Archive of ‘Library and information science’ category
In this Business Insider video:
https://www.facebook.com/businessinsider/videos/10154001218189071/
‘Shark Tank‘ investor Robert Herjavec reveals the biggest mistakes small businesses make:
- know your numbers. If you don’t know your accounting, problem
- branding and marketing. Most people think branding is your logo. Branding is your whole package. Everything that your customer sees, feels, touches and interacts with.
- success is in failure. if you cannot absorb failure, you will die
the difference between small business and academic institution, being that the library or the entire university, is that small business is reliant on itself; if it does not well, it perishes. The library and the university are reliant on external funds and can fester for a long time. But eventually it dies. In that sense, learning from the lessons for small business can help:
- Branding is not mimicking someone else (another library[s)). It is not a superficial activity. It is not slapping pictures on social media. “Interact” is the key word. “Likes” in FB does not reflect complete interaction
- know your numbers. Analytics is not about “likes” and “visits.” it deeper datamining, which can explain behavior and predict behavior
- if success is failure, why safeguarding the social media in particular and the entire behavior of the library from “failure.” Isolating students or staff from acting with the excuse to safeguard from failure is practically isolating innovation.
How Teachers Leverage Mobile Technology
https://thejournal.com/Articles/2016/10/11/How-Teachers-Leverage-Mobile-Technology.aspx
“Teachers and administrators continue to see the No. 1 benefit of any digital tool, content or resource as enhancing student engagement. While that is interesting, it has limited value. Lots of thing can engage kids — that does not necessarily point to an academic benefit or value proposition on its own. So, I always acknowledge the engagement benefit but look deeper at other benefits that can shed new insights into how the teachers are leveraging these powerful devices to transform education — or to change the trajectory of the learning process for their students.
among the more interesting or meaningful benefits were:
- Improvement of communications between stakeholders, such as the ability for students to ask question via e-mail. “Stronger communications between students and teachers is a huge benefit
- Extending learning beyond regular school hours: “Teachers giving that high marks as a real or perceived benefit means that they are also looking for ways to extend learning time beyond the school day but realize that kids need a device to make that a reality.”
- Student ownership of the learning process: “Students who are using mobile devices in class are empowered/enabled to be in the driver’s seat of their own learning
++++++++++++++++++++
more on mobile technology in this blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=mobile+technology

++++++++++++++++++++++++
more on digital citizenship in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=digital+citizenship

+++++++++++++++++++++
more on copyright in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=copyright
Save
Who better to learn about incorporating 3D printing into instruction than from an instructor who taught the curriculum?
Join us on October 26th to hear directly from Assistant Professor Steve Chomyszak who used Stratasys 3D Printing Curriculum to teach a “Special Topics” 3D printing course at the Wentworth Institute of Technology.
During this complimentary webcast, you’ll gain valuable insight into the successes and lessons learned, including:
- Overview of the 14-week project-based 3D printing curriculum
- How an interactive learning environment impacted and inspired WIT students
- How the WIT 3D printing lab went from crickets to buzzing
- How curriculum measured up according to students
- And so much more!
|
|
|
Photo-sharing Site as Library Tool : A Web-based Survey
peer-reviewed article for Digital Library Perspectives: https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/dlp
opportunity to user to develop a sense of ownership over the library resources.
Photo-sharing sites already have taken sharp inroads into the field of teaching-learnin encouraging a shift from teacher-led approach to user centred engagement (Kawka, et al,2012).
Introducing photo-sharing sites and integrating with other social networking sites, libraries are now making their web presence outside the “traditional web platform”. With facility of online managing and sharing of digital images, photo-sharing sites enable users to get remotely connected with others and interact with comment links. Photo-sharing sites that are commonly being used by libraries are Flickr (www.flickr.com), Instagram (instagram.com), Pinterest (in.pinterest.com), Photobucket (photobucket.com), Picasa (picasa.google.com), SmugMug (www.smugmug.com), etc (Bradley, 2007; Kroski, 2008; Salomon, 2013).
The results showed that blog and RSS are among the mostly used applications and web 0 applications are associated with overall website quality, particularly to the service quality.
Stvilia and Jörgensen (2010) suggests that controlled vocabulary terms may be
37 complemented with those user generated tags which users feel more comfortable with for information The study also reflects a growing interest among the user community to be involved in “social content creation and sharing communities in creating and enhancing the metadata of their photo collections to make the collections more accessible and visible”.
page 7-8.
2.1 Steps to increase accessibility to photo-sharing sites
a) Improve visibility: To make photo-sharing sites of the library easily visible, a direct link to library homepage is essential
p. 9
2.2 Purposes of using photo-sharing sites
a) Organising library tour
b) Community building
c) Tool for digitisation
d) Grabbing the users at their own place
e) Integrating Feeds with other application
f) Displaying new arrivals : Newly added books
g) Sharing news & events and publicize library activities
h) Archives of exhibits
i) Portal for academic and research activity: Photo-sharing sites may serve as platform tofoster teaching learning activity, particularly for those who may use these image resource sites for academic purpose
j) Experimentation : Being a relatively new approach to users service, these tools may be introduced on experimental basis to examine their proper utilisation before final implementation
k) Miscellaneous : Public library can reach out to the community physically, offer service to the traditionally underserved, homebound or people with disability, implement programmes to include marginalised section of the community and showcase its mobile outreach efforts in photo-sharing sites.
page 12-13
Before going to integrate photo-sharing site, a library should set the strategic objectives i.e., what purposes are to be served. “Purpose can provide clarity of vision when creating policies or guidelines” (Garofalo, 2013, p.28). The above discussedrange of purposes may help librarians to develop better understanding to makeinformed selection of photo-sharing utility and the nature of images to be posted through it. Goal setting should precede consideration of views of a sizeable section of all library stakeholders to know beforehand what they expect from the library.
• Once the purposes are outlined, a library should formulate policy/ guideline for photo-sharing practices, based on user requirement, staff resource, available time component and technological support base. Policy offers a clear guideline for the users and staff to decide the kind of images to be posted. A guideline is indeed essential for the optimum use of photo-sharing site. It also delineates the roles and responsibilities of the staff concerned and ensures regular monitoring of the posts. Policy may highlight fair use guidelines and allow re-use of images within the scope of copy-right.
• A best way to start is integrating an app, involving simple design with fewer images and let users be familiarized with the system. During the course of development more and more apps may be added, with more images to be posted to serve variety of purposes, depending on the institutional resource and user demand.
• Accessibility to photo-sharing site largely depends on its visibility to the audience. Icon of photo-sharing utility prominently located on website will increase the presentation of its visual identity. Library may set links to photo-sharing sites at home page or at drilled-down page.
• Being an emerging technology, photo-sharing site needs adequate exposure for optimum usage. Annotations associated to photo-sharing site will give an idea about the online tool and will guide users to better harness the application.
• Photo-sharing sites allow images to be organised in a variety of way. Categorising image resources under various topical headings at one location will improve resource identification and frees one from extensive searching.
• Regular posting of engaging images to photo-sharing site from the library and follow- up will attract users to tag and share images and strengthen community involvement with active user participation.
• “Social and informal photographs” of library staff will make them more approachable and strengthen patron-staff relationship.
• Library should seek user comments and suggestions to improve current photo-sharing application and to incorporate fresh element to library service provision. User feedback may be considered as a tool to evaluate the effectiveness of existing photo- sharing practices.
• To popularise the effort, usual promotional media like physical and online signs/ displays apart, library may use social media marketing platforms like blogs, Facebook, Twitter, etc., and increase awareness of photo-sharing tools.
• Imparting technology training may develop necessary knowledge; improve skill, and change the attitude and mindset of library professionals to handle issues related to using this web-based powered-tools and repurpose existing accessibility settings.
• To provide quick link to photo-sharing site from anywhere in the web, a library may use add-ons / plug-ins to embed image sharing tools.
• Photo-sharing site may be implemented to satisfy multiple approach options of users. A section of users use photo-sharing site to have a glimpse of the newly arrived documents, highlights of catalogue, rare books, etc. Some others may use it to find images of historical importance with context. New users may find it attractive to pay
How to add a bigger hard drive to the PlayStation 4.
https://www.facebook.com/techinsider/videos/595046657360361/
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
more on game consoles in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=playstation
Internet of Things: A Primer for Product Managers
https://medium.com/@delizalde/internet-of-things-a-primer-for-product-managers-5b6bef0a8b9b#.aitrbiy0h
The first step to becoming an IoT Product Manager is to understand the 5 layers of the IoT technology stack.
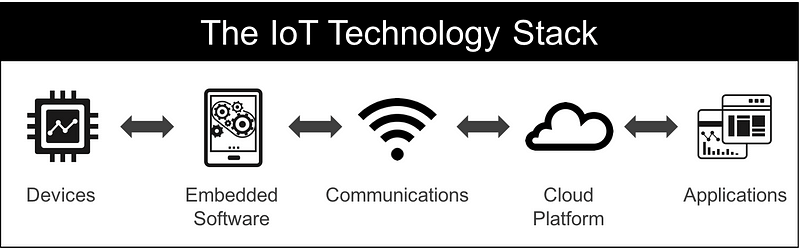
1. Devices
Devices constitute the “things” in the Internet of Things. They act as the interface between the real and digital worlds.
2. Embedded software
Embedded software is the part that turns a device into a “smart device”. This part of the IoT technology stack enables the concept of “software-defined hardware”, meaning that a particular hardware device can serve multiple applications depending on the embedded software it is running.
Embedded Operating System
The complexity of your IoT solution will determine the type of embedded Operating System (OS) you need. Some of the key considerations include whether your application needs a real-time OS, the type of I/O support you need, and whether you need support for the full TCP/IP stack.
Common examples of embedded OS include Linux, Brillo (scaled-down Android), Windows Embedded, and VxWorks, to name a few.
Embedded Applications
This is the application(s) that run on top of the embedded OS and provide the functionality that’s specific to your IoT solution.
3. Communications
Communications refers to all the different ways your device will exchange information with the rest of the world. This includes both physical networks and the protocols you will use.
4. Cloud Platform
The cloud platform is the backbone of your IoT solution. If you are familiar with managing SaaS offerings, then you are well aware of everything that is entailed here. Your infrastructure will serve as the platform for these key areas:
Data Collection and Management
Your smart devices will stream information to the cloud. As you define the requirements of your solution, you need to have a good idea of the type and amount of data you’ll be collecting on a daily, monthly, and yearly basis.
Analytics
Analytics are one of they key components of any IoT solution. By analytics, I’m referring to the ability to crunch data, find patterns, perform forecasts, integrate machine learning, etc. It is the ability to find insights from your data and not the data alone that makes your solution valuable.
Cloud APIs
The Internet of Things is all about connecting devices and sharing data. This is usually done by exposing APIs at either the Cloud level or the device level. Cloud APIs allow your customers and partners to either interact with your devices or to exchange data. Remember that opening an API is not a technical decision, it’s a business decision.
Related post: The Business of APIs: What Product Managers Need to Plan For
5. Applications
This is the part of the stack that is most easily understood by Product teams and Executives. Your end-user applications are the part of the system that your customer will see and interact with. These applications will most likely be Web-based, and depending on your user needs, you might need separate apps for desktop, mobile, and even wearables.
The Bottom Line
As the Internet of Things continues to grow, the world will need an army of IoT-savvy Product Managers. And those Product Managers will need to understand each layer of the stack, and how they all fit together into a complete IoT solution.
++++++++++++++
more on Internet of Things in this blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=internet+of+things
https://www.facebook.com/trustmewebdesigner/posts/1018089721650451
IP‐Please, design and development of an educational game on IT‐security
Peter Mozelius, Charlotte Lesley and Ola Olsson
Department of Computer and Systems Sciences, Stockholm University, Sweden
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308947931_IP-Please_design_and_development_of_an_educational_game_on_IT-security
Abstract:
Game‐based learning is a research field with rich discussions on the use of games in educational contexts. Many of the educational games that exist today focus on subjects such
as Language learning, Mathematics and History, and fewer on subjects in Computer Science
and IT‐security. Dissemination of information about IT‐security is important in today’s digital
society not at least in the industry. As an example many firewalls today are misconfigured
leading to decreased security at the same time as it is hard to motivate students or employees to read long detailed and tedious PDF‐files with security information. Might
things like firewall configuration instead be learnt by an educational game and how to design
a learning game that could be used in university courses on IT‐security?
++++++++++++++++++
more on gaming and gamification in this blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=gaming
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=gamification


