May
2022
Blockchain and money
++++++++++++
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=blockchain
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
++++++++++++
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=blockchain
Web 3.0 is the third generation of internet services which provide websites and applications with the technology to run. Web 3.0 is set to be powered by AI and peer-to-peer applications like blockchain. The key difference between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 is that Web 3.0 is more focused on using innovative technologies like machine learning and AI to create more personalized content for each user. It is also expected that Web 3.0 will be more secure than its predecessors because of the system it is built upon.
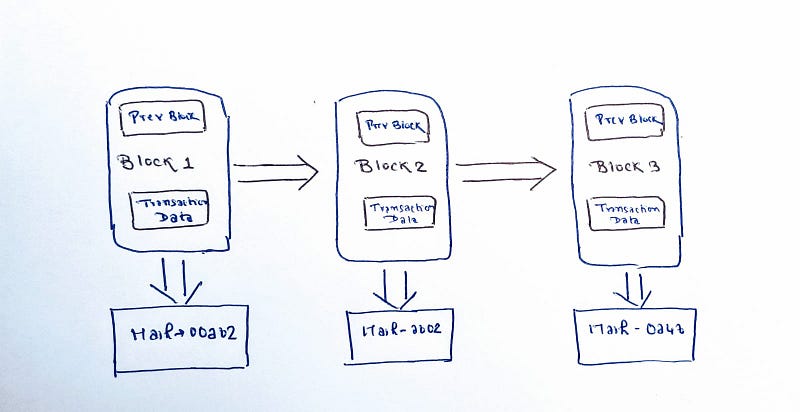
Blockchains are made up of blocks that store information. Each block has a unique “hash” that differentiates it from other blocks. These blocks are then connected by a chain in chronological order. The information stored in these blocks is permanent, which makes it a very secure way to complete online transactions.
This is why cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, are built on blockchain technology.
+++++++++++++++++
more on blockchain in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=blockchain
“Using #augmentedreality (#AR) and #blockchain technologies, the game featured ‘Vatoms’, virtual objects that players can interact with.
Due to pandemic restrictions, the game, originally developed as an outdoor activity in other markets, was adapted to allow people to hunt for the packs in and around their own homes. Packs contained either Playstation symbol chips or an instant-win prize, which would then be stored in a digital wallet.”
Imagine, if it was not Doritos, but bones to build a skeletal system (Biology, nursing, medicine, etc.), philosophers (Philosophy, political science, social sciences) and the rewards or badges in the leaderboard. #gaming and #gamification
Read more at: https://www.campaignasia.com/article/why-11-million-filipinos-went-hunting-for-virtual-doritos/470820
LinkedIn’s 2020 list of skills in most demand includes these soft skills at the very top:
And these hard skills at the very top:
Further steps have been taken independently by universities that are utilizing blockchain technology to disseminate transcripts containing rich detail and documentation not available in the traditional paper document.
+++++++++++++++
more on blockchain in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=blockchain
more on microcredentialing in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=microcredential
Build your own X, a collection of tutorials to build your own 3D renderer, Blockchain, Bot, Game, Neural Network, Search Engine, Text Editor, and much more! (27 things to build!) from r/programming
https://github.com/danistefanovic/build-your-own-x
+++++++++++++++
more on chatbots in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=chatbot
the service can be used for a variety of functions at schools and colleges, including verifying credentials, tracking donations and payments, or handling other student records.
a K-6 educational app called SpoonRead
Blockchain is a decentralized system where every record is linked and transparent, and any alterations leave a trail that supposedly can’t be hidden.
Some have questioned whether there is a need for blockchain in student records, considering that other kinds of encryption techniques already exist to protect and verify things like credentials.
+++++++++
more on blockchain in education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=blockchain+education
+++++++++++
more on blockchain for education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=blockchain+education
The fastest way to learn how Blockchains work is to build one
https://hackernoon.com/learn-blockchains-by-building-one-117428612f46
Remember that a blockchain is an immutable, sequential chain of records called Blocks. They can contain transactions, files or any data you like, really. But the important thing is that they’re chained together using hashes.
If you aren’t sure what a hash is, here’s an explanation.
reading and writing some basic Python, as well as have some understanding of how HTTP requests work, since we’ll be talking to our Blockchain over HTTP.
+++++++++++
more on blockchain in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=blockchain
https://medium.com/fintech-kellogg/quantum-computing-is-it-the-end-of-the-blockchain-10fa7e222b0a
Ajitesh Abhishek Jan 12, 2019
In simple words, a blockchain is a ledger that records transactions of a certain type. It uses mathematical functions such as integer factorization, which is easy to solve in one direction but hard in the other direction for security.
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon in which the quantum states of two or more objects have to be described with reference to each other, even though the individual objects may be spatially separated.
One of the potential solutions is Quantum Blockchain, which uses quantum cryptography. This has been proposed by Del Rajan and Matt Visser of Victoria University of Wellington in New Zealand. The idea is simple — if computers can compute fast, make the puzzle more complex.
+++++++++++
more on quantum computing in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=quantum+computing
and blockchain
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=blockchain
An interesting discussion on the use of blockchain for academic libraries on the LITA listserv
in response to a request from the Library Association in Pakistan for an hour long session on “block chain and its applications for Academic Libraries”.
While Nathan Schwartz, MSIS Systems & Reference Librarian find blockchain only related to cryptocurrencies, Jason Griffey offers a MOOC focused on Blockchain for the Information Professions: https://ischoolblogs.sjsu.edu/blockchains/
According to Jason, “Blockchain, as a data storage technology, can be separated from the idea of cryptocurrencies and expressions of value and coin.”
++++++++++
more on blockchain in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=blockchain