Nov
2016
21 century pedagogy
http://www.educatorstechnology.com/2013/03/awesome-graphic-on-21st-century-pedagogy.html
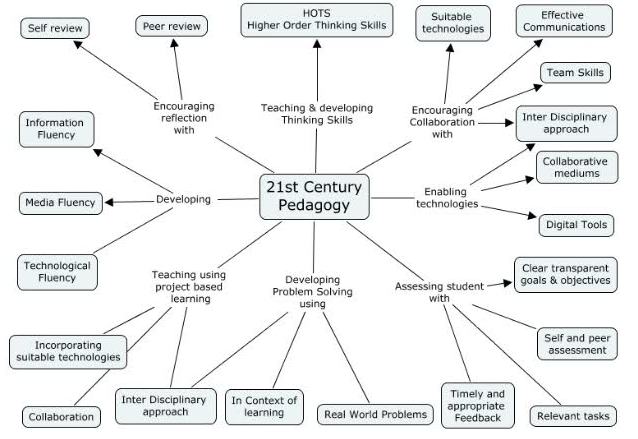
+++++++++++++++
more on modern pedagogy
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=pedagogy
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
http://www.educatorstechnology.com/2013/03/awesome-graphic-on-21st-century-pedagogy.html

+++++++++++++++
more on modern pedagogy
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=pedagogy
The 2015 Innovating Pedagogy Report proposes ten innovations that explore ways of teaching, learning, and assessment for an interactive, engaged world.
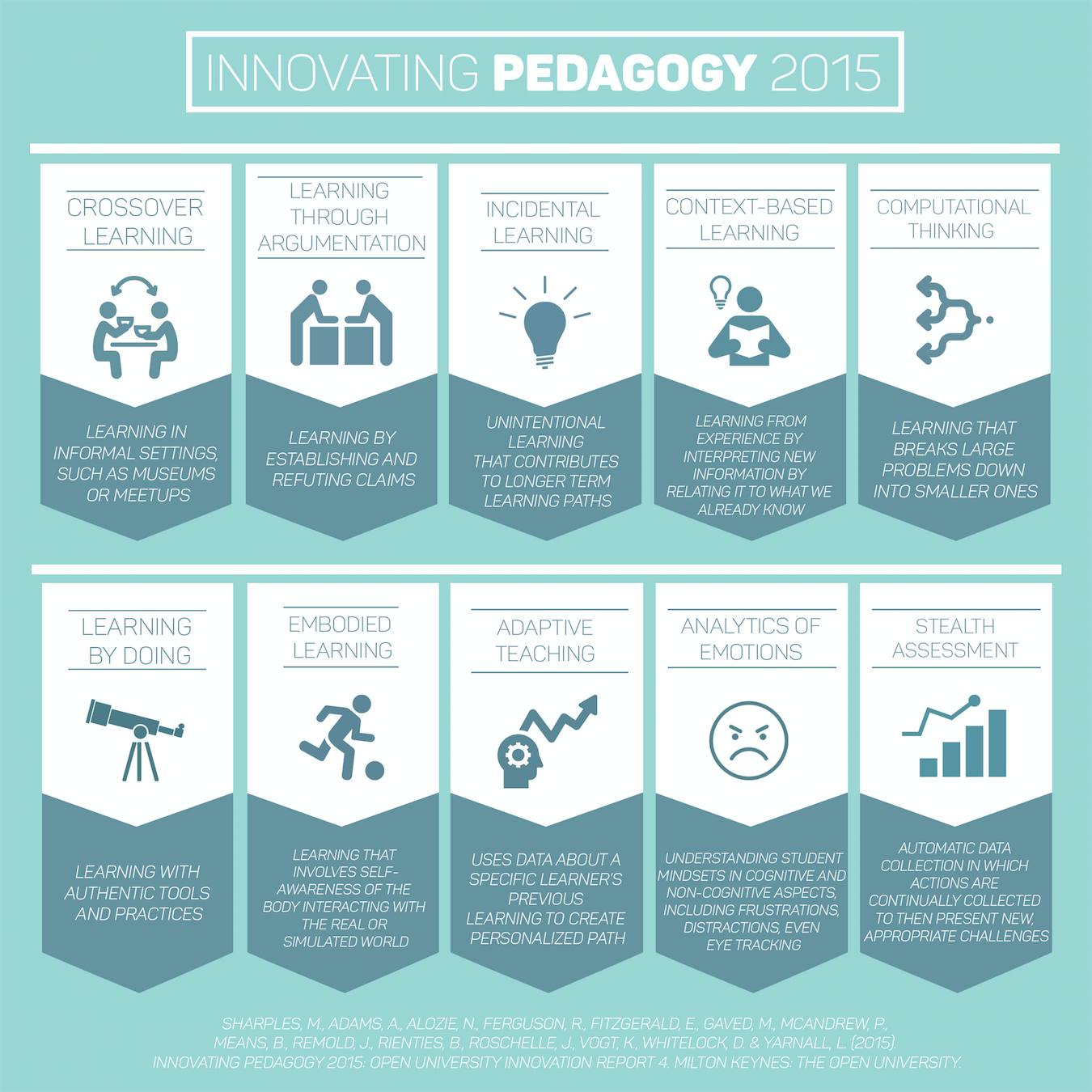
This article pleads for a consideration what now is a full-blown reform in Finland (replacing subjects with topics) and seriously considered in the UK, as reported in this IMS blog: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/03/24/education-reform-finland/
there’s a long-standing and still fairly widely held belief that the teaching needed for a particular kind of content is unique. Unless you know the content, you can’t know how to teach it.
What and how we teach are linked, but there are other connections besides those between method and material, and those connections aren’t all unique to the discipline. All (well, almost all) teachers want students engaged, and student engagement in physics and philosophy doesn’t look all that different. All teachers are concerned with classroom management issues. If students are dealing more with their phones than the material, the content is irrelevant. All teachers have a responsibility to prevent cheating. All teachers aspire to use fair and equitable grading practices. Course design principles transcend disciplines. The features of a good multiple-choice question are not discipline specific. And then there are those student characteristics that challenge teachers in every field: passivity, lack of motivation, low self-esteem, less than adequate study skills, and excessive grade-orientation start the list.
Mark Zuckerberg’s Sister Published A Book About A Child Whose Mom Takes Her iPad Away
http://www.businessinsider.com/randi-zuckerbergs-kids-book-dot-2013-11#ixzz2jmchiAAf
social media etiquette
unplug
http://www.nytimes.com/2013/11/03/books/review/randi-zuckerbergs-dot-complicated-and-dot.html
Contemplative Pedagogy and Dealing with Technology
Dan Barbezat, Amherst College; David Levy, University of Washington
The accelerating pace of life is reducing the time for thoughtful reflection and in particular for contemplative scholarship, within the academy. The loss of time to think is occurring at exactly the moment when scholars, educators, and students have gained access to digital tools of great value to scholarship. This interactive session reviews research on technology’s impacts and demonstrates some contemplative practices that can respond to them. Contemplative pedagogy can offset the distractions of our multi-tasking, multi-media culture, and show how the needs of this generation of students can be met through innovative teaching methods that integrate secular practices of contemplation.
Topics: Faculty Professional Development, Teaching & Learning
Walking the Labyrinth: Contemplative Instructional Techniques to Enhance Learner Engagement
Carol Henderson and Janice Monroe, Ithaca College
Bringing ancient traditional meditative skills into the contemporary classroom, con-templative learning techniques serve as an effective counterbalance to the speedi-ness and distractions of today’s fast-paced technology-based cultural environment. Applicable to both faculty development programs and to faculty working directlywith students, contemplative methods create a richer, more engaging learningenvironment by allowing participants to quiet their minds and focus deeply on the material at hand. This interactive session provides instruction and practice in con-templative techniques, offers examples of their use, and supports the integration of these techniques into any discipline or subject area.
Topics: Faculty Professional Development, Teaching & Learning
Contemplative Computing and Our Future of Education
Alex Soojung-Kim Pang, Stanford University
A generation of educators have spent their professional lives hearing that technol-
ogy is changing the world, transforming the way we think, and that higher educa-
tion must evolve or become obsolete. In case you didn’t get the message in the
1960s and 1970s, with cassette tapes, television and mainframe computers, it was
repeated in the 1980s when personal computers appeared; repeated again in the
1990s, with CD-ROMs (remember those) and the World Wide Web; repeated again
in the early 2000s with blogs and wikis; and recently, repeated once again in the
wake of social media, YouTube and the real-time Web.
This language of technological revolution and institutional reaction is backward. It
gives too much credit and agency to technology, and makes today’s changes seem
unprecedented and inevitable. Neither is actually true. Contemplative computing—
the effort to design technologies and interactions that aren’t perpetually demanding
and distracting, but help users be more mindful and focused—provides a language
for talking differently about the place of technology in teaching, learning, and edu-
cation. We think of today’s technologies as uniquely appealing to our reptilian, dopa-
mine- and stimulation-craving brains. In reality, distraction is an ancient problem,
and the rise of contemplative practices and institutions (most notably monasteries
and universities) is a response to that problem. Abandoning our traditional role as
stewards of contemplative life is as dangerous for the societies we serve as it is
short-sighted and counterproductive. Contemplative computing argues that even
today, people have choices about how to interact with technologies, how to use
them, and how to make the parts of our extended minds; and that part of our job
as educators is to show students how to exercise that agency.
https://www.edsurge.com/news/2021-12-10-in-china-online-degrees-on-hold-even-as-moocs-rise
With China muscling its way into the first ranks as a global power in science and technology—building vast new academic complexes, climbing to the top ranks of the world’s elite universities, surpassing the U.S. in PhD graduates in science and engineering, and on its way to outperforming all other nations in science and technology academic citations—I was puzzled to discover that China is on hold in offering online higher ed degrees.
To expand the nation’s technical talent pool, Chinese universities are upgrading their capacity to offer more up-to-date science and technology courses, with universities just beginning to introduce degrees in artificial intelligence, machine learning, software engineering and other advanced specialties. For China, the move is a departure from its centuries-old tradition of favoring literature and the liberal arts.
China has come a long way from cinema-style instruction to adopt more common digital learning practices, often closely following U.S. advances in online pedagogy, such as flipped classrooms and MOOCs.
Curiously, China’s reluctance to offer online degrees parallels the attitude toward online degrees in the Ivy League in the U.S.—both have embraced MOOCs while turning away from virtual degrees out of concern that remote degrees will damage their reputations.
+++++++++++++++++++++
more on online ed in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=online+education
Despite decades of evidence, good teaching is still considered more art than science. That’s hurting faculty and students alike.
https://www.chronicle.com/article/the-damaging-myth-of-the-natural-teacher
Even as universities have become more bureaucratic and centrally controlled, teaching continues to operate largely independent of oversight
when she was a college administrator, before becoming a professor, she was expected to spend two to four hours a week on professional development. It was written into her job description. Her training as a faculty member, by contrast, “has all been self directed, self led, things I want to do. It’s never been part of my annual evaluation.”
At most research universities if you were publishing in pedagogy journals they would not be counted or weighted as heavily as if you were publishing in a traditional journal.
Valencia College, a community college in Central Florida that relies heavily on part-time instructors, encourages them to improve their teaching by offering certificates and pay increases for participating in 60 hours of professional development.
Some of the most notable reform efforts are coming from external funders and academic associations. The National Science Foundation, the Association of American Universities, the John N. Gardner Institute for Excellence in Undergraduate Education, the American Historical Association, the National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine, and others have sponsored research and projects on teaching reform, including work on how to advance discipline-based education research.
a pilot program at Kansas to reinvent the evaluation process, as part of a multi-campus project called TEval. The new process, she says, considers seven benchmarks, including course planning, class climate, and evidence of student learning. Teaching reviews consider, for example, how well course content is aligned with the curriculum, whether a faculty member is involved in scholarship about pedagogy, and how much time they spend advising and mentoring students. Departments are also encouraged to develop “peer triads,” in which small groups of faculty members whose coursework is related meet regularly to talk about their teaching and course design.
He and his peers were heavily involved in pedagogical innovation on campus, including the Center for Project Based Learning and discipline-based education research.
++++++++++++++++++
More on teaching in this blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=teach
Annemaree Lloyd
https://www.alastore.ala.org/infolitresearch?_zs=HxthW1&_zl=7kkv7
+++++++++++++++++++++++
more on information literacy in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=information+literacy
https://www.universityworldnews.com/post.php?story=20210126142422302
The gate is now wide open
Teachers used to be the gatekeepers to information, to knowledge. The successive inventions of writing and reading, print, the library, and then the World Wide Web, mean that we teachers are no longer the gatekeepers.
Schools, universities and teachers to some extent remain the gatekeepers to knowledge, the definers of what comprises valid knowledge. We do this, of course, through holding the ultimate educational power – the power to assess.
But it is not clear how long we teachers will, or should, hold this power. Increasingly, students, and employers, nations, cultures, many groups in our societies, rightly want a say in defining what is valid knowledge, a valid curriculum.
Knowledge isn’t enough
Each year, vast amounts of new knowledge are produced. Also, each year, vast amounts of current knowledge become wrong, or redundant, or both. Knowledge dies. In some subjects, a significant proportion of what was taught in the first year will have died by the time the students who learned it graduate. So, what is education for?
Machines are doing more and more of the work
The bad news is, we are getting squeezed out of work. The good news is, we are getting squeezed up, into ever more interesting work. We will be able to stay ahead for a long time; because there are always still more difficult and important and exciting things for us to do, increasingly with the support of our increasingly capable machines.
Employers want graduates to be job-ready. They also want graduates to be fluent in the five Cs: Creativity, Communication, Collaboration and Criticality as well as Competence. Not all university education currently develops the first four Cs. Very little university education currently gives high priority to their development. Rarely are they formally assessed.
Changing outcomes, changing pedagogies
The architecture of a university expresses its views about pedagogy. This remains true with the great leap online. The old pedagogic architecture – of teaching as (mainly) telling, of learning as (mainly) listening and reading, of access in and through the library to specified stored knowledge, and of assessment as (mainly) recalling, repeating back what has been learned, perhaps with some application or interpretation – has for the most part been recreated in digital form, with varying degrees of success
+++++++++++
more on online education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=online+education