2020 best laptops to compare
the 2020 choice for best laptops to compare:
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
the 2020 choice for best laptops to compare:
Anya Kamenetz and Chloee Weiner Jun 30
https://www.kqed.org/mindshift/53910/at-your-wits-end-with-a-screen-obsessed-kid-read-this
The relationship between teens, screens and mental health is complex and multidirectional
Abby’s mom has sent her articles about research linking teen depression and suicide to screen use. A 2017 article in The Atlantic magazine — “Have Smartphones Destroyed a Generation?” — drew a link between negative trends in teens’ mental health and the rise of smartphones and social media.
The negative relationship between teens’ mental health and technology use is real — but tiny, the researchers found. “A teenager’s technology use can only predict less than 1% of variation in well-being. It’s so small that it’s surpassed by whether a teenager wears glasses to school.”
How to strike a balance? To start, try mentoring, not monitoring
Heitner’s work emphasizes a concept that’s also put forth by the American Academy of Pediatrics in its guidelines for parents: media mentoring.
Look for the good in your kids’ media interests
For Benji, Minecraft is a social space where he plays with other kids and pulls pranks. He says he wishes his parents understood more about his screen use — “why it’s entertaining and why we want to do it. And also, for YouTube, why I watch other people playing games. When you watch sports, you’re watching another person playing a game! Why is it so different when you’re watching a person play a video game?”
Work together as a family to make changes.
+++++++++++++
more on contemplative computing in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=contemplative+computing
#arvrinedu Denise, from SC, an AR app that translate sign language into spoken English https://t.co/ejeF8wjE2D
— Denise Wright (@DenisecWright) May 2, 2019
Authors: Published: Columns:
Device ownership alone doesn’t make people digitally literate; rather, digital literacy is about how and why they use devices to achieve particular goals and outcomes.
According to the 2018 EDUCAUSE Center for Analysis and Research (ECAR) Study of Undergraduate Students and Information Technology, 95% of undergraduate students own a smartphone and 91% own a laptop. This near-ubiquitous ownership of these devices might suggest that digital literacy is mainstream, but just because students own digital devices does not mean that they’ve developed digital literacy.
Definitions of digital literacy can include the ability to use and access digital devices, but studies from the past decade tend to deepen this definition. A commonly cited definition from Colin Lankshear and Michele Knobel asserts that digital literacy is “shorthand for the myriad social practices and conceptions of engaging in meaning making mediated by texts that are produced, received, distributed, exchanged etc., via digital codification.”
More recently, scholars including Jennifer Sparrow have suggested even adopting the term digital fluency instead of literacy in order to capture how students may need the “ability to leverage technology to create new knowledge, new challenges, and new problems and to complement these with critical thinking, complex problem solving, and social intelligence to solve the new challenges.”
two-thirds of faculty think that students are prepared to use software applications, but students themselves express discomfort with applying these tools for learning.
instructional designers are key players who could take a more visible role in higher education to support educators in bringing explicit instruction on digital literacy engagement into their classes. University staff in instructional design and educational/faculty development spaces consult with instructors, lead workshops, and develop support documentation on a regular basis. People in these roles could be more empowered to have conversations with the instructors they support around building in particular lessons
Douglas Belshaw can be a source of inspiration for understanding how his essential elements of digital literacy may contribute to the development of students’ digital fluencies. In particular, some practices may include:
June 7, 9:15 am – 10:45 am, Plamen Miltenoff, St. Cloud State University, MN, USA
++++++++++++++++++++
+++++++++++++++++++
+++++++++++++++++++++
Visuals from the slides available also here:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/04/13/instruments-methods-formative-assessment/
By Kelsey Ehnle 12/26/2018 BYOD Mobile learning Tools
Videos can express any type of learning in any style, from music videos to interviews, book trailers, historical re-enactments, tutorials and stop animations.
Flipgrid is the one of the best educational video-creation sites
Find synonyms in many languages at Open Thesaurus!
Linguee.
PONS or LEO. Question about a verb conjugation? Go to LEO or Canoo (for German)
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=kahoot
++++++++++++++++
Gartner predicts that nearly 38 percent of companies will stop providing devices to workers by 2017 — but 20 percent of those BYOD programs will fail because of overly restrictive mobile device management measures. So how can IT pros devise a BYOD strategy that stays afloat? Here are six guidelines to accommodate legitimate IT concerns without sinking a policy’s odds of success:
Before creating a BYOD policy, take a look at existing HR and legal procedures. Many email, VPN, and remote access security policies can be applied to mobile devices, as well.
Employees are using personal devices at work, whether the company realizes it or not. But that doesn’t mean they are using them correctly. Employees often use file-sharing and other tools of their choosing without IT’s knowledge, which could put sensitive corporate data at risk. Use a BYOD policy to trainemployees how to correctly use their applications
BYOD isn’t limited to smartphones. According to Gartner, a “new norm” is emerging in which employees manage up to four or five devices at work.
passwords aren’t foolprool. Data encryption is an additional security measure
A smart BYOD policy doesn’t mean IT is off the hook. Rather, successful policies rely on IT and employees sharing security obligations.
Employees often fail to realize that all data on their devices is discoverable, regardless of whether the device is personal or company-owned. The question of who owns what is still a legal gray area, though companies increasingly take the liberty to remote wipe employees’ personal devices once they leave their job. Avoid the guessing game with a clear exit strategy.
+++++++++++++++
more on BYOD in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=byod
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=mobile+learning
https://www.npr.org/2018/05/05/608164530/the-fortnite-craze-might-be-here-to-stay
In April, a PLAYlive Nation lounge in Tracy, Calif., hosted its first Fortnite tournament and sold out. Hundreds of players bought tickets to play against one another and win prizes.
Joost van Dreunen, the CEO of Superdata Research, a video game analytics firm, says most shooter games are serious and simulate violence. Fortnite, he says, is more like a friendly game of tag.
His company estimates the game has made about $223 million across all platforms in March alone. In lifetime sales, it had made about $614 million. The game is free to play, but Epic Games, the company that owns Fortnite, makes money through microtransactions. Players can spend real money to make cosmetic changes to their characters in the game. They can buy things like skins, which are like costumes, for their characters or emotes, which are celebratory dance moves their characters can do after winning or killing another player in the game.
Ninja, the gamer name taken by 26-year-old Tyler Blevins, is now a legend in the Fortnite world. He is a master at the game and rocketed into popularity after playing in an online battle with rap artists Drake and Travis Scott on March 14. That battle has been watched more than 9 million times.
++++++++++++++++++++
https://www.edweek.org/ew/articles/2018/05/03/educators-battle-fortnite-for-students-attention.html
Many educators want to ban the game from their classrooms, but some are taking the opposite approach, attempting to weave students’ interest in Fortnite into class discussions and assignments.
Nick Fisher, a science teacher at Fort Zumwalt North High School in O’Fallon, Mo., said his students like to take screenshots of gameplay and send them to friends over Snapchat. Teenagers want to broadcast their victories, and because the game is on their phones, it’s easy to post updates to social media, making Fortnite “the perfect concoction of addiction,” said Fisher.
North High blocks all social media and gaming sites on its WiFi, said Fisher, but students tell him how they circumvent the restriction: They use virtual private networks, or VPNs, to establish independent internet connections. (Dozens of YouTube videos provide step-by-step tutorials for students looking to get around school WiFi controls.)
“Kids can’t multitask,” she said. “Even having a digital device within sight can cognitively distract the student enough that they can’t focus on the academics.”
Schools and teachers should be guiding parents when it comes to appropriate limits around screen time, said Kolb. Most parents will appreciate research-based recommendations, such as turning off all screens a set amount of time before bed, she said.
Games like Fortnite can even have social benefits, said John Velez, an assistant professor of journalism and electronic media at Texas Tech University. Velez, who studies the positive effects of video games, has found that playing violent games cooperatively with helpful teammates promotes pro-social behavior.
Chris Aviles, the coordinator of innovation, technology, and 21st century skills for the Fair Haven Public Schools in New Jersey, wrote “A Teacher’s Guide to Surviving Fortnite,” an exploration of ways the game can be used for instructional purposes. The guide, posted to his blog Teched Up Teacher, suggests how to integrate the game into writing prompts, math lessons on probability, and physics.
Aviles doesn’t advocate playing the game at school. There isn’t any educational value in letting students engage in virtual combat during a lesson, he said. Instead, teachers can build a lesson around one aspect of the game, such as having students calculate the best angle of approach as they jump from the “Battle Bus,” the floating bus that drops players onto the map at the beginning of each match.
++++++++++++++++++
+++++++++++++++++++
more on gaming in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=gaming
+++++++++++++++
more on social media addiction in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/05/08/social-media-addiction/
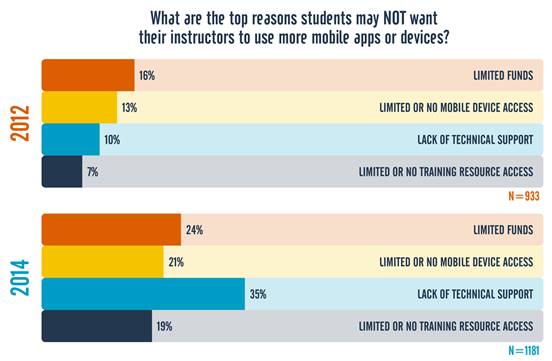
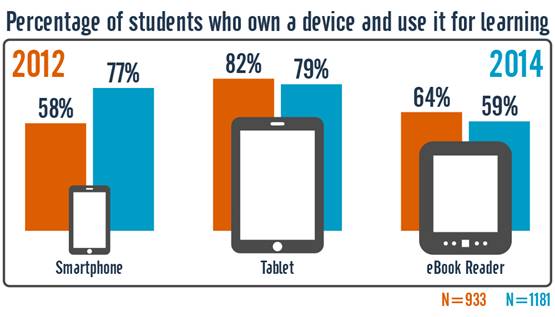
++++++++++++++
more about mobile use in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=mobile+use