https://www.theguardian.com/society/2020/nov/29/how-to-deal-with-a-conspiracy-theorist-5g-covid-plandemic-qanon
Fake authority
You may see articles by Vernon Coleman, for instance. As a former GP he would seem to have some credentials, yet he has a history of supporting pseudoscientific ideas, including misinformation about the causes of Aids. David Icke, meanwhile, has hosted videos by Barrie Trower, an alleged expert on 5G who is, in reality, a secondary school teacher. And Piers Corbyn cites reports by the Centre for Research on Globalisation, which sounds impressive but was founded by a 9/11 conspiracy theorist.
“pre-suasion” – essentially, removing the reflexive mental blocks that might make them reject your arguments.
+++++++++++++
more on conspiracy theories in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=conspiracy
more on fake news in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=fake+news
https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast/ted-radio-hour/id523121474?i=1000496568099
False information on the internet makes it harder and harder to know what’s true, and the consequences have been devastating. This hour, TED speakers explore ideas around technology and deception. Guests include law professor Danielle Citron, journalist Andrew Marantz, and computer scientist Joy Buolamwini.
+++++++++++++
more on deep fake in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=deepfake
Higher Ed Learning Collective
https://www.facebook.com/groups/onlinelearningcollective/permalink/711959409434760/
I am thinking about doing clicker-type questions as well as groupwork with instant response as the core of my online synchronous class. With this in mind, I am considering either Top Hat (which the students have used as clickers, but what I am not sure about is how well it works for groupwork) versus Learning Catalytics (which has a mode that I know works well and forces students to do the questions themselves first … which I have a love/hate relationship with – and has some question types that might be interesting but I am not as certain about the interface). I’d like to hear your thoughts.
Thanks!
FWIW: the class is general chemistry.
http://blogs.edweek.org/edweek/DigitalEducation/2020/11/student_data_future_criminals_pasco_privacy.html
Using Student Data to Identify Future Criminals: A Privacy Debacle
Under the federal Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), schools can share student records with a contractor or outside party to whom the school has outsourced certain functions, if that outside party (like a designated school resource officer) meets all three of these conditions:
- The outside party is performing a service that would otherwise be performed by school employees.
- The outside party’s use of education records is under the direct control of the school.
- The outside party does not use the education records for anything other than the reason they were originally shared, and does not share the education record with anyone else unless it secures written consent from the parent of the student.
Information Overload Helps Fake News Spread, and Social Media Knows It
Understanding how algorithm manipulators exploit our cognitive vulnerabilities empowers us to fight back
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/information-overload-helps-fake-news-spread-and-social-media-knows-it/
a minefield of cognitive biases.
People who behaved in accordance with them—for example, by staying away from the overgrown pond bank where someone said there was a viper—were more likely to survive than those who did not.
Compounding the problem is the proliferation of online information. Viewing and producing blogs, videos, tweets and other units of information called memes has become so cheap and easy that the information marketplace is inundated. My note: folksonomy in its worst.
At the University of Warwick in England and at Indiana University Bloomington’s Observatory on Social Media (OSoMe, pronounced “awesome”), our teams are using cognitive experiments, simulations, data mining and artificial intelligence to comprehend the cognitive vulnerabilities of social media users.
developing analytical and machine-learning aids to fight social media manipulation.
As Nobel Prize–winning economist and psychologist Herbert A. Simon noted, “What information consumes is rather obvious: it consumes the attention of its recipients.”
attention economy
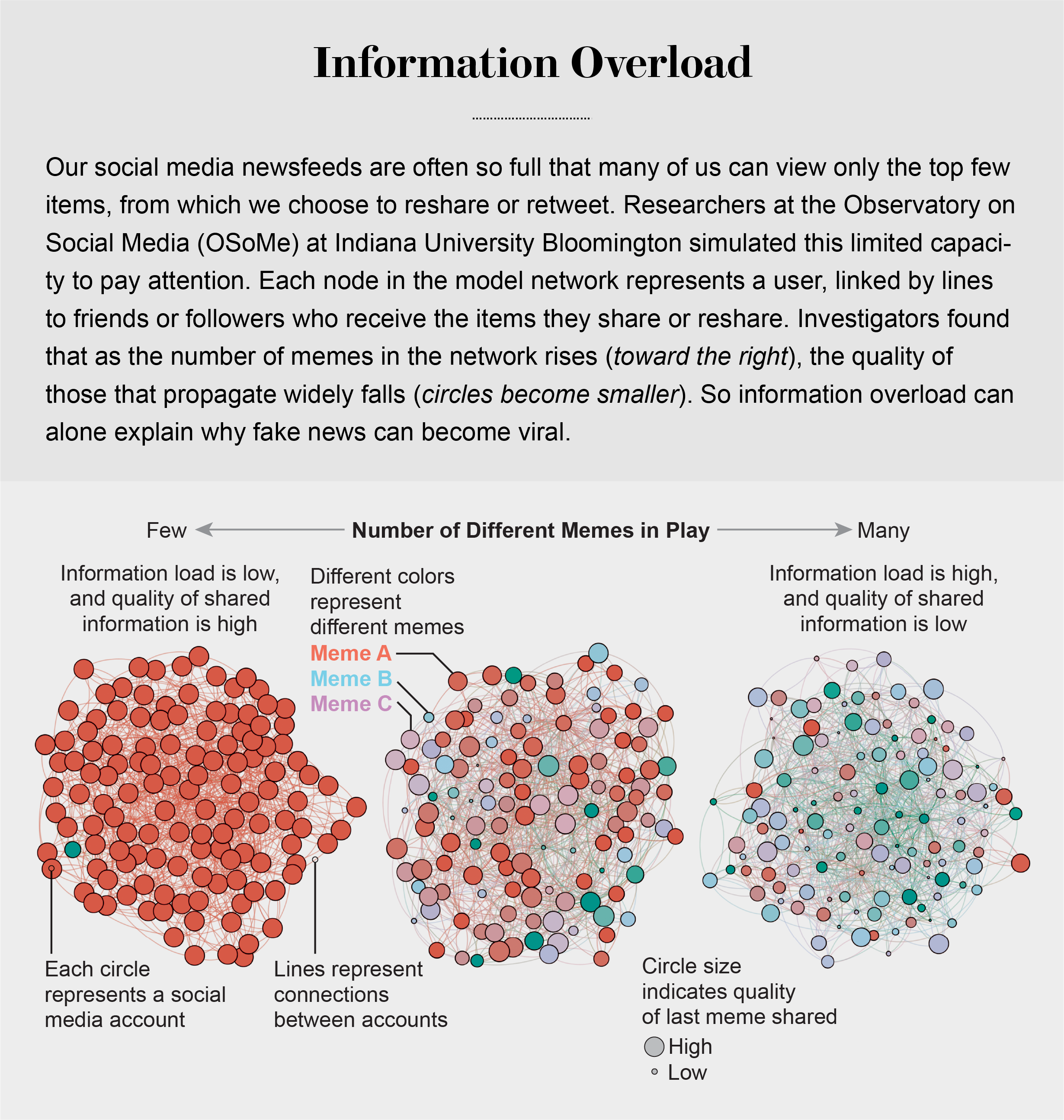
Our models revealed that even when we want to see and share high-quality information, our inability to view everything in our news feeds inevitably leads us to share things that are partly or completely untrue.
Frederic Bartlett
Cognitive biases greatly worsen the problem.
We now know that our minds do this all the time: they adjust our understanding of new information so that it fits in with what we already know. One consequence of this so-called confirmation bias is that people often seek out, recall and understand information that best confirms what they already believe.
This tendency is extremely difficult to correct.
Making matters worse, search engines and social media platforms provide personalized recommendations based on the vast amounts of data they have about users’ past preferences.
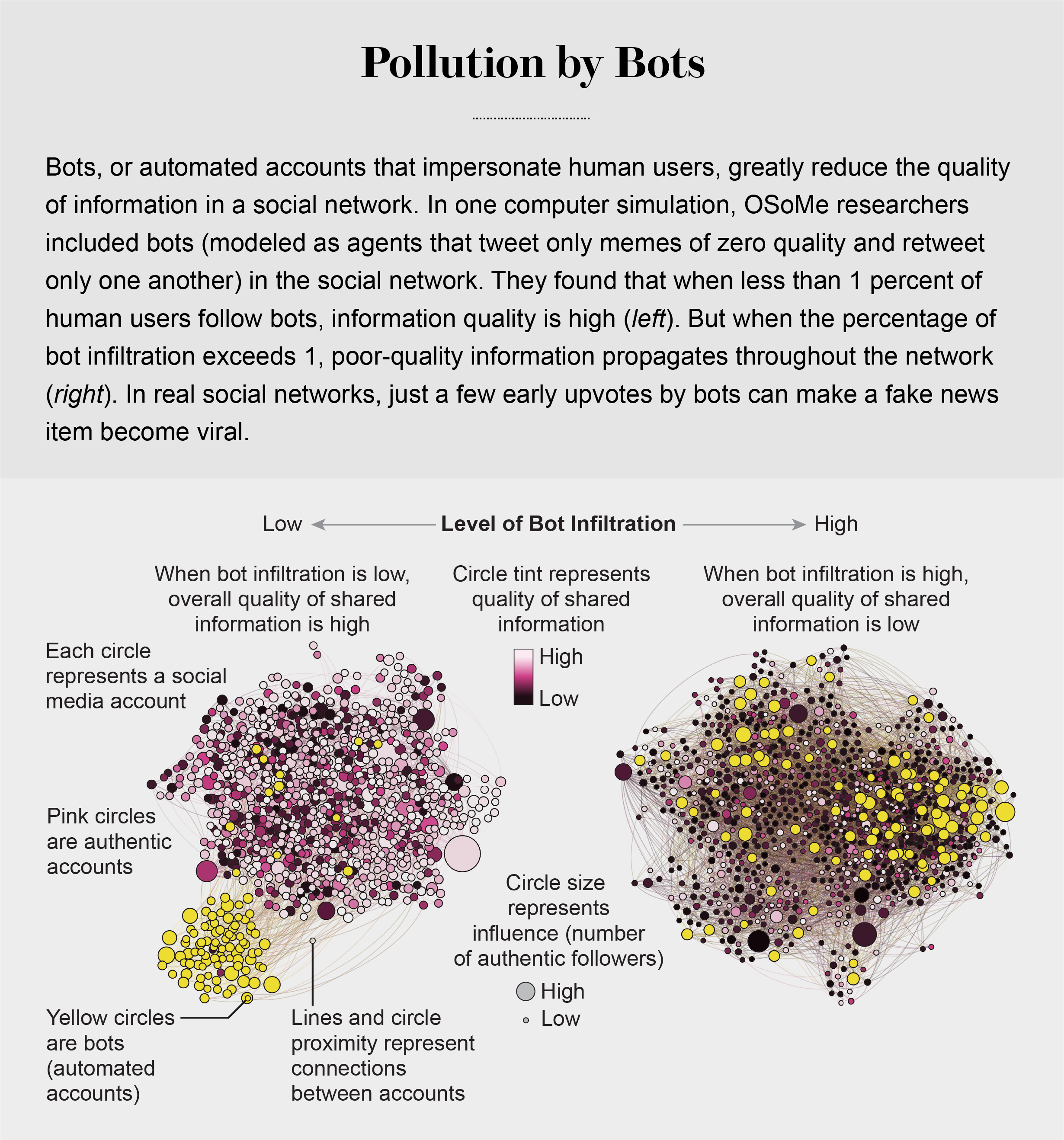
pollution by bots
Social Herding
social groups create a pressure toward conformity so powerful that it can overcome individual preferences, and by amplifying random early differences, it can cause segregated groups to diverge to extremes.
Social media follows a similar dynamic. We confuse popularity with quality and end up copying the behavior we observe.
information is transmitted via “complex contagion”: when we are repeatedly exposed to an idea, typically from many sources, we are more likely to adopt and reshare it.
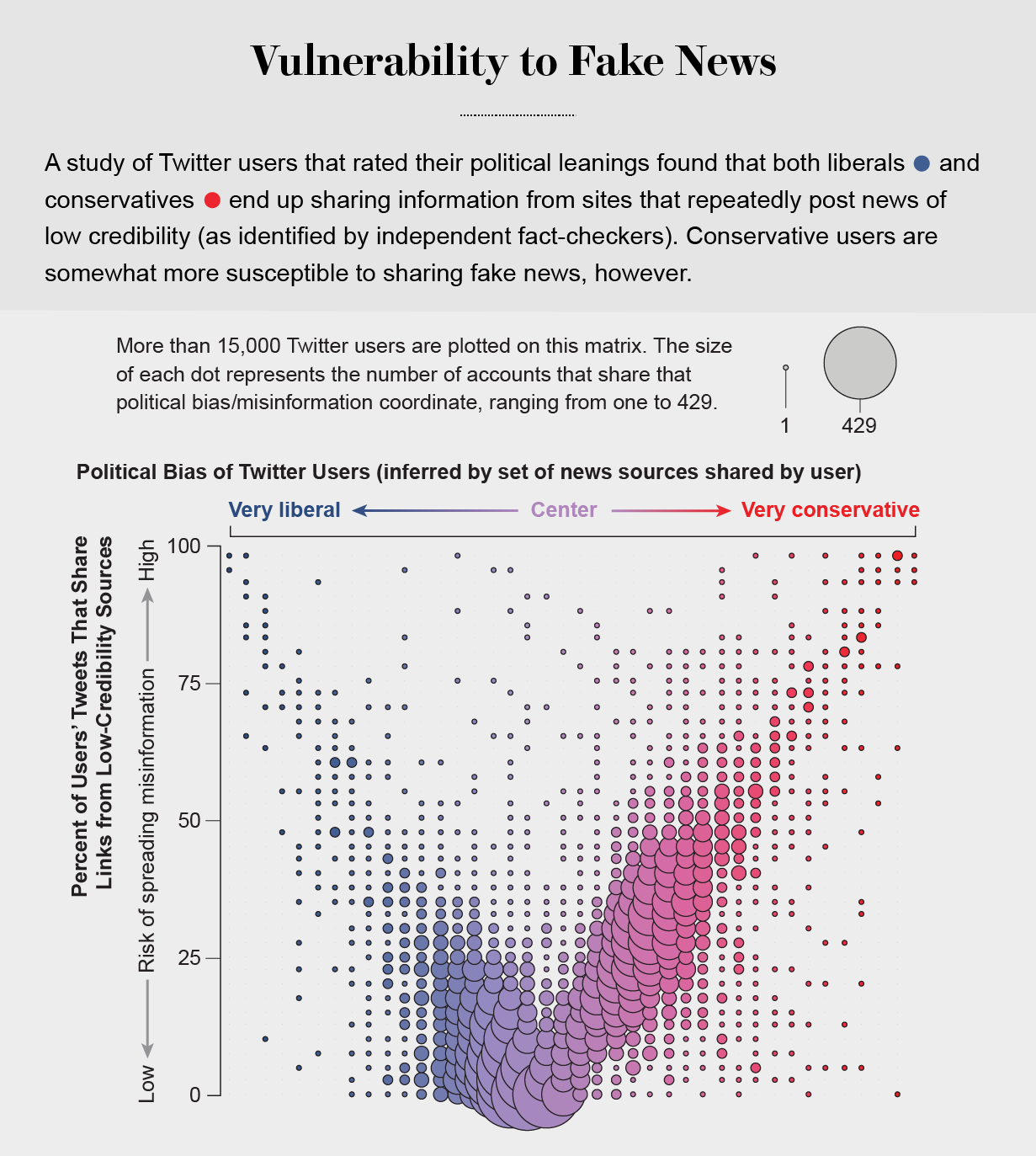
In addition to showing us items that conform with our views, social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and Instagram place popular content at the top of our screens and show us how many people have liked and shared something. Few of us realize that these cues do not provide independent assessments of quality.
programmers who design the algorithms for ranking memes on social media assume that the “wisdom of crowds” will quickly identify high-quality items; they use popularity as a proxy for quality. My note: again, ill-conceived folksonomy.
Echo Chambers
the political echo chambers on Twitter are so extreme that individual users’ political leanings can be predicted with high accuracy: you have the same opinions as the majority of your connections. This chambered structure efficiently spreads information within a community while insulating that community from other groups.
socially shared information not only bolsters our biases but also becomes more resilient to correction.
machine-learning algorithms to detect social bots. One of these, Botometer, is a public tool that extracts 1,200 features from a given Twitter account to characterize its profile, friends, social network structure, temporal activity patterns, language and other features. The program compares these characteristics with those of tens of thousands of previously identified bots to give the Twitter account a score for its likely use of automation.
Some manipulators play both sides of a divide through separate fake news sites and bots, driving political polarization or monetization by ads.
recently uncovered a network of inauthentic accounts on Twitter that were all coordinated by the same entity. Some pretended to be pro-Trump supporters of the Make America Great Again campaign, whereas others posed as Trump “resisters”; all asked for political donations.
a mobile app called Fakey that helps users learn how to spot misinformation. The game simulates a social media news feed, showing actual articles from low- and high-credibility sources. Users must decide what they can or should not share and what to fact-check. Analysis of data from Fakey confirms the prevalence of online social herding: users are more likely to share low-credibility articles when they believe that many other people have shared them.
Hoaxy, shows how any extant meme spreads through Twitter. In this visualization, nodes represent actual Twitter accounts, and links depict how retweets, quotes, mentions and replies propagate the meme from account to account.
Free communication is not free. By decreasing the cost of information, we have decreased its value and invited its adulteration.
https://cognitiontoday.com/pros-and-cons-of-online-education-and-learning/
- Access to variety
- More autonomy, flexibility, & control
- Native digital habits
- Extended brain
- Easier Relatability
- Easier self-expression
- Distribution of learning resources
- Competition for quality
Cons/Disadvantages of learning online
-
Gateway to procrastination
-
Online disinhibition & psychological distance
-
Merging of formal & informal environments
-
Opportunities for technological & human errors
-
High cost of transition
-
Weak boundaries & monotony
-
Lack of social connections & collaboration
-
Lack of buffer activities and time gaps
-
Cyberbullying & threats
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Generation_Alpha
https://bestlifeonline.com/generation-alpha-facts/
Baby Boomers, Gen X, Millennials, Gen Z: What Generation Am I?
+++++++++++++++
more on online ed in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=online+education
https://www.npr.org/2020/11/14/934833214/conservatives-flock-to-mercer-funded-parler-claim-censorship-on-facebook-and-twi
Parler, founded in 2018, touts itself as “the world’s premier free speech platform.” On Saturday, CEO and co-founder John Matze said one of the privately owned company’s early investors is Rebekah Mercer, who along with her father, hedge fund billionaire Robert Mercer, has been a backer of President Trump and is also a major donor to conservative causes, including Breitbart News and former White House strategist Steve Bannon.
It has hit 10 million members — more than double the 4.5 million it had last week, according to Jeffrey Wernick, the company’s chief operating officer.
Still, that is just a tiny fraction of Twitter’s 187 million daily users and Facebook’s nearly 2 billion.
Experts say “free speech” approach lets false claims flourish
Gab, an alternative social network that has become notorious for hosting anti-Semitic and white nationalist content. It was used by the accused 2018 shooter at a Pittsburgh synagogue.
+++++++++++
more on echo chambers in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=echo+chamber


