalo Company, Kngine.com and similar
– Google Search, Yahoo Answers and similar
– Wikipedia
– Facebook groups, LinkedIn groups and similar
– SlideShare https://www.slideshare.net/ and similar
++++++++++++++
more on the research process in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=search
























