Message to SDSU students regarding RESPONDUS software. #1 We will not rely solely on faculty interpretation of video evidence from Respondus when evaluating claims of academic dishonesty. #2 – Beginning in Jan 2021, IT will not support the campuswide use of Respondus by faculty. pic.twitter.com/I2Ssim4LVW
— Dr. Luke Wood (@DrLukeWood) December 8, 2020
++++++++++++++
more on proctoring in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=proctorio
more on proctoring in the Higher Ed Learning Collective
https://www.facebook.com/groups/539260760037960/search/?q=proctor
U.S. Policy on China May Move from ‘America First’ to America & Co.
A tech entrepreneur in the State Department is using network theory to counter Chinese pressure.
According to Krach, the Clean Network includes 180 telecom companies and 50 national governments that represent two-thirds of the world’s gross domestic product. Although that’s impressive, all countries aren’t equally committed.
The task of forming networks to counter China’s influence has been made easier by China itself, which has frightened and angered trading partners with its “wolf warrior” diplomacy, a newly belligerent pursuit of China’s national interests.
The Clean Network is to China what George Kennan’s “long telegram” [PDF] of 1946 was to the Soviet Union, wrote David Fidler, adjunct senior fellow for cybersecurity and global health at the Council on Foreign Relations, in a blog post in October.
But trade deals alone are not enough, says Martijn Rasser, a senior fellow at the Center for a New American Security. For instance, they wouldn’t stop China from exporting its surveillance technology to countries such as Venezuela and Uganda, where it’s been used to target political activists, he says.
The Impacts of COVID-19 on Academic Library Budgets: Fall 2020
not all institutions have targeted their libraries equally. On average, libraries at private institutions fared better than those at public institutions, and those at baccalaureate colleges were most likely to not report a change in their budgets.
In light of present circumstances, publishers and other vendors have several opportunities to support the sector beyond the free access offers and price caps that have been extended. To take one example, in light of staffing austerity measures, there could be renewed attention to reducing the administrative burden faced by librarians to acquire, configure, and maintain products. And, with so many users working remotely, bringing greater seamlessness by reducing authorization, authentication, and other discovery to access barriers in an off-campus environment has never been more important. Libraries and publishers alike are only beginning to understand the impacts of reduced budgets, changes in work locations, and future higher education and funder priorities on strategies for achieving open access.
Information Overload Helps Fake News Spread, and Social Media Knows It
Understanding how algorithm manipulators exploit our cognitive vulnerabilities empowers us to fight back
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/information-overload-helps-fake-news-spread-and-social-media-knows-it/
a minefield of cognitive biases.
People who behaved in accordance with them—for example, by staying away from the overgrown pond bank where someone said there was a viper—were more likely to survive than those who did not.
Compounding the problem is the proliferation of online information. Viewing and producing blogs, videos, tweets and other units of information called memes has become so cheap and easy that the information marketplace is inundated. My note: folksonomy in its worst.
At the University of Warwick in England and at Indiana University Bloomington’s Observatory on Social Media (OSoMe, pronounced “awesome”), our teams are using cognitive experiments, simulations, data mining and artificial intelligence to comprehend the cognitive vulnerabilities of social media users.
developing analytical and machine-learning aids to fight social media manipulation.
As Nobel Prize–winning economist and psychologist Herbert A. Simon noted, “What information consumes is rather obvious: it consumes the attention of its recipients.”
attention economy
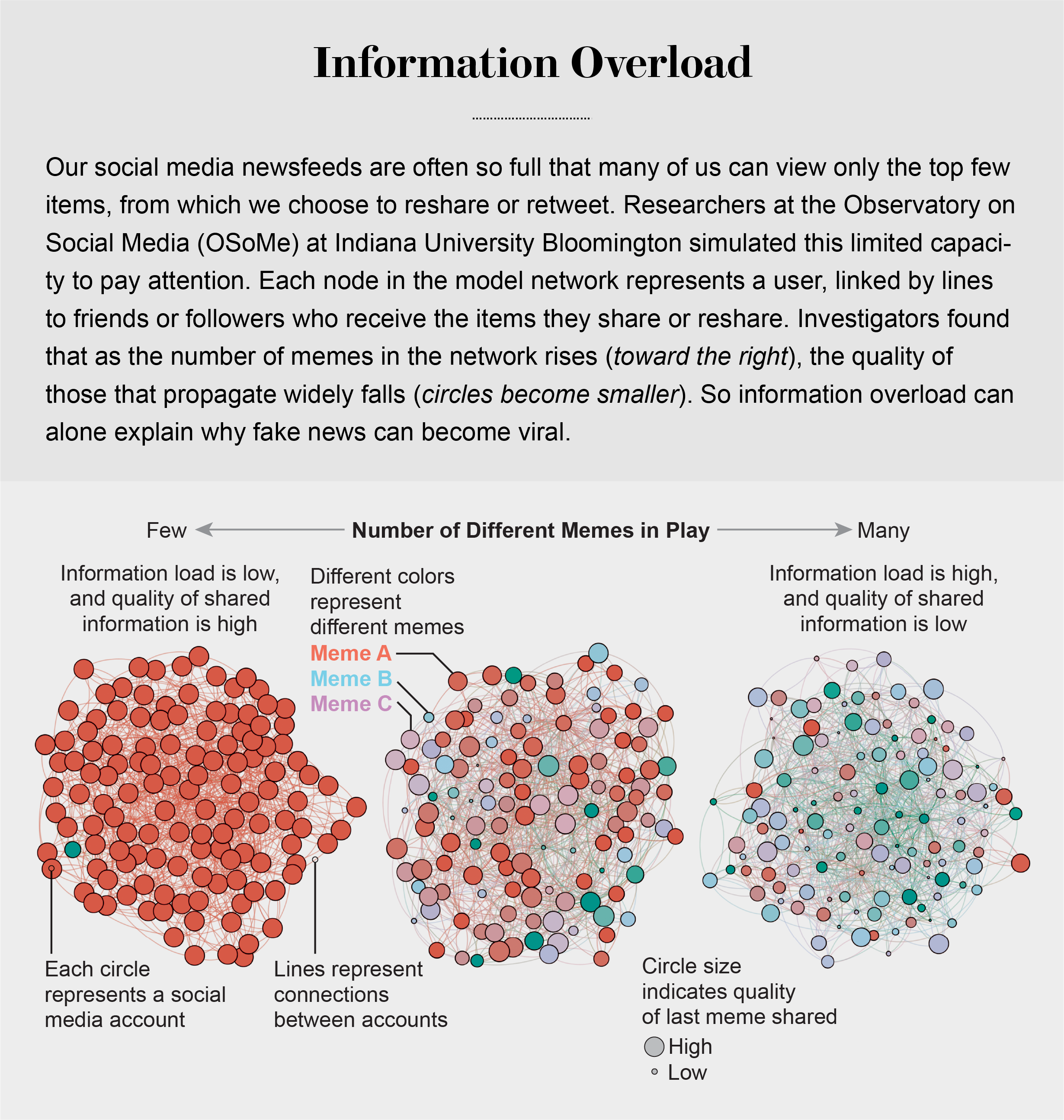
Our models revealed that even when we want to see and share high-quality information, our inability to view everything in our news feeds inevitably leads us to share things that are partly or completely untrue.
Frederic Bartlett
Cognitive biases greatly worsen the problem.
We now know that our minds do this all the time: they adjust our understanding of new information so that it fits in with what we already know. One consequence of this so-called confirmation bias is that people often seek out, recall and understand information that best confirms what they already believe.
This tendency is extremely difficult to correct.
Making matters worse, search engines and social media platforms provide personalized recommendations based on the vast amounts of data they have about users’ past preferences.
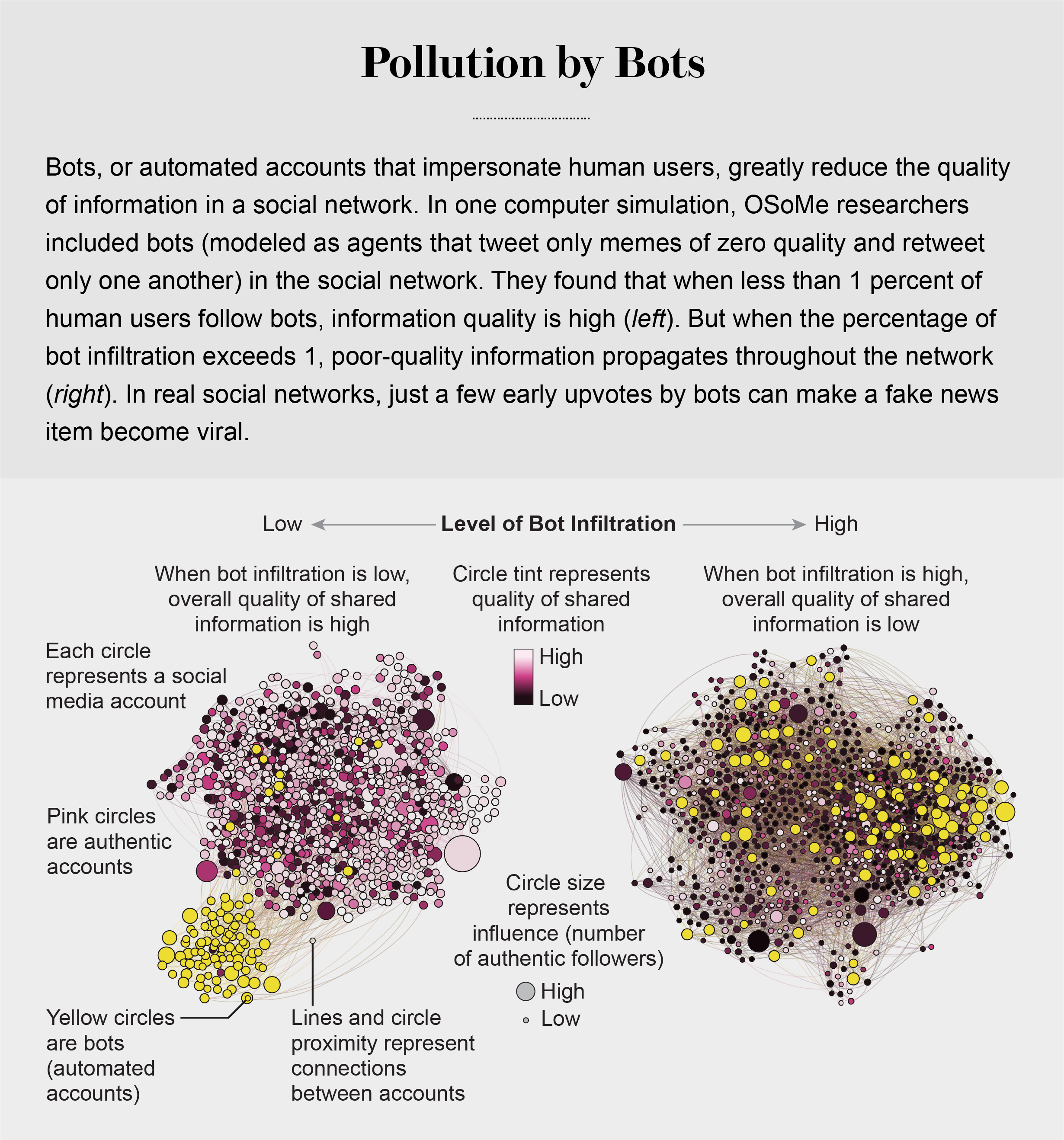
pollution by bots
Social Herding
social groups create a pressure toward conformity so powerful that it can overcome individual preferences, and by amplifying random early differences, it can cause segregated groups to diverge to extremes.
Social media follows a similar dynamic. We confuse popularity with quality and end up copying the behavior we observe.
information is transmitted via “complex contagion”: when we are repeatedly exposed to an idea, typically from many sources, we are more likely to adopt and reshare it.
In addition to showing us items that conform with our views, social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and Instagram place popular content at the top of our screens and show us how many people have liked and shared something. Few of us realize that these cues do not provide independent assessments of quality.
programmers who design the algorithms for ranking memes on social media assume that the “wisdom of crowds” will quickly identify high-quality items; they use popularity as a proxy for quality. My note: again, ill-conceived folksonomy.
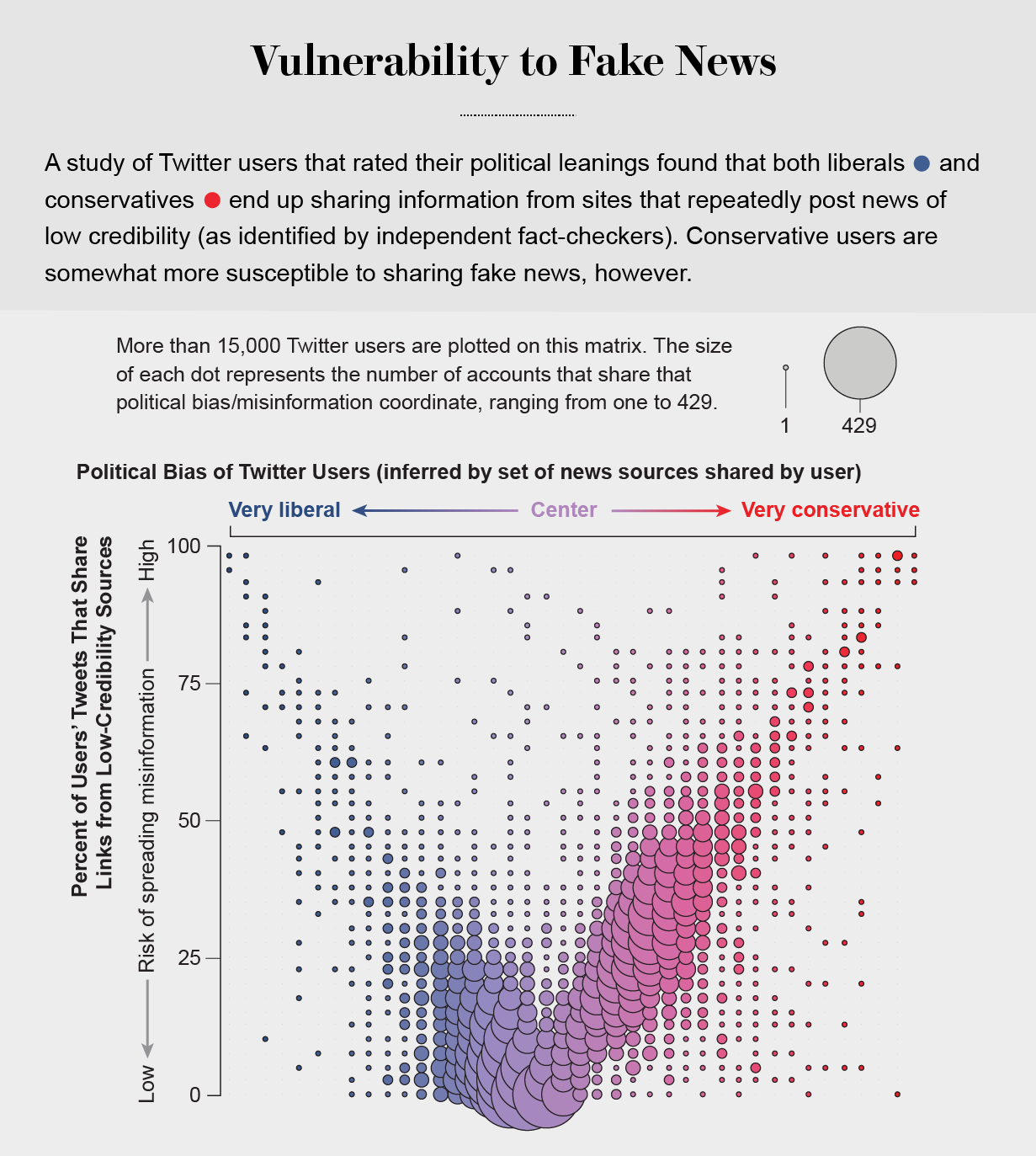
Echo Chambers
the political echo chambers on Twitter are so extreme that individual users’ political leanings can be predicted with high accuracy: you have the same opinions as the majority of your connections. This chambered structure efficiently spreads information within a community while insulating that community from other groups.
socially shared information not only bolsters our biases but also becomes more resilient to correction.
machine-learning algorithms to detect social bots. One of these, Botometer, is a public tool that extracts 1,200 features from a given Twitter account to characterize its profile, friends, social network structure, temporal activity patterns, language and other features. The program compares these characteristics with those of tens of thousands of previously identified bots to give the Twitter account a score for its likely use of automation.
Some manipulators play both sides of a divide through separate fake news sites and bots, driving political polarization or monetization by ads.
recently uncovered a network of inauthentic accounts on Twitter that were all coordinated by the same entity. Some pretended to be pro-Trump supporters of the Make America Great Again campaign, whereas others posed as Trump “resisters”; all asked for political donations.
a mobile app called Fakey that helps users learn how to spot misinformation. The game simulates a social media news feed, showing actual articles from low- and high-credibility sources. Users must decide what they can or should not share and what to fact-check. Analysis of data from Fakey confirms the prevalence of online social herding: users are more likely to share low-credibility articles when they believe that many other people have shared them.
Hoaxy, shows how any extant meme spreads through Twitter. In this visualization, nodes represent actual Twitter accounts, and links depict how retweets, quotes, mentions and replies propagate the meme from account to account.
Free communication is not free. By decreasing the cost of information, we have decreased its value and invited its adulteration.


