Open Textbook Faculty Development
Purpose and Overview
Education is expensive. If we can reduce textbook costs, students may be able to take more classes, complete their programs more quickly, and be more successful. Once faculty have participated in an introductory webinar, they may review an open textbook that is located in the Open Textbook Library (open.umn.edu). Working with the Open Textbook Network and Library, faculty will receive a $200.00 honorarium once the review is completed.
Round 1
| September 7, 2017 |
Round 4: Deadline to register for open textbook webinar |
| September 12, 2017, 1:00pm-2:30pm |
Round 4: Open textbook webinar |
| September 12 – October 17, 2017 |
Round 4: Faculty complete reviews |
For more information: http://asa.mnscu.edu/educationalinnovations/open/facultyreviews.html or contact Karen Pikula, the Minnesota State OER Coordinator, at karen.pikula@minnstate.edu
@OpenMinnState
++++++++++++++++++++
more on open textbook in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=open+textbooks
learning from real life experience
Today’s report on the use of Zello (http://www.marketwatch.com/story/houston-residents-and-civilians-turn-to-zello-app-to-coordinate-rescue-efforts-2017-08-29) by Houston residents during Hurricane Harvey has parallels with the organizational efforts of using Zello by the Venezuelan people (https://zello.com/channels/k/b2dDl) in 2014. (https://advox.globalvoices.org/2014/02/23/walkie-talkie-app-zello-blocked-in-venezuela/)
Zello, HeyTell and Voxer Make Your Smartphone a Walkie-Talkie (NYT, 2012) are apps for smart phones and mobile devices.
They are free.
They do much more than a physical walkie-talkie (e.g. send visuals, record messages)
They are more environment friendly, since do not require physical presence and so much battery power: https://www.compareninja.com/tables/single/60573
Yo is a similar messaging app: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/07/09/social-media-yo/
Library and University use:
In 2014, we proposed to the middle management the consideration of Yo as alarm system:
From: Miltenoff, Plamen
Sent: Tuesday, July 08, 2014 9:17 PM
To: ??????, Mark A. <???????@stcloudstate.edu>
Subject: FW: Yo at LRS
Good evening Mark
Based on the article below:
http://www.businessinsider.com/yo-updates-on-israel-missile-attacks-2014-7
The upper management might consider fire and/or tornado alarm app for SCSU students similarly to the one, which the Israelis are using to back up their alarm system.
I am confident that some other US school is already thinking about the same and developing probably the app.
Thanks for considering…
Plamen
++++++++++++++++++
From: Miltenoff, Plamen
Sent: Tuesday, July 8, 2014 8:59 PM
To: ???????, Colette ?????????
Cc: ??????, Joseph
Subject: Yo at LRS
Collette,
I am not sure if this news
http://www.businessinsider.com/yo-updates-on-israel-missile-attacks-2014-7
will increase your interest toward “Yo” since you said that you are not interested in politics
As shared with Joe several months ago about “Zello” being used in Venezuela (http://www.huffingtonpost.ca/2014/02/21/venezuela-blocks-zello-ap_n_4830452.html ), ingenuity during political events can give us great ideas how to use social media apps in daily work
I would like to ask you again to consider testing Yo and sharing your ideas how we can apply it at LRS
It is worth checking the penetration of Yo among SCSU students and use it.
Thank you and lkng forward to hearing your opinion
Plamen
+++++++++++++++++++
benefits for the library and potentially for the campus:
- reduce financial cost: batteries for the walkie talkies and the wear off of the walkie talkie can be replaced by a virtual app (again, apps for each of the three potential candidates are free)
- environmentally friendly. Apps are virtual. Walkie talkies are physical
- improve productivity. walkie talkie allow only talk. Apps allow: audio, video (images) and text
- raise the level of critical thinking (increase productivity by proxy): the use of several media: text, visuals, audio will allow users to think in a wider diapason when troubleshooting and/or doing their tasks
- the library can be the sandbox to smooth out details of the application and lessons learned can help replace walkie talkies across campus with 21st century tools and increase productivity campus wide.
+++++++++++++++++++
previous posts on Zello in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=zello
NMC/CoSN Horizon Report 2017 K–12 Edition
p. 16 Growing Focus on Measuring Learning
p. 18 Redesigning Learning Spaces
Biophilic Design for Schools : The innate tendency in human beings to focus on life and lifelike processes is biophilia
p. 20 Coding as a Literacy
p. 24
Significant Challenges Impeding Technology Adoption in K–12 Education
Improving Digital Literacy.
Schools are charged with developing students’ digital citizenship, ensuring mastery of responsible and appropriate technology use, including online etiquette and digital rights and responsibilities in blended and online learning settings. Due to the multitude of elements comprising digital literacy, it is a challenge for schools to implement a comprehensive and cohesive approach to embedding it in curricula.
Rethinking the Roles of Teachers.
Pre-service teacher training programs are also challenged to equip educators with digital and social–emotional competencies, such as the ability to analyze and use student data, amid other professional requirements to ensure classroom readiness.
p. 28 Improving Digital Literacy
Digital literacy spans across subjects and grades, taking a school-wide effort to embed it in curricula. This can ensure that students are empowered to adapt in a quickly changing world
Education Overview: Digital Literacy Has to Encompass More Than Social Use
What Web Literacy Skills are Missing from Learning Standards? Are current learning standards addressing the essential web literacy skills everyone should know?https://medium.com/read-write-participate/what-essential-web-skills-are-missing-from-current-learning-standards-66e1b6e99c72

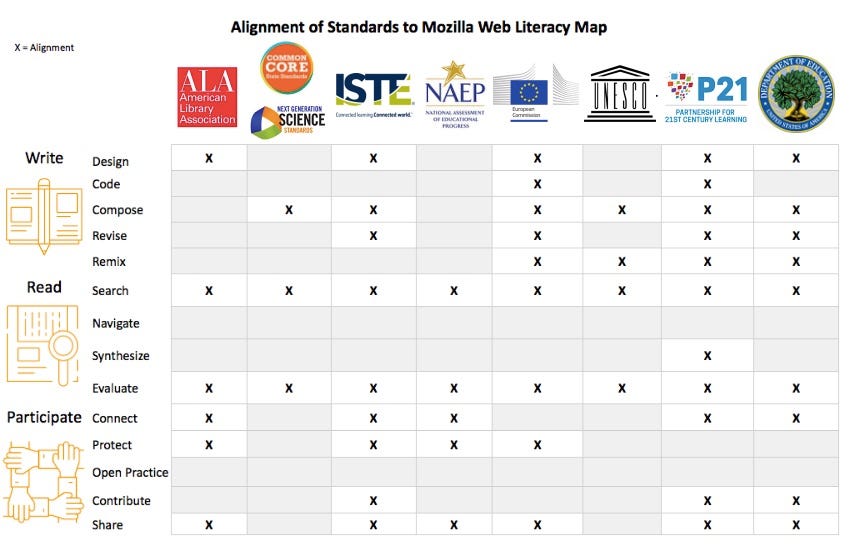
The American Library Association (ALA) defines digital literacy as “the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate or share information, requiring both cognitive and technical skills.” While the ALA’s definition does align to some of the skills in “Participate”, it does not specifically mention the skills related to the “Open Practice.”
The library community’s digital and information literacy standards do not specifically include the coding, revision and remixing of digital content as skills required for creating digital information. Most digital content created for the web is “dynamic,” rather than fixed, and coding and remixing skills are needed to create new content and refresh or repurpose existing content. Leaving out these critical skills ignores the fact that library professionals need to be able to build and contribute online content to the ever-changing Internet.
p. 30 Rethinking the Roles of Teachers
Teachers implementing new games and software learn alongside students, which requires
a degree of risk on the teacher’s part as they try new methods and learn what works
p. 32 Teaching Computational Thinking
p. 36 Sustaining Innovation through Leadership Changes
shift the role of teachers from depositors of knowledge to mentors working alongside students;
p. 38 Important Developments in Educational Technology for K–12 Education
Consumer technologies are tools created for recreational and professional purposes and were not designed, at least initially, for educational use — though they may serve well as learning aids and be quite adaptable for use in schools.
Drones > Real-Time Communication Tools > Robotics > Wearable Technology
Digital strategies are not so much technologies as they are ways of using devices and software to enrich teaching and learning, whether inside or outside the classroom.
> Games and Gamification > Location Intelligence > Makerspaces > Preservation and Conservation Technologies
Enabling technologies are those technologies that have the potential to transform what we expect of our devices and tools. The link to learning in this category is less easy to make, but this group of technologies is where substantive technological innovation begins to be visible. Enabling technologies expand the reach of our tools, making them more capable and useful
Affective Computing > Analytics Technologies > Artificial Intelligence > Dynamic Spectrum and TV White Spaces > Electrovibration > Flexible Displays > Mesh Networks > Mobile Broadband > Natural User Interfaces > Near Field Communication > Next Generation Batteries > Open Hardware > Software-Defined Networking > Speech-to-Speech Translation > Virtual Assistants > Wireless Powe
Internet technologies include techniques and essential infrastructure that help to make the technologies underlying how we interact with the network more transparent, less obtrusive, and easier to use.
Bibliometrics and Citation Technologies > Blockchain > Digital Scholarship Technologies > Internet of Things > Syndication Tools
Learning technologies include both tools and resources developed expressly for the education sector, as well as pathways of development that may include tools adapted from other purposes that are matched with strategies to make them useful for learning.
Adaptive Learning Technologies > Microlearning Technologies > Mobile Learning > Online Learning > Virtual and Remote Laboratories
Social media technologies could have been subsumed under the consumer technology category, but they have become so ever-present and so widely used in every part of society that they have been elevated to their own category.
Crowdsourcing > Online Identity > Social Networks > Virtual Worlds
Visualization technologies run the gamut from simple infographics to complex forms of visual data analysis
3D Printing > GIS/Mapping > Information Visualization > Mixed Reality > Virtual Reality
p. 46 Virtual Reality
p. 48 AI
p. 50 IoT
NMC Releases Second Horizon Project Strategic Brief on Digital Literacy
http://www.nmc.org/news/nmc-releases-second-horizon-project-strategic-brief-on-digital-literacy/
The New Media Consortium (NMC) has released Digital Literacy in Higher Education, Part II: An NMC Horizon Project Strategic Brief, a follow-up to its 2016 strategic brief on digital literacy.
PDF available here.
2017-nmc-strategic-brief-digital-literacy-in-higher-education-II-ycykt3
But what does it really mean to be digitally literate, and which standards do we use?” said Dr. Eden Dahlstrom, NMC Executive Director. “This report sheds light on the meaning and impact of digital literacy using cross-cultural and multi-disciplinary approaches, highlighting frameworks and exemplars in practice.
NMC’s report has identified a need for institutions and thought leaders to consider the ways in which content creation is unequally expressed throughout the world. In an examination of digital literacy within European, Middle Eastern, and African nations (EMEA), research has surfaced unequal access to information technology based on inequalities of economics, gender, race, and political divides.
| 2020 |
|
2015 |
|
| 1. |
Complex Problem Solving |
1. |
Complex Problem Solving |
| 2. |
Critical Thinking |
2. |
Coordinating with Others |
| 3. |
Creativity |
3. |
People Management |
| 4. |
People Management |
4. |
Critical Thinking |
| 5. |
Coordinating with Others |
5. |
Negotiation |
| 6. |
Emotional Intelligence |
6. |
Quality Control |
| 7. |
Judgment and Decision Making |
7. |
Service Orientation |
| 8. |
Service Orientation |
8. |
Judgment and Decision Making |
| 9. |
Negotiation |
9. |
Active Listening |
| 10. |
Cognitive Flexibility |
10. |
Creativity |
Digital tools themselves are merely enablers, pushing the envelope of what learners can create. No longer is it acceptable for students to be passive consumers of content; they can contribute to the local and global knowledge ecosystem, learning through the act of producing and discussing rich media, applications, and objects. In the words of many institutional mission statements, students do not have to wait until they graduate to change the world.
Using readily available digital content creation tools (e.g., video production and editing, web and graphic tools), students are evolving into digital storytellers,
digital literacy now encompasses the important skills of being able to coordinate with others to create something truly original that neither mind would fathom independently.
The ability to discern credible from inaccurate resources is foundational to digital literacy. my note: #Fakenews
A lack of broad consensus on the meaning of digital literacy still hinders its uptake, although a growing body of research is helping higher education professionals better navigate the continuous adjustments to the field brought about by emerging pedagogies and technologies.
Information literacy is a nearly universal component within these digital literacy frameworks. Critically finding, assessing, and using digital content within the vast and sometimes chaotic internet appears as a vital skill in almost every account, including those published beyond libraries. In contrast, media literacy is less widely included in digital literacy publications, possibly due to a focus on scholarly, rather than popular, materials. Digital literacies ultimately combine information and media literacy.
United States digital literacy frameworks tend to focus on educational policy details and personal empowerment, the latter encouraging learners to become more effective students, better creators, smarter information consumers, and more influential members of their community.
National policies are vitally important in European digital literacy work, unsurprising for a continent well populated with nation-states and struggling to redefine itself… this recommendation for Balkan digital strategy: “Media and information education (with an emphasis on critical thinking and switching from consumption to action) should start at early ages, but address all ages.”
African digital literacy is more business-oriented. Frameworks often speak to job skills and digital entrepreneurship. New skills and professions are emphasized, symbolized by the call for “new collar” positions.
Middle Eastern nations offer yet another variation, with a strong focus on media literacy. As with other regions, this can be a response to countries with strong state influence or control over local media. It can also represent a drive to produce more locally-sourced content, as opposed to consuming
Digital literacy is a complex phenomenon in 2017, when considered internationally. Nations and regions are creating ways to help their populations grapple with the digital revolution that are shaped by their local situations. In doing so, they cut across the genealogy of digital literacies, touching on its historical components: information literacy, digital skills, and media literacy.
2017-nmc-strategic-brief-digital-literacy-in-higher-education-II-ycykt3 
How Does Digital Literacy Change Pedagogy?
Students are not all digital natives, and do not necessarily have the same level of capabilities. Some need to be taught to use online tools (such as how to navigate a LMS) for learning. However, once digital literacy skills for staff and students are explicitly recognized as important for learning and teaching, critical drivers for pedagogical change are in place.
Pedagogy that uses an inquiry based/problem solving approach is a great framework to enhance the use and practice of digital skills/capabilities in the classroom.
The current gap between students’ information literacy skills and their need to internalize digital literacy competencies creates an opportunity for academic librarians to support students in the pursuit of civic online reasoning at the core of NMC’s multimodal model of three digital literacies. Academic librarians need a new strategy that evolves information literacy to an expanded role educating digitally literate students. Let’s build a new model in which academic librarians are entrepreneurial collaborators with faculty,55 supporting their classroom efforts to help students become responsible sharers and commentators of news on social media.
“Digital literacy is not just about ensuring that students can use the latest technologies, but also developing skills to select the right tools for a particular context to deepen their learning outcomes and engage in creative problem-solving”
There is a disconnect between how students experience and interact with technology in their personal lives and how they use technology in their roles as students. Yes, students are digitally savvy, and yes, universities have a role in questioning (insightfully of course) their sometimes brash digital savviness. We have a situation where students are expecting more, but (as I see it) cannot provide a clear demand, while faculty are unable to walk in the shoes of the students.
+++++++++++++++++++
more on digital literacy in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=digital+literacy
Conference 16th to 17th October 2017 Rockville, Maryland, United States of America
Website: http://rais.education/the-future-of-education-mass-media-and-communication/
Contact person: Eduard David
We gladly invite you to attend the International Conference “The Future of Education, Mass-Media and Communication” which will be held at Johns Hopkins University, just 20 miles away from Washington DC.



