An excellent example of practical approach to a real digital storytelling case:
https://plus.google.com/+GeorgeCohn/posts/XfaXtgp5amA
++++++++++++++++++++
more on digital storytelling in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=digital+storytelling
Blackboard Learn Gets Dropbox Integration
By David Nagel 10/25/2016
https://thejournal.com/articles/2016/10/25/blackboard-learn-gets-dropbox-integration.aspx
Announced at the Educause 2016 conference, Blackboard Learn users will now be able to collaborate on documents using the cloud sharing platform Dropbox.
My note: BB is only catching up with Google, which has Google Drive (~ Dropbox) and Google Classroom (~ BB). It doesn’t matter how much hype BB is trying to produce, the fact is that BB is behind.
D2L is even farther behind, without an integration of any video tool. Google has Google Hangouts and BB purchased several video conferencing tools until it got “the right one.”
D2L announce in 2010 an integration with Skype but it has not happened. Now, D2L will be double behind without integration of a cloud-based file space.
++++++++++++++++++
more on LMS in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=lms
Stanford VR Project Shows Students Oceans of the Future
By Dian Schaffhauser 10/19/16
https://thejournal.com/articles/2016/10/19/stanford-vr-project-shows-students-oceans-of-the-future.aspx
A new, free virtual reality program allows users to explore just what happens as climate change kills off coral reefs. The Stanford Ocean Acidification Experience is a free science education tool that takes students to the bottom of the sea and then fast-forwards their experience to the end of this century, when, as scientists predict, many coral reefs are expected to corrode through ocean acidification. By putting the experience in VR, the collaborators say they are hoping to change people’s behavior in the real world.
The project came out of Stanford’s Virtual Human Interaction Lab, which created a related 360-degree video project that also examines the problem of global warming and its impact on the ocean’s life forms. But it’s the VR version that allows the viewer to deep-sea dive and collect samples off of the ocean floor.
The lab created the software in partnership with marine biologists Fiorenza Micheli from Stanford and Kristy Kroeker, formerly at Stanford and now at the University of California, Santa Cruz, as well as Roy Pea, a professor at Stanford’s Graduate School of Education. The development process took two years to recreate a virtual replica of an actual rocky reef around the Italian island of Ischia
A related video, “The Crystal Reef,” filmed in 360 degrees and developed as part of a master’s degree project by a lab member, premiered during the Tribeca Film Festival earlier this year. There, people could watch the film on VR headgear. “We had a line of dozens of people for 11 hours a day, six days straight,” said Bailenson, in a Stanford article about the project.
The VR project has also gone to Washington, where lawmakers and staffers tried it out during a Capitol Hill event organized by non-profit Ocean Conservancy.
+++++++++++++++++++
more on virtual reality in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+reality
NMC Releases Horizon Project Strategic Brief on Digital Literacy
Anaheim, California (October 25, 2016) — The New Media Consortium (NMC) has released Digital Literacy: An NMC Horizon Project Strategic Brief in conjunction with the 2016 EDUCAUSE Annual Conference.
This project was launched because there is a lack of consensus across the field about how to define digital literacy and implement effective programs. A survey was disseminated throughout the NMC community of higher education leaders and practitioners to understand how digital literacy initiatives are impacting their campuses. The NMC’s research examines the current landscape to illuminate multiple models of digital literacy — universal literacy, creative literacy, and literacy across disciplines — around which dedicated programs can proliferate a spectrum of skills and competencies.
p. 8-10 examples across US universities on digital literacy organization
p. 12 Where does support for digital literacy come from your institution? Individual people

p. 13. campus libraries must be deeply embedded in course curriculum. While libraries have always supported academic institutions, librarians can play a more critical role in the development of digital literacy skills. Historically, these types of programs have been implemented in “one-off” segments, which are experienced apart from a student’s normal studies and often delivered in a one-size-fits-all method. However, an increasing number of academic libraries are supporting a more integrated approach that delivers continuous skill development and assessment over time to both students and faculty. This requires deeper involvement with departments and agreeing on common definitions of what capacities should be achieved, and the most effective pedagogical method. Librarians are tasked with broadening their role in the co-design of curriculum and improving their instruction techniques to work alongside faculty toward the common goal of training students to be savvy digital researchers. University of Arizona Libraries, for example, found that a key step in this transition required collaborating on a common instructional philosophy.
 +++++++++++++++
+++++++++++++++
more on digital literacy in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=digital+literacy
Save
Book Announcement: Implementing Mobile Language Learning Technologies in Japan
New book: Implementing Mobile Language Learning Technologies in Japan
by Steve McCarty, Hiroyuki Obari, and Takeshi Sato
Publisher: Springer Singapore / SpringerBriefs in Education (107 pages)
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction: Contextualizing Mobile Language Learning in Japan
Chapter 2 Mobile Language Learning Pedagogy: A Sociocultural Perspective
Chapter 3 Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Case Study:
Smartphone App LINE for EFL Peer Learning
Chapter 4 Osaka Jogakuin University Case Study:
Mobilizing the EFL Curriculum and Campus Infrastructure with iPods and iPads
Chapter 5 Aoyama Gakuin University Case Study:
Blended Learning and Flipped Classrooms utilizing Mobile Devices
Chapter 6 Conclusion: Implementing Language Learning in a Mobile-Oriented Society
Abstract
This book explores theoretical and practical aspects of implementing mobile language learning in university classrooms for English as a Foreign Language in Japan. The technologies utilized, such as smartphones, iPads, and wi-fi, integrate students’ hand-held devices into the campus network infrastructure. The pedagogical aims of ubiquitous mobile learning further incorporate social media, blended learning, and flipped classroom approaches into the curriculum. Chapter 1 defines mobile language learning within dimensions of e-learning and technology-assisted language learning, prior to tracing the development of mobile learning in Japan. Chapter 2 documents the sociocultural theory underpinning the authors’ humanistic approach to implementation of mobile technologies. The sociocultural pedagogy represents a global consensus of leading educators that also recognizes the agency of Asian learners and brings out their capability for autonomous learning. Case studies of universities, large and small, public and private, are organized similarly in Chapters 3 to 5. Institutional/pedagogical and technological context sections are followed by detailed content on the implementation of initiatives, assessment of effectiveness, and recommendations for other institutions. Distinct from a collection of papers, this monograph tells a story in brief book length about theorizing and realizing mobile language learning, describing pioneering and original initiatives of importance to practitioners in other educational contexts.
Authors
Steve McCarty lectures for Kansai University, Osaka Jogakuin University, KIC Graduate School of IT, and the government agency JICA.
Hiroyuki Obari, PhD in Computer Science, is a Professor at the Aoyama Gakuin University College of Economics in Tokyo.
Takeshi Sato is an Associate Professor at the Division of Language and Culture Studies, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology.
Ordering information from Springer
Paperback (ISBN: 978-981-10-2449-8):
http://www.springer.com/us/book/9789811024498
eBook (ISBN: 978-981-10-2451-1) or individual chapters:
http://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-981-10-2451-1
++++++++++++++++++++++
more on mobile technologies in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=mobile+devices
5 ways virtual reality is being used in education right now
By Meris Stansbury
1. For new research: using a state-of-the-art “haptic” floor of aeronautic metal that vibrates and moves to stimulate the physical world for research on how VR has the potential to change the way users feel and behave. There may also be implications for confronting racism, sexism, and aiding in
empathy and humanitarian efforts, says Bailenson.
2. For coding and 3D design:
According to Bob Nilsson, director of Vertical Solutions Marketing for Extreme Networking, the University of Maryland, College Park, now offers a class on virtual reality that gives students the opportunity to design their own interactive world, work with 3D audio and experiment with immersive technology through a combination of hands-on learning and case studies. Also, the University of Georgia is offering similar classes where students design and explore applications for VR. Conrad Tucker, an assistant professor of engineering at Pennsylvania State University, has received funding to build a virtual engineering lab where students hold, rotate, and fit together virtual parts as they would with their real hands.
3. For anatomy and dissection: Said one Extreme Networks survey respondent, “Our students have been developing a VR model of a cow’s anatomy for dissection and study. You have the ability to drill down to the circulatory system, brain, muscle, skeleton, etc. Our applied tech program is using VR in conjunction with Autocad for models of projects they design.”
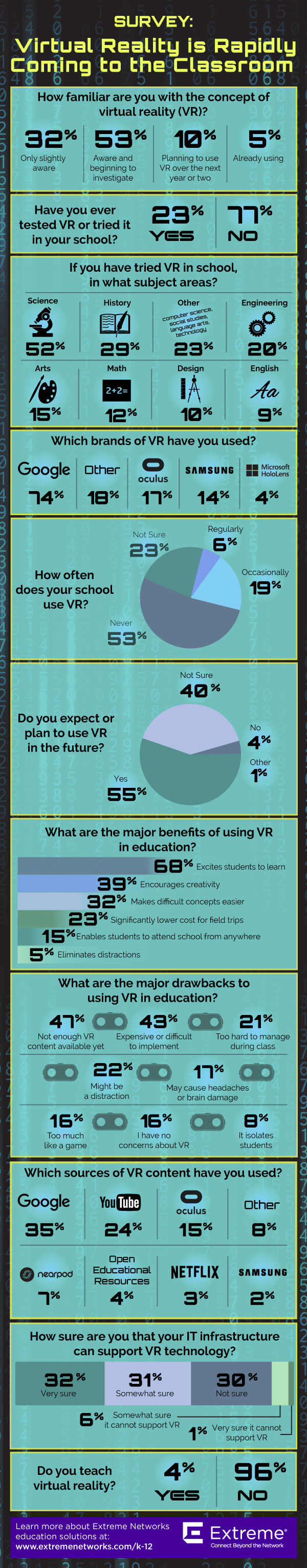
4. For engagement: A whopping 68 percent of survey respondents said the major benefit of using VR in education is to excite students about the subject matter. 39 percent said it’s great for encouraging creativity.
5. For field trips: Google has eliminated restrictions on Expeditions, their VR field trips program. Google Expeditions was cited in the survey as one of the most popular sources of VR content, but with the complaint that it was a restricted program.
comment:
·
Virtual reality may have its place, but until traditional education moves away from their 20th century teaching methodology and replaces it with educationally innovative, 21st century learning methodology, within a blended and flipped learning environment, virtual reality is currently, much ado about nothing.
Unless any new application is educationally innovative and directly and measurably contributes to effective, efficient, consistent, affordable, relevant advanced student success outcomes for ALL students, future innovations must wait for current innovations to be implemented.
This process of appriate choice and appropriate implemention must start at the top and be beta tested for measured student success before its rolled out system wide.
+++++++++++++++
more on VR in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=virtual+reality
Save






