We define immersive scholarship as any scholarly work developed through or implemented utilizing technologies including Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Mixed Reality, Visualization (i.e., large format displays and visualization walls, GIS, Tableau), and any related hardware, programs or software.
We are seeking survey participants who are employed in an academic library and who currently support immersive scholarship and technologies at their institution.
how your academic library has developed tools, implemented third party hardware/software, and in what barriers you have identified at your institution in supporting immersive scholarship.
Link to Online Survey
third Library 2.019 mini-conference: “Emerging Technology,” which will be held online (and for free) on Wednesday, October 30th, from 12:00 – 3:00 pm US-Pacific Daylight Time (click for your own time zone).
Tomorrow’s technologies are shaping our world today, revolutionizing the way we live and learn. Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Blockchain, Internet of Things, Drones, Personalization, the Quantified Self. Libraries can and should be the epicenter of exploring, building and promoting these emerging techs, assuring the better futures and opportunities they offer are accessible to everyone. Learn what libraries are doing right now with these cutting-edge technologies, what they’re planning next and how you can implement these ideas in your own organization.
This is a free event, being held live online and also recorded.
REGISTER HERE
Library Leadership Your Way
https://www.alastore.ala.org/content/library-leadership-your-way
core issues
- discovering why you want to lead;
- research findings on the five most desirable traits in library leaders;
- wrestling with the constraints of organizational culture;
- a tour of practical leadership models such as Theory Z, Situational Leadership, Transformational Leadership, and emotional intelligence;
- how to develop habits that will bolster your confidence through inevitable moments of doubt;
- cultivating a “people first, mission always” mentality;
- self-care for leaders; and
- living out your unique leadership vision through goal setting, self-evaluation, and other key steps.
Survey of Academic Library Leadership: Evaluation of Library Info Technology Lending Programs (ISBN No:978-1-57440-591-0 )
https://www.primaryresearch.com/AddCart.aspx?ReportID=566
survey of 116 directors, deans and other high level officials of academic libraries about how they feel about their library’s info technology lending programs.
data on the level of satisfaction with such programs, plans for library budget support
for these programs, and plans for new acquisitions of tablets, virtual reality
technology, laptops, digital cameras and other types of information
technology. In addition to looking at plans for the future, the report gives
detailed data on the level and nature of budgetary support for technology
lending programs over the past few years. Survey participants also comment on
which library constituencies use the programs the most.
- Administrators over age 65 were much more likely than others to want to contract the program while those under age 50 were much less likely.
- In general, the more sophisticated the degree offered by the college, the greater the likelihood that it had increased spending on its technology lending program over the past three years.
- Art and architecture students were frequently cited as prime users of academic library technology lending programs.
Bedi, S., & Walde, C. (2017). Transforming Roles: Canadian Academic Librarians Embedded in Faculty Research Projects.
College & Research Libraries,
78(3), undefined-undefined.
https://doi.org/10.5860/crl.78.3.314
As collections become increasingly patron-driven, and libraries share evolving service models, traditional duties such as cataloguing, reference, and collection development are not necessarily core duties of all academic librarians.1
Unlike our American colleagues, many Canadian academic librarians are not required to do research for tenure and promotion; however, there is an expectation among many that they do research, not only for professional development, but to contribute to the profession.
using qualitative inquiry methods to capture the experiences and learning of Canadian academic librarians embedded in collaborative research projects with faculty members.
The term or label “embedded librarian” has been around for some time now and is often used to define librarians who work “outside” the traditional walls of the library. Shumaker,14 who dates the use of the term to the 1970s, defines embedded librarianship as “a distinctive innovation that moves the librarians out of libraries [and] emphasizes the importance of forming a strong working relationship between the librarian and a group or team of people who need the librarian’s information expertise.”15
This model of embedded librarianship has been active on campuses and is most prevalent within professional disciplines like medicine and law. In these models, the embedded librarian facilitates student learning, extending the traditional librarian role of information-literacy instruction to becoming an active participant in the planning, development, and delivery of course-specific or discipline-specific curriculum. The key feature of embedded librarianship is the collaboration that exists between the librarian and the faculty member(s).17
However, with the emergence of the librarian as researcher… More often than not, librarians have had more of a role in the literature-search process with faculty research projects as well as advising on appropriate places for publication.
guiding research question became “In what ways have Canadian academic librarians become embedded in faculty research projects, and how have their roles been transformed by their experience as researchers?”
Rubin and Rubin20 support this claim, noting that qualitative inquiry is a way to learn about the thoughts and feelings of others. Creswell confirms this, stating:
Qualitative research is best suited to address a research problem in which you do not know the variable and need to explore. The literature might yield little information about the phenomenon of study, and you need to learn more from participants through exploration. [Thus] a central phenomenon is the key concept, idea, or process studied in qualitative research.21
eight participants
As Janke and Rush point out, librarians are no longer peripheral in academic research but are now full members of investigative teams.30 But, as our research findings have highlighted, they are making this transition as a result of prior relationships with faculty brought about through traditional liaison work involving collection development, acquisitions, and information-literacy instruction. As our data demonstrates, the extent to which our participants were engaged within all aspects of the research process supports our starting belief that librarians have a vital and important contribution to make in redefining the role of the librarian in higher education.
++++++++++++++++++
Carlson, J., & Kneale, R. (2017). Embedded librarianship in the research context: Navigating new waters.
College & Research Libraries News,
72(3), 167–170.
https://doi.org/10.5860/crln.72.3.8530
Embedded librarianship takes a librarian out of the context of the traditional
library and places him or her in an “on-site” setting or situation that enables close coordination and collaboration with researchers or teaching faculty
+++++++++++++++++++
Summey, T. P., & Kane, C. A. (2017). Going Where They Are: Intentionally Embedding Librarians in Courses and Measuring the Impact on Student Learning. Journal of Library and Information Services in Distance Learning, 11(1–2), 158–174.
Wu, L., & Thornton, J. (2017). Experience, Challenges, and Opportunities of Being Fully Embedded in a User Group. Medical Reference Services Quarterly, 36(2), 138–149.
+++++++++++++++
more on embedded librarian in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=embedded
The Role of Librarians in Supporting ICT Literacy
Lesley Farmer May 9, 2019,
https://er.educause.edu/blogs/2019/5/the-role-of-librarians-in-supporting-ict-literacy
Academic librarians increasingly provide guidance to faculty and students for the integration of digital information into the learning experience.
TPACK: Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge
Many librarians have shied away from ICT literacy, concerned that they may be asked how to format a digital document or show students how to create a formula in a spreadsheet. These technical skills focus more on a specific tool than on the underlying nature of information.
librarians have begun to use an embedded model as a way to deepen their connection with instructors and offer more systematic collection development and instruction. That is, librarians focus more on their partnerships with course instructors than on a separate library entity.
If TPACK is applied to instruction within a course, theoretically several people could be contributing this knowledge to the course. A good exercise is for librarians to map their knowledge onto TPACK.
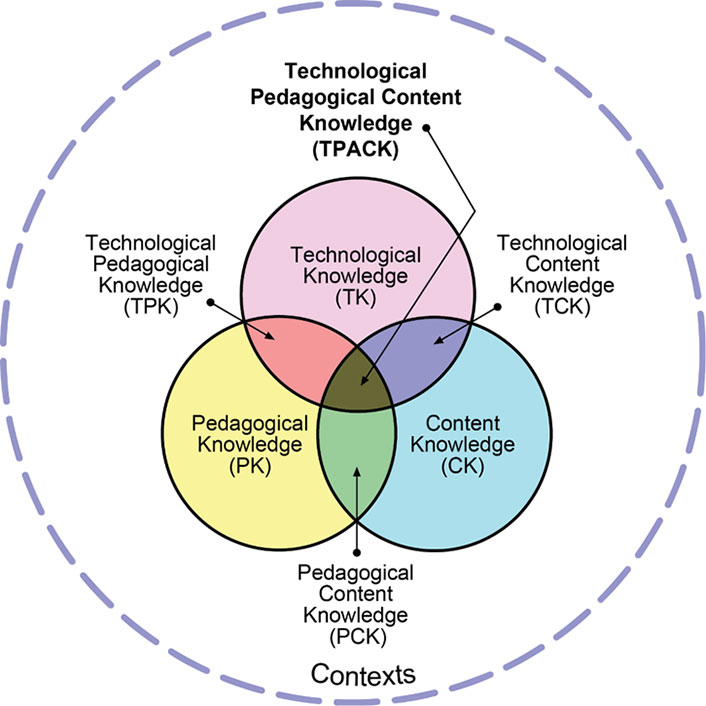
ICT reflects the learner side of a course. However, ICT literacy can be difficult to integrate because it does not constitute a core element of any academic domain. Whereas many academic disciplines deal with key resources in their field, such as vocabulary, critical thinking, and research methodologies, they tend not to address issues of information seeking or collaboration strategies, let alone technological tools for organizing and managing information.
Instructional design for online education provides an optimal opportunity for librarians to fully collaborate with instructors.
The outcomes can include identifying the level of ICT literacy needed to achieve those learning outcomes, a task that typically requires collaboration between the librarian and the program’s faculty member. Librarians can also help faculty identify appropriate resources that students need to build their knowledge and skills. As education administrators encourage faculty to use open educational resources (OERs) to save students money, librarians can facilitate locating and evaluating relevant resources. These OERs not only include digital textbooks but also learning objects such as simulations, case studies, tutorials, and videos.
Reading online text differs from reading print both physically and cognitively. For example, students scroll down rather than turn online pages. And online text often includes hyperlinks, which can lead to deeper coverage—as well as distraction or loss of continuity of thought. Also, most online text does not allow for marginalia that can help students reflect on the content. Teachers and students often do not realize that these differences can impact learning and retention. To address this issue, librarians can suggest resources to include in the course that provide guidance on reading online.
My note – why specialist like Tom Hergert and the entire IMS is crucial for the SCSU library and librarians and how neglecting the IMS role hurts the SCSU library –
Similarly, other types of media need to be evaluated, comprehended, and interpreted in light of their critical features or “grammar.” For example, camera angles can suggest a person’s status (as in looking up to someone), music can set the metaphorical tone of a movie, and color choices can be associated with specific genres (e.g., pastels for romances or children’s literature, dark hues for thrillers). Librarians can explain these media literacy concepts to students (and even faculty) or at least suggest including resources that describe these features
My note – on years-long repetition of the disconnect between SCSU ATT, SCSU library and IMS –
instructors need to make sure that students have the technical skills to produce these products. Although librarians might understand how media impacts the representation of knowledge, they aren’t necessarily technology specialists. However, instructors and librarians can collaborate with technology specialists to provide that expertise. While librarians can locate online resources—general ones such as Lynda.com or tool-specific guidance—technology specialists can quickly identify digital resources that teach technical skills (my note: in this case IMS). My note: we do not have IDs, another years-long reminder to middle and upper management. Many instructors and librarians have not had formal courses on instructional design, so collaborations can provide an authentic means to gain competency in this process.
My note: Tom and I for years have tried to make aware SCSU about this combo –
Instructors likely have high content knowledge (CK) and satisfactory technological content knowledge (TCK) and technological knowledge (TK) for personal use. But even though newer instructors acquire pedagogical knowledge (PK), pedagogical content knowledge (PCK), and technological pedagogical knowledge (TPK) early in their careers, veteran instructors may not have received this training. The same limitations can apply to librarians, but technology has become more central in their professional lives. Librarians usually have strong one-to-one instruction skills (an aspect of PK), but until recently they were less likely to have instructional design knowledge. ICT literacy constitutes part of their CK, at least for newly minted professionals. Instructional designers are strong in TK, PK, and TPK, and the level of their CK (and TCK and TPK) will depend on their academic background. And technology specialists have the corner on TK and TCK (and hopefully TPK if they are working in educational settings), but they may not have deep knowledge about ICT literacy.
Therefore, an ideal team for ICT literacy integration consists of the instructor, the librarian, the instructional designer, and the technology specialist. Each member can contribute expertise and cross-train the teammates. Eventually, the instructor can carry the load of ICT literacy, with the benefit of specific just-in-time support from the librarian and instructional designer.
My note: I have been working for more then six years as embedded librarian in the doctoral cohort and had made aware the current library administrator (without any response) about my work, as well as providing lengthy bibliography (e.g. https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/08/24/embedded-librarian-qualifications/ and have had meeting with the current SOE administrator and the library administrator (without any response).
I also have delivered discussions to other institutions (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/04/12/embedded-librarian-and-gamification-in-libraries/)
Librarians should seriously consider TPACK as a way to embed themselves into the classroom to incorporate information and ICT literacy.
+++++++++++++
more about academic library in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=academic+library
more on SAMR and TRACK models in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/05/17/transform-education-digital-tools/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/07/29/mn-esummit-2015/
