Google book scanning project
What do we know about Google’s enormous book-scanning project? How far are we in the quest for a universal digital library? What does it mean for higher education?
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
What do we know about Google’s enormous book-scanning project? How far are we in the quest for a universal digital library? What does it mean for higher education?
https://www.insidehighered.com/digital-learning/blogs/online-trending-now/higher-ed-static-dynamic
Other than gross number analysis, many colleges previously did not take a deep dive into demographics of students every semester to detect and adapt to subtle changes in other than the broadest terms. This is especially the case for comparison to competitors that are not degree-granting, such as code academies, Google, Amazon, LinkedIn and others. Curriculum and degree/certificate offerings had not been reviewed every semester to determine how directly they serve the dual customer base of employers and students.
the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center show that the number of undergraduate students will likely drop 3.2 percent in the current academic year. All this after losing 3.4 percent last year. Over all, accounting for 6.6 percent fewer undergraduates than prior to the COVID pandemic, online institutions saw a similar dip of 5.5 percent. However, those online institutions are faring better, after seeing an increase of 8.6 percent enrollment in the fall 2020 semester. With the recent dip in enrollment, it is clear young adults increasingly are choosing work over college.
fewer than half of all high schoolers want to go to a four-year college
Not only are the numbers of male students enrolled on the decline, but the numbers of male dropouts exceed those of female students. (my note: this issue has been raised by me several times in the last decade, without any response whatsoever).
There is reason to believe that shorter, competency-based programs will play an important role in the university landscape in the coming years.
Australian commentator Stephen Matchett expands: “MCs are the wild west of post-compulsory education and training, with neither law on what they actually are or order as to how they interact with formal providers. … Until (or if) this is sorted by regulators there needs to be a sheriff providing workable rules that stop the cowboys running riot.”
The lack of standards is also an issue in Canada. While degree standards have been agreed upon – the Canadian Degree Qualification framework, contained in the Council of Ministers of Education, Canada (CMEC)’s 2007 Ministerial Statement on Quality Assurance of Degree Education in Canada, outlines expectations for bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees – the CMEC has yet to issue a pan-Canadian framework for microcredentials.
In the absence of a pan-Canadian model or definition, for the purposes of this column I will use the Higher Education Quality Council of Ontario (HEQCO)’s definition, put forward in its May 2021 report, Making Sense of Microcredentials:
“A microcredential is a representation of learning, awarded for completion of a short program that is focused on a discrete set of competencies (i.e., skills, knowledge, attributes), and is sometimes related to other credentials.”
Developing and running effective microcredential programs is not simply a matter of bundling a group of existing classes into a new sub-degree level program (although there will certainly be some who try that approach). Effective microcredential programming needs to be an institution-wide effort, with appropriate resourcing and guidelines, along with effective recruiting and student support.
department chairs and other unit leaders to lead collegial discussions about the following questions:
+++++++++++++++
more on microcredentials in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=microcredential
The report forecast China’s growth in ed tech spending to be 15.6 percent over the same period, reaching $34.2 billion by 2026. Japan, Canada and Germany are all expected to see double-digit growht in ed tech spending over the report period as well: Japan at 14.5 percent, Canada at 14 percent and Germany at 11.9 percent CAGR.
+++++++++++++++++++
More on educational technology in this blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=Educational+technology
Better questions to ask might be:
iPads have come a long way since our initial investment in interactive whiteboards.
+++++++++++++
more on SAMR in this blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=samr
a law student sued an automated proctoring company, students have complained about their use in student newspaper editorials and professors have compared them to Big Brother.
ProctorU, which has decided not to sell software that uses algorithms to detect cheating
A recent Educause study found that 63 percent of colleges and universities in the U.S. and Canada mention the use of remote proctoring on their websites.
One reason colleges are holding onto proctoring tools, Urdan adds, is that many colleges plan to expand their online course offerings even after campus activities return to normal. And the pandemic also saw rapid growth of another tech trend: students using websites to cheat on exams.
++++++++++++++++
More on proctoring in this blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=proctoring
https://www.govtech.com/network/infrastructure-bill-promises-historic-boost-for-digital-equity
The recently signed $1.2 trillion federal infrastructure package includes $2.75 billion for digital equity and inclusion work, delivering an investment that advocates are calling unprecedented and historic.
Within the $65 billion going toward broadband, the $2.75 billion for digital equity and inclusion is set for two programs made up of grants. First, the money will go toward a digital equity capacity grant program for states.
+++++++++++++++++++++
More on digital equity in this blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=digital+equity
https://www.d2l.com/events/regional/gamification-network


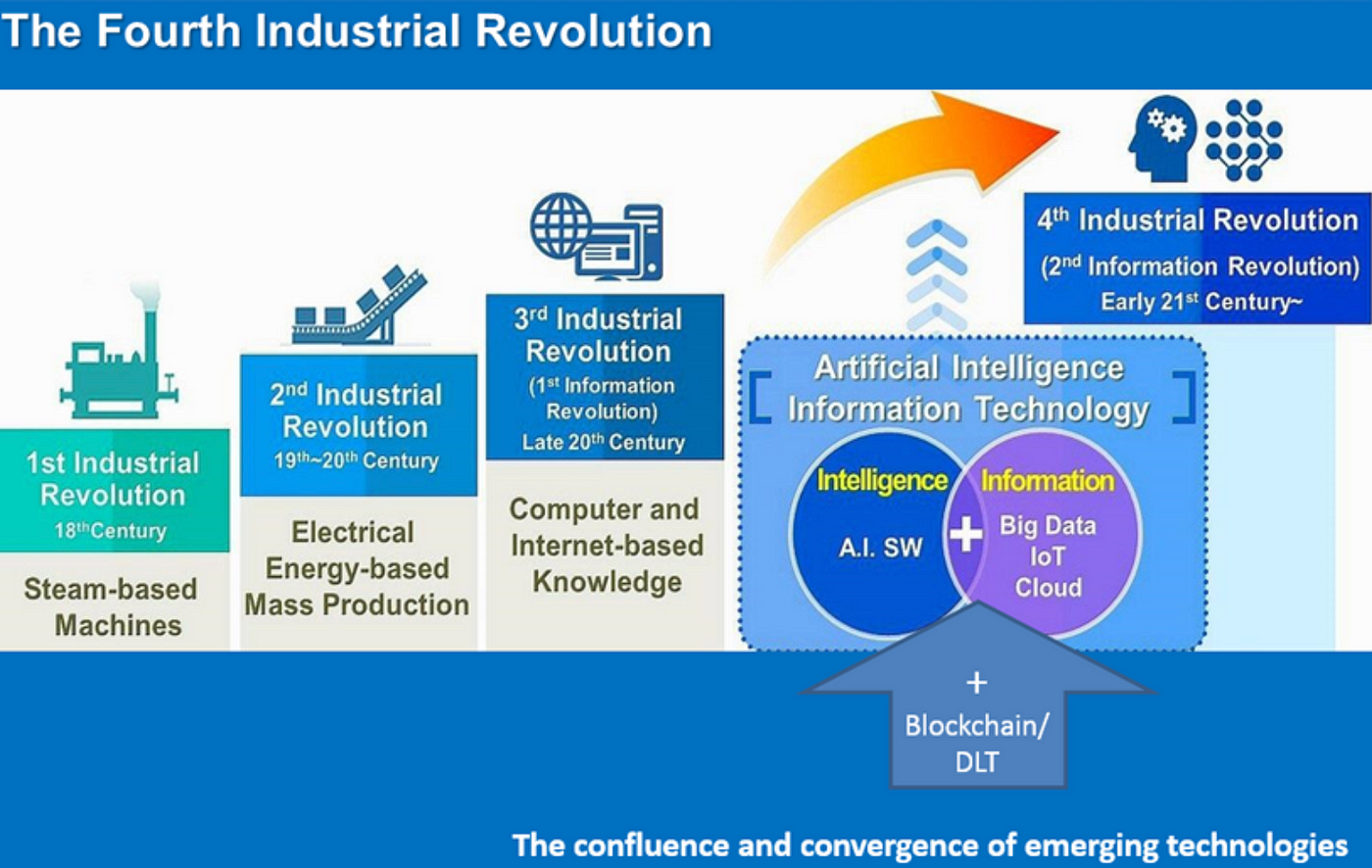
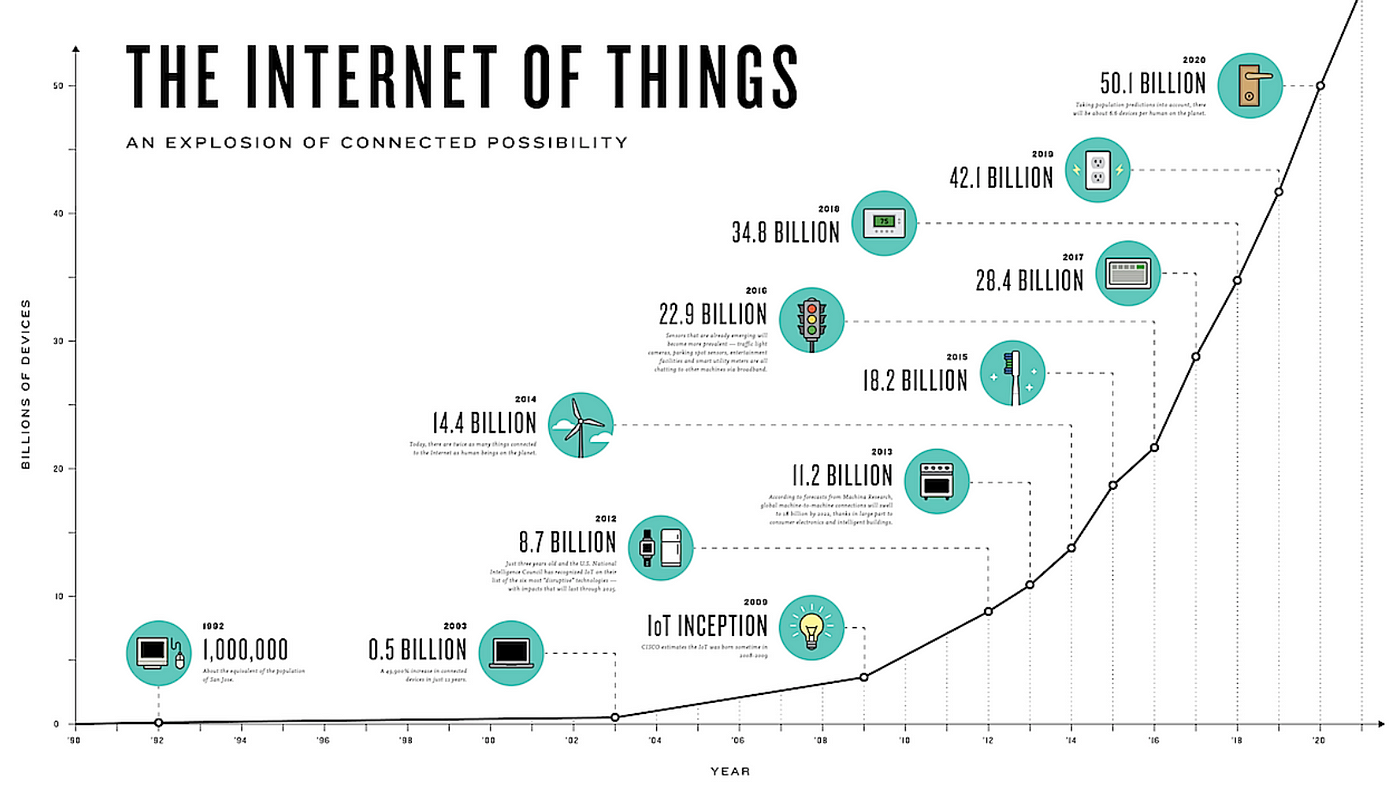
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
https://www.weforum.org/projects/learning-4-0
Based on the framework developed in Schools of the Future: Defining New Models of Education for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the Education 4.0 initiative aims to better prepare the next generation of talent through primary and secondary education transformation. The initiative will drive impact through four interconnected interventions:
+++++++++++++
more on education 3.0 and 2.0
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/03/16/education-2-0-vs-education-3-0/