Searching for "artificial intelligence "
An Imaginary Interview with Lev Vygotsky on Immersive Storytelling and Learning
Ulla, Founder and CEO of ThingLink
https://medium.com/@ulla/an-imaginary-interview-with-lev-vygotsky-on-immersive-storytelling-and-learning-5bbb211c6e50
digital storytelling at the Festival Della Didattica Digitale (Digital Teaching Festival) in Italy.
the trending but undefined concepts of digital storytelling and immersive learning
definition
Storytelling is a logical form of thought. It is an analytical process including perception, labeling, organizing, categorizing real and imaginary objects and their real and imaginary relations in speech.
Q: What do you think immersive documentation technologies such as 360 images and videos can bring to this process?
V: 360 degree media and virtual reality are cultural-historically developed tools that mediate our relationship to the world in a new way. They expand the possible fields of perception transcending space and time. Perception precedes other psychological functions.
Definition
Immersive storytelling can be understood as an activity through which students use language to visualize relations and meaning in 360 degree digital environments. Naming or describing relations between objects in our field of perception using verbal or visual language awakens intellectual processes fundamental to learning.
Q: Would you say immersive storytelling is a form of creative play?
V: That is a possible interpretation. Play is a psychological process through which we create an imaginary situation or place, reflecting or separating objects and their actual meaning, or creating new meanings. The ability to digitally create and modify situations and environments can be understood as a form of play, opening a realm of spontaneity and freedom, connected with pleasure.
Q: Can robots help us learn? Is AI already the More Knowledgeable Other?
V: The More Knowledgeable Other (MKO) refers to anyone or anything who has a better understanding or a higher ability level than the learner, with respect to a particular task, process, or concept. If a robot with artificial intelligence can function as an MKO and support our problem solving, it can expand our Zone of Proximal Development.
++++++++++++
more on artificial intelligence in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=artifical+intelligence
more on augmented reality in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=augmented+reality
+++++++++++++
more on AR in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=artificial+intelligence
more on China education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/01/06/chinas-transformation-of-higher-education/
AI, Autonomous Cars, and Libraries
at RMG’s Annual Presidents’ Seminar:
The View from the Top on Friday February 9, 2018, 2:00 p.m. – 4:00 p.m.
ALA Midwinter Conference, Denver Colorado Convention Center Room 505
Who, When, Where?
- How will these disruptive technologies enter the
Library Industry ?
- Who will lead the innovation?
- And what about Robots, Blockchain, and the loss of Net Neutrality?
- How will Artificial Intelligence and Self-Driving Cars improve library services and performance?
- • In the age of click and digital download, will driverless library (or Uber or Lyft) delivery services plus robots-to-the-door put printed books and other physical items into readers’ hands with comparable ease? Or transport and escort readers to Library programs and browsing opportunities?
- • Alexa: Please deliver to my weekend address the Hungarian cookbook I checked out from my Branch Library last year and fresh — not frozen — ingredients for goulash for six. Text me by Thursday if I can’t get all this by Friday 6pm. Also, could you recommend a suitable under $15 red wine available at my weekend Whole Foods?
- • Siri or Alexa: Call the Library and make reservations for my two grandchildren and me for the February program on Spring solstice, and ask them to text each of us confirmations. Also, could you ask the Library to send them links to e-books that explain the history of astronomy? And deliver to Amy a book in English or Mandarin about ancient Chinese astronomy a week before the program?
The Seminar is open to everyone for dialogue on topical issues and concerns — registration is not required.
Attendees are invited to ask questions of Library Industry executives entrusted with delivering platforms and solutions for global library systems, services, and content to thousands of libraries serving millions of library users worldwide.
Participating companies & executives include:
Axiell (Ann Maelerts), BiblioLabs (Mitchell Davis),
Demco Software (Ravi Singh), Easy Mile, Index Data (Sebastian Hammer), Innovative Interfaces (James Tallman), Overdrive (Steve Potash), ProQuest (Rich Belanger), SirsiDynix (Bill Davison), The Library Corporation (Annette Murphy)
Rob McGee will moderate the session with assistance from Marshall Breeding and RMG’s Geoff Payne (Melbourne Office).
++++++++++++++
more on artificial intelligence in this ims blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=artificial+intelligence
NMC/CoSN Horizon Report 2017 K–12 Edition
p. 16 Growing Focus on Measuring Learning
p. 18 Redesigning Learning Spaces
Biophilic Design for Schools : The innate tendency in human beings to focus on life and lifelike processes is biophilia
p. 20 Coding as a Literacy
p. 24
Significant Challenges Impeding Technology Adoption in K–12 Education
Improving Digital Literacy.
Schools are charged with developing students’ digital citizenship, ensuring mastery of responsible and appropriate technology use, including online etiquette and digital rights and responsibilities in blended and online learning settings. Due to the multitude of elements comprising digital literacy, it is a challenge for schools to implement a comprehensive and cohesive approach to embedding it in curricula.
Rethinking the Roles of Teachers.
Pre-service teacher training programs are also challenged to equip educators with digital and social–emotional competencies, such as the ability to analyze and use student data, amid other professional requirements to ensure classroom readiness.
p. 28 Improving Digital Literacy
Digital literacy spans across subjects and grades, taking a school-wide effort to embed it in curricula. This can ensure that students are empowered to adapt in a quickly changing world
Education Overview: Digital Literacy Has to Encompass More Than Social Use
What Web Literacy Skills are Missing from Learning Standards? Are current learning standards addressing the essential web literacy skills everyone should know?https://medium.com/read-write-participate/what-essential-web-skills-are-missing-from-current-learning-standards-66e1b6e99c72

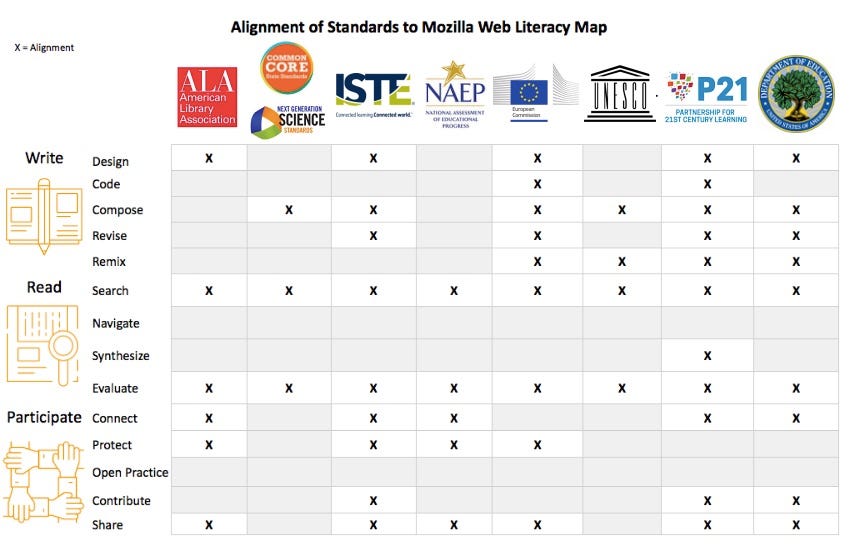
The American Library Association (ALA) defines digital literacy as “the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate or share information, requiring both cognitive and technical skills.” While the ALA’s definition does align to some of the skills in “Participate”, it does not specifically mention the skills related to the “Open Practice.”
The library community’s digital and information literacy standards do not specifically include the coding, revision and remixing of digital content as skills required for creating digital information. Most digital content created for the web is “dynamic,” rather than fixed, and coding and remixing skills are needed to create new content and refresh or repurpose existing content. Leaving out these critical skills ignores the fact that library professionals need to be able to build and contribute online content to the ever-changing Internet.
p. 30 Rethinking the Roles of Teachers
Teachers implementing new games and software learn alongside students, which requires
a degree of risk on the teacher’s part as they try new methods and learn what works
p. 32 Teaching Computational Thinking
p. 36 Sustaining Innovation through Leadership Changes
shift the role of teachers from depositors of knowledge to mentors working alongside students;
p. 38 Important Developments in Educational Technology for K–12 Education
Consumer technologies are tools created for recreational and professional purposes and were not designed, at least initially, for educational use — though they may serve well as learning aids and be quite adaptable for use in schools.
Drones > Real-Time Communication Tools > Robotics > Wearable Technology
Digital strategies are not so much technologies as they are ways of using devices and software to enrich teaching and learning, whether inside or outside the classroom.
> Games and Gamification > Location Intelligence > Makerspaces > Preservation and Conservation Technologies
Enabling technologies are those technologies that have the potential to transform what we expect of our devices and tools. The link to learning in this category is less easy to make, but this group of technologies is where substantive technological innovation begins to be visible. Enabling technologies expand the reach of our tools, making them more capable and useful
Affective Computing > Analytics Technologies > Artificial Intelligence > Dynamic Spectrum and TV White Spaces > Electrovibration > Flexible Displays > Mesh Networks > Mobile Broadband > Natural User Interfaces > Near Field Communication > Next Generation Batteries > Open Hardware > Software-Defined Networking > Speech-to-Speech Translation > Virtual Assistants > Wireless Powe
Internet technologies include techniques and essential infrastructure that help to make the technologies underlying how we interact with the network more transparent, less obtrusive, and easier to use.
Bibliometrics and Citation Technologies > Blockchain > Digital Scholarship Technologies > Internet of Things > Syndication Tools
Learning technologies include both tools and resources developed expressly for the education sector, as well as pathways of development that may include tools adapted from other purposes that are matched with strategies to make them useful for learning.
Adaptive Learning Technologies > Microlearning Technologies > Mobile Learning > Online Learning > Virtual and Remote Laboratories
Social media technologies could have been subsumed under the consumer technology category, but they have become so ever-present and so widely used in every part of society that they have been elevated to their own category.
Crowdsourcing > Online Identity > Social Networks > Virtual Worlds
Visualization technologies run the gamut from simple infographics to complex forms of visual data analysis
3D Printing > GIS/Mapping > Information Visualization > Mixed Reality > Virtual Reality
p. 46 Virtual Reality
p. 48 AI
p. 50 IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality, and advancements in online learning have changed the way universities reach prospective students, engage with their current student body, and provide them the resources they need.
Online Learning
+++++++++++++++++++++
more on disruptive technologies in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=disruptive+technologies
Emerging Directions in Immersive Learning
Presented by: Maya Georgieva and Emory Craig, May 17, 1:00 – 2:00pm (EDT)
http://events.shindig.com/event/campus-tech
Digital Bodies cofounders Emory Craig and Maya Georgieva for an interactive session that will examine five developments in virtual, augmented, and mixed reality with the greatest potential to impact teaching and learning. Ask your questions live as they explore how groundbreaking developments in VR, AR, MR, and artificial intelligence will power immersive technologies and transform learning.
Hololense $3000 and it is difficult to use outside. persistent digital objects
https://mixed.reality.news/news/whats-difference-between-hololens-meta-magic-leap-0171361/
https://events.google.com/io/
https://unity3d.com/sundance2017
education: new media, gaming
storytelling: immersive storytelling and AI
Jeremy Bailenson https://vhil.stanford.edu/
Julie Johnston – https://uits.iu.edu/learning-spaces
11 Ed Tech Trends to Watch in 2017
Five higher ed leaders analyze the hottest trends in education technology this year.
http://pdf.101com.com/CampusTech/2017/701921020/CAM_1702DG.pdf
new forms of human-computer interaction (HCI) such as augmented reality (AR),virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR).
p. 21
combining AR/VR/MR with cognitive computing and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies (such as machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing and chatbots).
Some thought-provoking questions include:
- Will remote workers be able to be seen and interacted with via their holograms (i.e., attending their meetings virtually)? What would this mean for remote learners?
- Will our smartphones increasingly allow us to see information overlaid on the real world? (Think Pokémon Go, but putting that sort of technology into a vast array of different applications, many of which could be educational in nature)
- How do/will these new forms of HCI impact how we design our learning spaces?
- Will students be able to pick their preferred learning setting (i.e., studying by a brook or stream or in a virtual Starbucks-like atmosphere)?
- Will more devices/platforms be developed that combine the power of AI with VR/AR/MR-related experiences? For example, will students be able to issue a verbal question or command to be able to see and experience walking around ancient Rome?
- Will there be many new types of learning experiences,like what Microsoft was able to achieve in its collaboration with Case Western Reserve University [OH]? Its HoloLens product transforms the way human anatomy can be taught.
p. 22 Extensive costs for VR design and development drive the need for collaborative efforts.
Case Western Reserve University, demonstrates a collaboration with the Cleveland Clinic and Microsoft to create active multi-dimensional learning using holography.
the development of more affordable high-quality virtual reality solutions.
AR game developed by the Salzburg University of Applied Sciences [Austria] (
http://www.fh-salzburg.ac.at/en/) that teaches about sustainability, the environment and living green.
Whether using AR for a gamified course or to acclimate new students to campus, the trend will continue into 2017.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
15 Tech Tool Favorites From ISTE 2016
list of resources that can help educators find what they need
Google Expeditions
This virtual reality field trip tool works in conjunction with Google Cardboard and has just been officially released. The app allows teachers to guide students through an exploration of 200 (and growing) historical sites and natural resources in an immersive, three-dimensional experience. The app only works on Android devices and is free.
Flippity
This app works in conjunction with Google Sheets and allows teachers to easily make a Jeopardy-style game.
Google Science Journal
This Android app allows users to do science experiments with mobile phones. Students can use sensors in the phone or connect external sensors to collect data, but can also take notes on observations, analyze and annotate within the app.
Google Cast
This simple app solves issues of disparate devices in the classroom. When students download the app, they can project from their devices onto the screen at the front of the room easily. “You don’t have to have specific hardware, you just have to have Wi-Fi,”
Constitute
This site hosts a database of constitutions from around the world. Anything digitally available has been aggregated here. It is searchable by topic and will pull out specific excerpts related to search terms like “freedom of speech.”
YouTube
a database of YouTube Channels by subject to help educators with discoverability (hint subjects are by tab along the bottom of the document).
Zygote Body
This freemium tool has a lot of functionality in the free version, allowing students to view different parts of human anatomy and dig into how various body systems work.
Pixlr
This app has less power than Photoshop, but is free and fairly sophisticated. It works directly with Google accounts, so students can store files there.
uild With Chrome
This extension to the Chrome browser lets kids play with digital blocks like Legos. Based on the computer’s IP address, the software assigns users a plot of land on which to build nearby. There’s a Build Academy to learn how to use the various tools within the program, but then students can make whatever they want.
Google CS First
Built on Scratch’s programming language, this easy tool gives step-by-step instructions to get started and is great for the hesitant teacher who is just beginning to dip a toe into coding.
+++++++++++++++
More on VR in this IMS bloghttps://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+reality
Google Researchers Create AI That Builds Its Own Encryption
BY TOM BRANT OCTOBER 28, 2016 04:45PM EST
http://www.pcmag.com/news/349154/google-researchers-create-ai-that-builds-its-own-encryption
Alice and Bob have figured out a way to have a conversation without Eve being able to overhear, no matter how hard she tries.
They’re artificial intelligence algorithms created by Google engineers, and their ability to create an encryption protocol that Eve (also an AI algorithm) can’t hack is being hailed as an important advance in machine learning and cryptography.
Martin Abadi and David G. Andersen, explained in a paper published this week that their experiment is intended to find out if neural networks—the building blocks of AI—can learn to communicate secretly.
As the Abadi and Anderson wrote, “instead of training each of Alice and Bob separately to implement some known cryptosystem, we train Alice and Bob jointly to communicate successfully and to defeat Eve without a pre-specified notion of what cryptosystem they may discover for this purpose.”
same in German
Googles AI entwickelt eigenständig Verschlüsselung
Google-Forscher Martin Abadi und David G. Andersen des Deep-Learning-Projekts “Google Brain” eine neue Verschlüsselungsmethode entwickelt beziehungsweise entwickeln lassen. Die Forscher haben verschiedene neurale Netze damit beauftragt, eine abhörsichere Kommunikation aufzustellen.
++++++++++++++++
more on AI in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=artificial+intelligence
http://diyubook.com/2013/07/the-mooc-is-dead-long-live-open-learning/
We’re at a curious point in the hype cycle of educational innovation, where the hottest concept of the past year–Massive Open Online Courses, or MOOCs–is simultaneously being discovered by the mainstream media, even as the education-focused press is declaring them dead. “More Proof MOOCs are Hot,” and “MOOCs Embraced By Top Universities,” said the Wall Street Journal and USA Today last week upon the announcement that Coursera had received a $43 million round of funding to expand its offerings;
“Beyond MOOC Hype” was the nearly simultaneous headline in Inside Higher Ed.
Can MOOCs really be growing and dying at the same time?
The best way to resolve these contradictory signals is probably to accept that the MOOC, itself still an evolving innovation, is little more than a rhetorical catchall for a set of anxieties around teaching, learning, funding and connecting higher education to the digital world. This is a moment of cultural transition. Access to higher education is strained. The prices just keep rising. Questions about relevance are growing. The idea of millions of students from around the world learning from the worlds’ most famous professors at very small marginal cost, using the latest in artificial intelligence and high-bandwidth communications, is a captivating one that has drawn tens of millions in venture capital. Yet, partnerships between MOOC platforms and public institutions like SUNY and the University of California to create self-paced blended courses and multiple paths to degrees look like a sensible next step for the MOOC, but they are far from that revolutionary future. Separate ideas like blended learning and plain old online delivery seem to be blurring with and overtaking the MOOC–even Blackboard is using the term.
The time seems to be ripe for a reconsideration of the “Massive” impact of “Online” and “Open” learning. TheReclaim Open Learning initiative is a growing community of teachers, researchers and learners in higher education dedicated to this reconsideration. Supporters include the MIT Media Lab and the MacArthur Foundation-supported Digital Media and Learning Research Hub. I am honored to be associated with the project as a documentarian and beater of the drum.
Entries are currently open for our Innovation Contest, offering a $2000 incentive to either teachers or students who have projects to transform higher education in a direction that is connected and creative, is open as in open content and open as in open access, that is participatory, that takes advantage of some of the forms and practices that the MOOC also does but is not beholden to the narrow mainstream MOOC format (referring instead to some of the earlier iterations of student-created, distributed MOOCscreated by Dave Cormier, George Siemens, Stephen Downes and others.)
Current entries include a platform to facilitate peer to peer language learning, a Skype-based open-access seminar with guests from around the world, and a student-created course in educational technology. Go hereto add your entry! Deadline is August 2. Our judges include Cathy Davidson (HASTAC), Joi Ito (MIT), and Paul Kim (Stanford).
Reclaim Open Learning earlier sponsored a hackathon at the MIT Media Lab. This fall, September 27 and 28, our judges and contest winners will join us at a series of conversations and demo days to Reclaim Open Learning at the University of California, Irvine. If you’re interested in continuing the conversation, join us there or check us out online.


