https://www.npr.org/2019/08/29/751116338/china-intercepts-wechat-texts-from-u-s-and-abroad-researcher-says
Chinese cyberspace is one of the most surveilled and censored in the world. That includes WeChat. Owned by Tencent, one of China’s biggest companies, the chat-meets-payment app has more than 1 billion monthly users in China and now serves users outside the country, too, although it does not divulge how many. Researchers say its use abroad has extended the global reach of China’s surveillance and censorship methods.
“The intention of keeping people safe by building these systems goes out the window the moment you don’t secure them at all,” says Victor Gevers, co-founder of the nonprofit GDI Foundation, an open-source data security collective.
Every day, Gevers scans the Internet for vulnerabilities to find unsecured databases, and he has exposed a large number of them, particularly linked to China.
++++++++++
more on WeChat and surveillance in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=wechat
Early Adopters Pioneer Virtual Reality Use in Higher Education
Colleges deliver personalized learning experiences with custom VR content
by Erin Brereton
Arizona State University used a grant to obtain 140 Mirage Solo headsets from Lenovo. Just over one third of students have elected to receive one, at no cost, since the program piloted their use in 2018. Alternately, students can view simulations on a computer or a Google Daydream device
A lot of people wear corrective lenses. Designers may need to start thinking about how the devices accommodate glasses.”
For some disciplines and pedagogical objectives, VR experiences may not be readily available, says Dr. Matthew Bramlet, pediatric cardiologist and physician at OSF Children’s Hospital of Illinois, assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Illinois College of Medicine at Peoria,
my note: Mark Gill, it seems similar to the WYSWYG interface you want to create:
To address that, U of I’s medical college developed its own content. Approximately 40 faculty members have created more than 250 VR lectures. The college provides access to Enduvo, a VR authoring tool Bramlet helped create, and lab space, featuring ceiling-mounted workstations equipped with HTC VIVE headsets powered by a variety of Dell, HP and other computers.
Martina, do you want to approach them and ask how willing they would be to share their learning objects for our nursing programs?
my note: Martina, do same – approach this program
Alice Butzlaff, an assistant professor with The Valley Foundation School of Nursing at San Jose State University, created original teaching exercises through a program sponsored by eCampus, a university resource that offers design and training assistance to help faculty integrate AR/VR technology, including workshops and demos of its HTC VIVE, Samsung Gear VR and other equipment.
My note: Martina
Reality Check
Keep these factors in mind when designing a campus VR lab.
Connectivity: On-campus and online students may have different considerations in order to stream VR content smoothly, so plan accordingly to ensure everyone has high-quality access.
Staff oversight: A program manager or faculty member can manage access to equipment, particularly if limited headsets are available.
Alternative options: Some users experience vertigo or “VR sickness,” says EDUCAUSE’s D. Christopher Brooks, so instructors should consider other ways they can participate in VR-based projects.
+++++++++++
more on VR in higher ed in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+reality+education
We define immersive scholarship as any scholarly work developed through or implemented utilizing technologies including Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Mixed Reality, Visualization (i.e., large format displays and visualization walls, GIS, Tableau), and any related hardware, programs or software.
We are seeking survey participants who are employed in an academic library and who currently support immersive scholarship and technologies at their institution.
how your academic library has developed tools, implemented third party hardware/software, and in what barriers you have identified at your institution in supporting immersive scholarship.
Link to Online Survey
third Library 2.019 mini-conference: “Emerging Technology,” which will be held online (and for free) on Wednesday, October 30th, from 12:00 – 3:00 pm US-Pacific Daylight Time (click for your own time zone).
Tomorrow’s technologies are shaping our world today, revolutionizing the way we live and learn. Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Blockchain, Internet of Things, Drones, Personalization, the Quantified Self. Libraries can and should be the epicenter of exploring, building and promoting these emerging techs, assuring the better futures and opportunities they offer are accessible to everyone. Learn what libraries are doing right now with these cutting-edge technologies, what they’re planning next and how you can implement these ideas in your own organization.
This is a free event, being held live online and also recorded.
REGISTER HERE
The Role of Librarians in Supporting ICT Literacy
Lesley Farmer May 9, 2019,
https://er.educause.edu/blogs/2019/5/the-role-of-librarians-in-supporting-ict-literacy
Academic librarians increasingly provide guidance to faculty and students for the integration of digital information into the learning experience.
TPACK: Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge
Many librarians have shied away from ICT literacy, concerned that they may be asked how to format a digital document or show students how to create a formula in a spreadsheet. These technical skills focus more on a specific tool than on the underlying nature of information.
librarians have begun to use an embedded model as a way to deepen their connection with instructors and offer more systematic collection development and instruction. That is, librarians focus more on their partnerships with course instructors than on a separate library entity.
If TPACK is applied to instruction within a course, theoretically several people could be contributing this knowledge to the course. A good exercise is for librarians to map their knowledge onto TPACK.
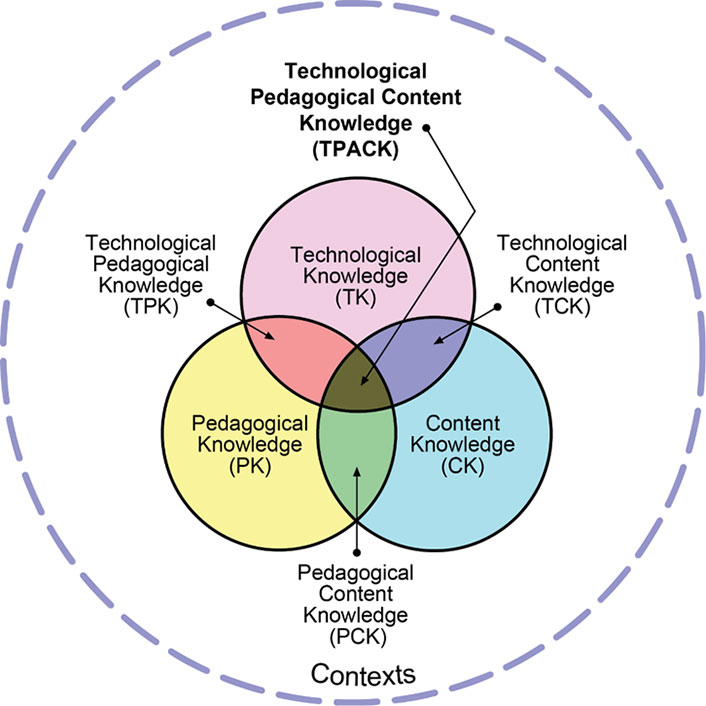
ICT reflects the learner side of a course. However, ICT literacy can be difficult to integrate because it does not constitute a core element of any academic domain. Whereas many academic disciplines deal with key resources in their field, such as vocabulary, critical thinking, and research methodologies, they tend not to address issues of information seeking or collaboration strategies, let alone technological tools for organizing and managing information.
Instructional design for online education provides an optimal opportunity for librarians to fully collaborate with instructors.
The outcomes can include identifying the level of ICT literacy needed to achieve those learning outcomes, a task that typically requires collaboration between the librarian and the program’s faculty member. Librarians can also help faculty identify appropriate resources that students need to build their knowledge and skills. As education administrators encourage faculty to use open educational resources (OERs) to save students money, librarians can facilitate locating and evaluating relevant resources. These OERs not only include digital textbooks but also learning objects such as simulations, case studies, tutorials, and videos.
Reading online text differs from reading print both physically and cognitively. For example, students scroll down rather than turn online pages. And online text often includes hyperlinks, which can lead to deeper coverage—as well as distraction or loss of continuity of thought. Also, most online text does not allow for marginalia that can help students reflect on the content. Teachers and students often do not realize that these differences can impact learning and retention. To address this issue, librarians can suggest resources to include in the course that provide guidance on reading online.
My note – why specialist like Tom Hergert and the entire IMS is crucial for the SCSU library and librarians and how neglecting the IMS role hurts the SCSU library –
Similarly, other types of media need to be evaluated, comprehended, and interpreted in light of their critical features or “grammar.” For example, camera angles can suggest a person’s status (as in looking up to someone), music can set the metaphorical tone of a movie, and color choices can be associated with specific genres (e.g., pastels for romances or children’s literature, dark hues for thrillers). Librarians can explain these media literacy concepts to students (and even faculty) or at least suggest including resources that describe these features
My note – on years-long repetition of the disconnect between SCSU ATT, SCSU library and IMS –
instructors need to make sure that students have the technical skills to produce these products. Although librarians might understand how media impacts the representation of knowledge, they aren’t necessarily technology specialists. However, instructors and librarians can collaborate with technology specialists to provide that expertise. While librarians can locate online resources—general ones such as Lynda.com or tool-specific guidance—technology specialists can quickly identify digital resources that teach technical skills (my note: in this case IMS). My note: we do not have IDs, another years-long reminder to middle and upper management. Many instructors and librarians have not had formal courses on instructional design, so collaborations can provide an authentic means to gain competency in this process.
My note: Tom and I for years have tried to make aware SCSU about this combo –
Instructors likely have high content knowledge (CK) and satisfactory technological content knowledge (TCK) and technological knowledge (TK) for personal use. But even though newer instructors acquire pedagogical knowledge (PK), pedagogical content knowledge (PCK), and technological pedagogical knowledge (TPK) early in their careers, veteran instructors may not have received this training. The same limitations can apply to librarians, but technology has become more central in their professional lives. Librarians usually have strong one-to-one instruction skills (an aspect of PK), but until recently they were less likely to have instructional design knowledge. ICT literacy constitutes part of their CK, at least for newly minted professionals. Instructional designers are strong in TK, PK, and TPK, and the level of their CK (and TCK and TPK) will depend on their academic background. And technology specialists have the corner on TK and TCK (and hopefully TPK if they are working in educational settings), but they may not have deep knowledge about ICT literacy.
Therefore, an ideal team for ICT literacy integration consists of the instructor, the librarian, the instructional designer, and the technology specialist. Each member can contribute expertise and cross-train the teammates. Eventually, the instructor can carry the load of ICT literacy, with the benefit of specific just-in-time support from the librarian and instructional designer.
My note: I have been working for more then six years as embedded librarian in the doctoral cohort and had made aware the current library administrator (without any response) about my work, as well as providing lengthy bibliography (e.g. https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/08/24/embedded-librarian-qualifications/ and have had meeting with the current SOE administrator and the library administrator (without any response).
I also have delivered discussions to other institutions (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/04/12/embedded-librarian-and-gamification-in-libraries/)
Librarians should seriously consider TPACK as a way to embed themselves into the classroom to incorporate information and ICT literacy.
+++++++++++++
more about academic library in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=academic+library
more on SAMR and TRACK models in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/05/17/transform-education-digital-tools/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/07/29/mn-esummit-2015/
Mental health of college students and Lee’s new book: “Delivering College Mental Health”
Join Bryan Alexander and Lee Keyes, executive director, Counseling Center at the University of Alabama, and author of Delivering Effective College Mental Health Services for an engaging live discussion on the future of mental health in higher education.
Bryan plans to ask Lee about unfolding trends in college student mental health and his thoughts around the rise in anxiety and stress. We will explore how universities are changing their approaches to student mental health and what roles technology may play in harming or helping psychological well-being.
What questions or thoughts do you have? Join and take part in the discussion!
Registration at:
++++++++++++++++++++++++++
My notes from the webinar:
Lee about “Mobile First” – like First Aid. Often by text and email. after Bryan asked how Adjuncts can deal with such situations, if
Counseling Centers need those additions.
Mobile First apps.
most crisis situations are a form of panic. if addressed quickly, one can prevent growing and turning into a major episode.
mindfulness can be different for the different type of issues of students.
libraries as the campus community center.
can be done on
conflation of immaturity and irresponsibility with stress and panic. Latter might be expressed in a way it is immature, but one has to meet them where they are, not judgement and denial, which will make it worse. Tough love will not help. Upholding classroom expectations and rules, but can be supportive at the same time. When pressed by time
Daniel Stanford De Paul. Cohort fundamentals of good teaching. instead of “fail safely”
academic hazing hasn’t changed since medieval time. the trauma instructors starts their career with.
+++++++++++++++++

