Chun, L. (2017). Discipline and power: knowledge of China in political science. Critical Asian Studies, 49(4), 501-522. doi:10.1080/14672715.2017.1362321
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3daph%26AN%3d125811392%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
Lin Chun or ResearchGate: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Chun_Lin18
p. 501 – is political science “softer” than the other soft social sciences?
thus… political science “may never live up to its lofty ambition of scientific explanation and prediction. Indeed, like other social sciences, it can be no more than a ‘ science in formation’ permanently seeking to surmount obstacles to objectivity.”
p. 502 disciplinary parochialism
the fetishes of pure observation, raw experience, unambiguous rationality, and one-way causality were formative influences in the genesis of the social sciences. the ‘unfortunate positivism” of such impulses, along with the illusion of a value-free science, converged to produce a behavioral revolution in the interwar period Behaviorism was then followed through an epistemological twist, by boldly optimistic leaps to an “end of ideology” and ultimately to a claimed “end of history” itself.
p. 503
early positivism was openly underpinned by an European condescension toward Asians’ “ignorance and prejudice.” Behind similar depictions lay a comprehensive Eurocentric social and political philosophy.
this is illustrated its view of China through the grand narrative of modernization.
p. 504
Robert McNamara famously reiterated that if World War I was a chemist’s war and Word War II a physicist’s, Vietnam “might well have to be considered the social scientists’ war.”
Although China nominally remains a communist state, it has doubtlessly changed color without a color revolution.
p. 505
In the fixed disciplinary eye, “China” is to specific to produce anything generalizable beyond descriptive and self-containing narratives. The area studies approach, in contrast to disciplinary approaches, is all about cultural, historical, and ethnographic specificities.
If first-hand information contradicts theoretical conclusions, redress is sought only at the former end (my note – ha ha ha, such an elegant but scathing criticism of [Western] academia).
The catch [is] that Chinese otherness is in essence not a matter of cultural difference (hence limitations of criticizing Eurocentrism and Orientalism) and does not merely reproduce itself by inertia.
Given a long omitted self-critical rethinking of the discipline’s parochial base, calling for cross-fertilizing alone would be fruitless or even lead only to a one-way colonization of seemingly particularistic histories by an illusive universal science.
p. 506
political culture, once a key concept of political science’s hope for unified theorization, has turned out to be no answer
Long after its heyday, modernization theory – now with its new face of globalization – remains a primary signifier and legitimating benchmark. To those, who use it to gauge developments since 1945, private property and liberal democracy are permanent, unquestioned norms that are to be globally homogenized.
Moreover, since modernity is assumed to be a liberal capitalists condition, the revolutionary nationalism of an oppressed people remaking itself into a new historical subject noncompliant with capitalism cannot be modernizational.
p. 507
Political scientists and historical sociologists… saw the communist in power as formidable modernizers, but distinguished the Maoist model from the Stalinist in economic management and campaign politics.
Their analyses showed how organic connections between top-down mobilization and bottom-up participation cultivated in an active citizenry and high intensity politics. My note: I disagree here with the author, since such statement can be arbitrary from a historical point of view; indeed, for a short period of time, such “organic connection” can produce positive results, but once calcitrated (as it is in China for the past 6-7 decades), it turns stagnant.
p. 510
the state’s altered support base is essentially a matter of class power, involving both adaptive cultivation of new economic elites and iron-fist approaches to protest and dissent. By the same weight of historical logic, the party’s internal decay, loss of its founding ideological vision and commitment, and collusion with capital will do more than any outside force ever could do to destroy the regime.
That the Party stays in power is not primarily because the country’s economy continues to grow, but is more attributable to a residual social reliance on its credentials and organizational capacities accumulated in earlier revolutionary and socialist struggles. This historical promise has so far worked to the extent that cracks within the leadership are more or less held in check, resentment against local wrongs are insulated from central intentions, and social policies in one way or another respond to common outcries, consultative deliberations, and pressure groups.
p. 511
The word “madness” has indeed been freely employed to describe nations and societies judged inept at modern reason, as found in contemporary academic publications on epi- sodes of the PRC history.
My note: I agree with this – the deconstructionalists: (Jaques Derrida, Tzvetan Todorov) linguistically prove the inability of Western cultures to understand and explain other cultures. In this case, Lin Chun is right; just because western political scientist cannot comprehend foreign complex societal problems and/or juxtaposing them to their own “schemes,” prompts the same western researchers to announce them as “mad.”
p. 513aa
This is the best and worst of times for the globalization of knowledge. In one scenario, an eventual completion of the political science parameters can now seal both knowledge, sophisticatedly canalized, and ideology, universally uncontested – even if the two are never separable in the foundation of political science. In another scenario, causes and effects no longer rule out atypical polities, but the differences are presented as culturally incompatible. In either case, the trick remains to let anormalies make the norms validate preexist- ing disciplinary sanctions.
p. 514
Overcoming outmoded rigidities will nurture a robust scholarship committed to universally resonant theories.
+++++++++++++
more on China in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=china
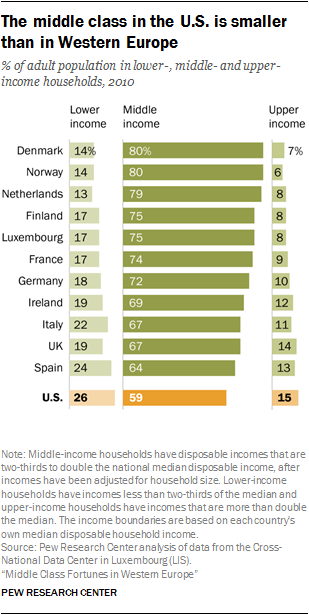
Middle Class Fortunes in Western Europe
From 1991 to 2010, the middle class expands in France, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, but, as in the United States, shrinks in Germany, Italy and Spain
BY RAKESH KOCHHAR
http://www.pewglobal.org/2017/04/24/middle-class-fortunes-in-western-europe/
The role of the middle class in developed economies
The size and the well-being of the middle class are intertwined with some of the key economic challenges facing the developed world this century – income inequality is rising in many countries, economic growth is anemic, and economic mobility is lesser than in the past.
A smaller middle class or a relatively less well-off middle class often reflects a more unequal income distribution. In turn, increases in income inequality present an adverse climate for economic growth. A relative decline in the incomes of lower- and middle-income families may create a drag on overall consumption in the economy, lead to excessive borrowing by these families, or provide disincentives to invest in education.
A more vibrant middle class may also improve the economic outlook for future generations. In the U.S., for example, communities with larger middle classes offer a greater likelihood that children will experience upward mobility relative to their parents’ status in the income distribution. A similar relationship has also been found to exist across countries, whereby intergenerational mobility is greater in countries with less income inequality.
Many countries in Western Europe have significantly larger middle classes than the U.S.
The U.S. has larger lower- and upper-income tiers than the selected countries from Western Europe
Income inequality is related to the size of the middle class in a country
Zygmunt Bauman: “Social media are a trap.”The Polish-born sociologist is skeptical about the possibilities for political change
Since developing his theory of liquid modernity in the late 1990s – which describes our age as one in which “all agreements are temporary, fleeting, and valid only until further notice” – he has become a leading figure in the field of sociology.
Q. You are skeptical of the way people protest through social media, of so-called “armchair activism,” and say that the internet is dumbing us down with cheap entertainment. So would you say that the social networks are the new opium of the people?
A. The question of identity has changed from being something you are born with to a task: you have to create your own community. But communities aren’t created, and you either have one or you don’t. What the social networks can create is a substitute. The difference between a community and a network is that you belong to a community, but a network belongs to you. You feel in control. You can add friends if you wish, you can delete them if you wish. You are in control of the important people to whom you relate. People feel a little better as a result, because loneliness, abandonment, is the great fear in our individualist age. But it’s so easy to add or remove friends on the internet that people fail to learn the real social skills, which you need when you go to the street, when you go to your workplace, where you find lots of people who you need to enter into sensible interaction with. Pope Francis, who is a great man, gave his first interview after being elected to Eugenio Scalfari, an Italian journalist who is also a self-proclaimed atheist. It was a sign: real dialogue isn’t about talking to people who believe the same things as you. Social media don’t teach us to dialogue because it is so easy to avoid controversy… But most people use social media not to unite, not to open their horizons wider, but on the contrary, to cut themselves a comfort zone where the only sounds they hear are the echoes of their own voice, where the only things they see are the reflections of their own face. Social media are very useful, they provide pleasure, but they are a trap.
http://socioint15.org
SOCIO-INT15- 2nd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON EDUCATION SOCIAL SCIENCES AND HUMANITIES will be held in Istanbul (Turkey), on the 8th, 9th and 10th of June 2015 is an interdisciplinary international conference that invites academics, independent scholars and researchers from around the world to meet and exchange the latest ideas and discuss issues concerning all fields of Education, Social Sciences and Humanities.
Socioint15_Accepted_Abstracts1
SOCIO-INT15 provides the ideal opportunity to bring together professors, researchers and high education students of different disciplines, discuss new issues, and discover the most recent developments, new trends and researches in education, social sciences and humanities.
Academics making efforts in education, subfields of which might include higher education, early childhood education, adult education, special education, e-learning, language education, etc. are highly welcomed. People without papers can also participate in this conference as audience so long as they find it interesting and meaningful.
Due to the nature of the conference with its focus on innovative ideas and developments, papers also related to all areas of social sciences including communication, accounting, finance, economics, management, business, marketing, education, sociology, psychology, political science, law and other areas of social sciences; also all areas of humanities including anthropology, archaelogy, architecture, art, ethics, folklore studies, history, language studies, literature, methodological studies, music, philosophy, poetry and theater are invited for the international conference.
Submitted papers will be subject to peer review and evaluated based on originality and clarity of exposition.
Gamification: It’s Easier than You Think!
https://desire2learn.adobeconnect.com/_a707373752/p3mhvdh5gfb/
BONUS: several cool infographics on gamification of education: http://elearninginfographics.com/tag/gamification-infographic/
this is a recording of a webinar, which took place yesterday, September 3, 2014. The presenter is Canadian. Sean Isles
https://www.google.com/?gws_rd=ssl#q=ontario+sociology+gamification+sean
Gamification versus game based education
Gamification is application of typical elements of game play to unconventional areas
Game based is learning that takes place withing a game simulated environment itself
D2L offers options for gamified education
Leveling / Gating: turn off/on content modules by weekly increments.
Bosses/Challenges – simple quiz at the end of each module (training quizzes, open to take unlimited times)
Celebration of successes – emails from intelligent agents, short funny video, etc.
Intelligent agent send an email not only to student, but to an office, where top scoring students can get a gift.
Game-based
simulator. used Unity to create the game
Shaun Iles: shaun.iles@mohawkcollege.ca and Brian Gould: brian.gould@mohawkcollege.ca
Leaderboard – Brightspace.com – Brightspace by D2L. needs to be purchased, but allows modify and customize with HTML and CSS
Badges: meaningless if the entire institution is not on board. google and mozilla badges platforms. D2L is about to roll out badges, only if the entire institution and the business recognize them. otherwise, the badges are dead upon exit from class.
make discussion interactive through upvote: http://www.reddit.com/r/upvote/
Scavenger hunt mentioned. Bluetooth info beacons used across campus to enable scavenger hunt. Across mobile devices.
Librarians and instructional designers mentioned.
His D2L home page has twitter widget and skype widget. He says the Skype widget enormously used. When will my proposal for Adobe Connect Widget will be addressed, am asking I for years?
