Emotional Intelligence Has 12 Elements. Which Do You Need to Work On?
https://hbr.org/2017/02/emotional-intelligence-has-12-elements-which-do-you-need-to-work-on
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
https://hbr.org/2017/02/emotional-intelligence-has-12-elements-which-do-you-need-to-work-on
As more jobs require postsecondary training, more providers jump in to offer it — including fakes and scammers
https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2021/12/26/education-credential-certificate-scams/
a “maze” of nearly a million unique education credentials in the United States, the nonprofit Credential Engine reports, including not only degrees but also badges, certificates, licenses, apprenticeships and industry certifications.
The way new kinds of credentials are being developed and awarded is “a bit like the wild West,” a study by the Rutgers University Education and Employment Research Center found.
Even before the pandemic and the subsequent labor squeeze, 39 percent of human resources managers said they spent less than a minute reading a resume, according to a survey by CareerBuilder.
Conventional higher education institutions are increasingly alarmed about the holes that have developed in a system that was previously much simpler.
A quarter of American adults now hold nondegree credentials, meaning something short of an associate or bachelor’s degree, according to federal data, and they’ve become more popular in recent years.
“As online education becomes normalized, as a credential from Google or Microsoft can get someone a job, all of a sudden we’re in an environment where higher education doesn’t have a monopoly on education,” Ahluwalia said.
The Credential Engine Registry so far includes full or partial information on about 30,000 educational credentials. That’s about 3 percent of the total it eventually hopes to list.
+++++++++++++
more on credentials in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=credentials
BLEND-ONLINE : Call for Chapter Proposals– Privacy and Remote Learning
Digital Scholarship Initiatives at Middle Tennessee State University invites you to propose a chapter for our forthcoming book.
Proposal submission deadline: January 21, 2022
Interdisciplinary perspectives are highly encouraged
Topics may include but are not limited to:
More details, timelines, and submission instructions are available at dsi.mtsu.edu/cfpBook2022
Alan Liu, Urszula Pawlicka-Deger, and James Smithies, Editors
Deadline for 500-word abstracts: December 15, 2021
Part of the Debates in the Digital Humanities Series A book series from the University of Minnesota Press Matthew K. Gold and Lauren F. Klein, Series Editors
Defintion
Critical infrastructure studies has emerged as a framework for linking thought on the complex relations between society and its material structures across fields such as science and technology studies, design, ethnography, media infrastructure studies, feminist theory, critical race and ethnicity studies, postcolonial studies, environmental studies, animal studies, literary studies, the creative arts, and others (see the CIstudies.org Bibliography )
https://dhdebates.gc.cuny.edu/projects/debates-in-the-digital-humanities-2019
teaching quantitative methods:
https://dhdebates.gc.cuny.edu/read/untitled-f2acf72c-a469-49d8-be35-67f9ac1e3a60/section/620caf9f-08a8-485e-a496-51400296ebcd#ch19
An informal consensus seems to have emerged that if students in the humanities are going to make use of quantitative methods, they should probably first learn to program. Introductions to this dimension of the field are organized around programming languages: The Programming Historian is built around an introduction to Python; Matthew Jockers’s Text Analysis with R is at its heart a tutorial in the R language; Taylor Arnold and Lauren Tilton’s Humanities Data in R begins with chapters on the language; Folgert Karsdorp’s Python Programming for the Humanities is a course in the language with examples from stylometry and information retrieval.[11] “On the basis of programming,” writes Moretti in “Literature, Measured,” a recent retrospective on the work of his Literary Lab, “much more becomes possible”
programming competence is not equivalent to competence in analytical methods. It might allow students to prepare data for some future analysis and to produce visual, tabular, numerical, or even interactive summaries; Humanities Data in R gives a fuller survey of the possibilities of exploratory data analysis than the other texts.[15] Yet students who have focused on programming will have to rely on their intuition when it comes to interpreting exploratory results. Intuition gives only a weak basis for arguing about whether apparent trends, groupings, or principles of variation are supported by the data.
Bobby L. Smiley
First hired as a “digital humanities librarian,” I saw my title changed within less than a year to “digital scholarship librarian,” with a subject specialty later appended (American History). Some three-plus years later at a different institution, I now find myself a digital-less “religion and theology librarian.” At the same time, in this position, my experience and expertise in digital humanities (or “digital scholarship”) are assumed, and any associated duties are already baked into the job description itself.
Jonathan Senchyne has written about the need to reimagine library and information science graduate education and develop its capacity to recognize, accommodate, and help train future library-based digital humanists in both computational research methods and discipline-focused humanities content (368–76). However, less attention has been paid to tracking where these digital humanities and digital scholarship librarians come from, the consequences and opportunities that arise from sourcing librarians from multiple professional and educational stations, and the more ontological issues associated with the nature of their labor—that is, what is understood as work for the digital humanist in the library and what librarians could be doing.
++++++++++++++++++++++
More on digital humanities in this blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=Digital+humanities
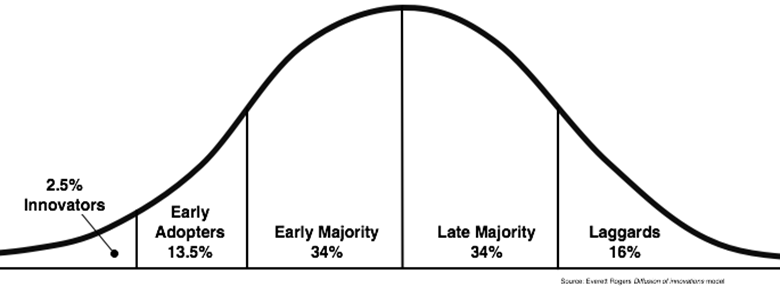
This theory has been used successfully in many fields including communication, agriculture, public health, criminal justice, social work, and marketing.
++++++++++++++++++
more on instructional design in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=instructional+design
+++++++++++++++
more on flipped classroom in this iMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=flipped+classroom
https://cognitiontoday.com/pros-and-cons-of-online-education-and-learning/
Cons/Disadvantages of learning online
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Generation_Alpha
https://bestlifeonline.com/generation-alpha-facts/
Baby Boomers, Gen X, Millennials, Gen Z: What Generation Am I?
+++++++++++++++
more on online ed in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=online+education
https://www.edweek.org/ew/articles/2020/11/18/why-school-board-diversity-matters.html
Both superintendents and board members have a role to play in elevating different voices, say school board members. District leaders can’t pick candidates, but they can create “leadership academies” to teach interested community members about the workings of their school systems. They can also create committees and other advisory boards that allow parents an entry point into getting more involved in their school district, if they choose.
A 2017 study that examined middle and high schools in Florida found that districts with diverse school boards have lower rates of school suspensions for all students, and that disparities in suspension rates between minority and white students are reduced overall.
+++++++++++++++
more on school board in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=school+board
https://www.gse.harvard.edu/news/20/10/harvard-edcast-making-online-learning-work
There’s a distinction between online and using technology versus distance learning.
It’s going to become a lot more interactive, a lot more personal, and then teachers are going to be able to zero in a lot more on what the kids need.
A lot of teachers feel a lot of pressure to have these perfectly planned lesson plans that go exactly as intended when you get into the classroom. In this environment, it’s okay to not have the planning perfect. It’s okay if things get a little bit extemporaneous, a little improvisational in the classroom.
If I’m a teacher looking at the pie of time and energy that I have in a given week, I would try to minimize the energy that I have to put into things where I’m not interacting with students …
Teachers putting a lot of time and energy getting a setup like I have with a microphone and a pen tablet and all of that. That takes a lot of work, a lot of energy, and it’s energy that once again gets taken away from time that they could be interacting with students.
++++++++++++++
more on online learning in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=online+learning