NMC Horizon Report > 2017 Library Edition
http://www.nmc.org/publication/nmc-horizon-report-2017-library-edition/
PDF file 2017-nmc-horizon-report-library-EN-20ml00b
p. 26 Improving Digital Literacy
As social networking platforms proliferate and more interactions take place digitally, there are more opportunities for propagation of misinformation, copyright infringement, and privacy breaches.
p. 34 Embracing the need for radical change
40% of faculty report that their students ” rarely” interact with campus librarians.
Empathy as the Leader’s Path to Change | Leading From the Library, By Steven Bell on October 27, 2016, http://lj.libraryjournal.com/2016/10/opinion/leading-from-the-library/empathy-as-the-leaders-path-to-change-leading-from-the-library/
Empathy as a critical quality for leaders was popularized in Daniel Goleman’s work about emotional intelligence. It is also a core component of Karol Wasylyshyn’s formula for achieving remarkable leadership. Elizabeth Borges, a women’s leadership program organizer and leadership consultant, recommends a particular practice, cognitive empathy.
Leadership in disruptive times, James M. Matarazzo, Toby Pearlstein, First Published September 27, 2016, http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0340035216658911
What is library leadership? a library leader is defined as the individual who articulates a vision for the organization/task and is able to inspire support and action to achieve the vision. A manager, on the other hand, is the individual tasked with organizing and carrying out the day-to-day operational activities to achieve the vision.Work places are organized in hierarchical and in team structures. Managers are appointed to administer business units or organizations whereas leaders may emerge from all levels of the hierarchical structures. Within a volatile climate the need for strong leadership is essential.
Leaders are developed and educated within the working environment where they act and co-work with their partners and colleagues. Effective leadership complies with the mission and goals of the organization. Several assets distinguish qualitative leadership:
Mentoring. Motivation. Personal development and skills. Inspiration and collaboration. Engagement. Success and failure. Risk taking. Attributes of leaders.
Leaders require having creative minds in shaping strategies and solving problems. They are mentors for the staff, work hard and inspire them to do more with less and to start small and grow big. Staff need to be motivated to work at their optimum performance level. Leadership entails awareness of the responsibilities inherent to the roles of a leader. However, effective leadership requires the support of the upper management.
p. 36. Developments in Technology for Academic and Research Libraries
http://horizon.wiki.nmc.org/Horizon+Topics
- consumer technologies
- Digital strategies are not so much technologies as they are ways of using devices and software to enrich teaching, learning, research and information management, whether inside or outside the library. Effective Digital strategies can be used in both information and formal learning; what makes them interesting is that they transcended conventional ideas to create something that feels new, meaningful, and 21st century.
- enabling technologies
this group of technologies is where substantive technological innovation begins to be visible.
- Internet technologies.
- learning technologies
- social media technologies. could have been subsumed under the consumer technology category, but they have become so ever-present and so widely used in every part of society that they have been elevated to their own category. As well-established as social media is, it continues to evolve at a rapid pace, with new ideas, tools, and developments coming online constantly.
- Visualization technologies. from simple infographics to complex forms of visual data analysis. What they have in common is that they tap the brain’s inherent ability to rapidly process visual information, identify patterns, and sense order in complex situations. These technologies are a growing cluster of tools and processes for mining large data sets, exploring dynamic processes, and generally making the complex simple.

p. 38 Big Data
Big data has significant implications for academic libraries in their roles as facilitators and supporters of the research process. big data use in the form of digital humanities research. Libraries are increasingly seeking to recruit for positions such as research data librarians, data curation specialists, or data visualization specialists
p. 40 Digital Scholarship Technologies
digital humanities scholars are leveraging new tools to aid in their work. ubiquity of new forms of communication including social media, text analysis software such as Umigon is helping researchers gauge public sentiment. The tool aggregates and classifies tweets as negative, positive, or neutral.
p. 42 Library Services Platforms
Diversity of format and materials, in turn, required new approaches to content collection and curation that were unavailable in the incumbent integrated library systems (ILS), which are primarily designed for print materials. LSP is different from ILS in numerous ways. Conceptually, LSPs are modeled on the idea of software as a service (SaaS),which entails delivering software applications over the internet.
p. 44 Online Identity.
incorporated the management of digital footprints into their programming and resources
simplify the idea of digital footprint as“data about the data” that people are searching or using online. As resident champions for advancing digital literacy,304 academic and research libraries are well-positioned to guide the process of understanding and crafting online identities.
Libraries are becoming integral players in helping students understand how to create and manage their online identities. website includes a social media skills portal that enables students to view their digital presence through the lens in which others see them, and then learn how they compare to their peers.
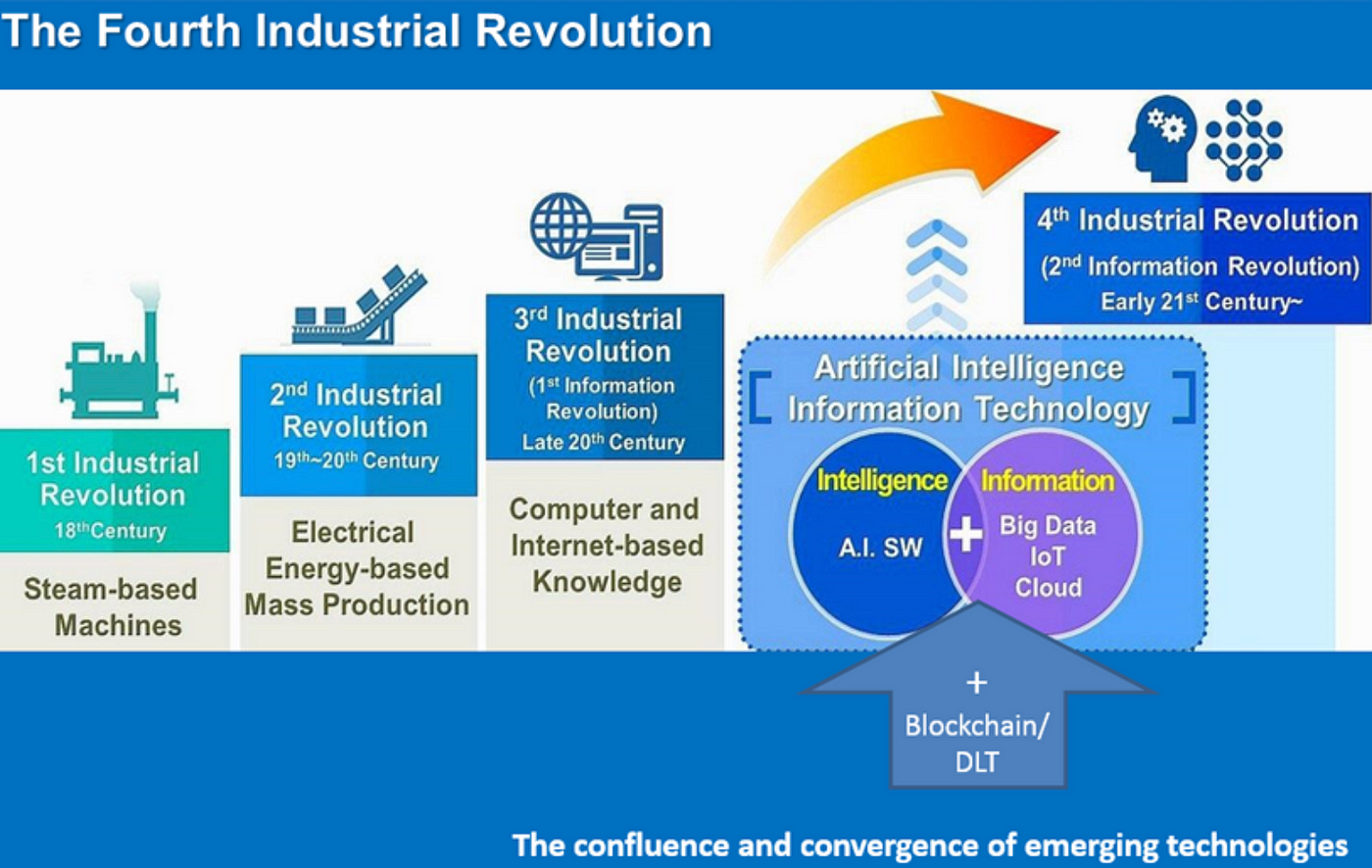
p. 46 Artificial Intelligence
https://www.semanticscholar.org/
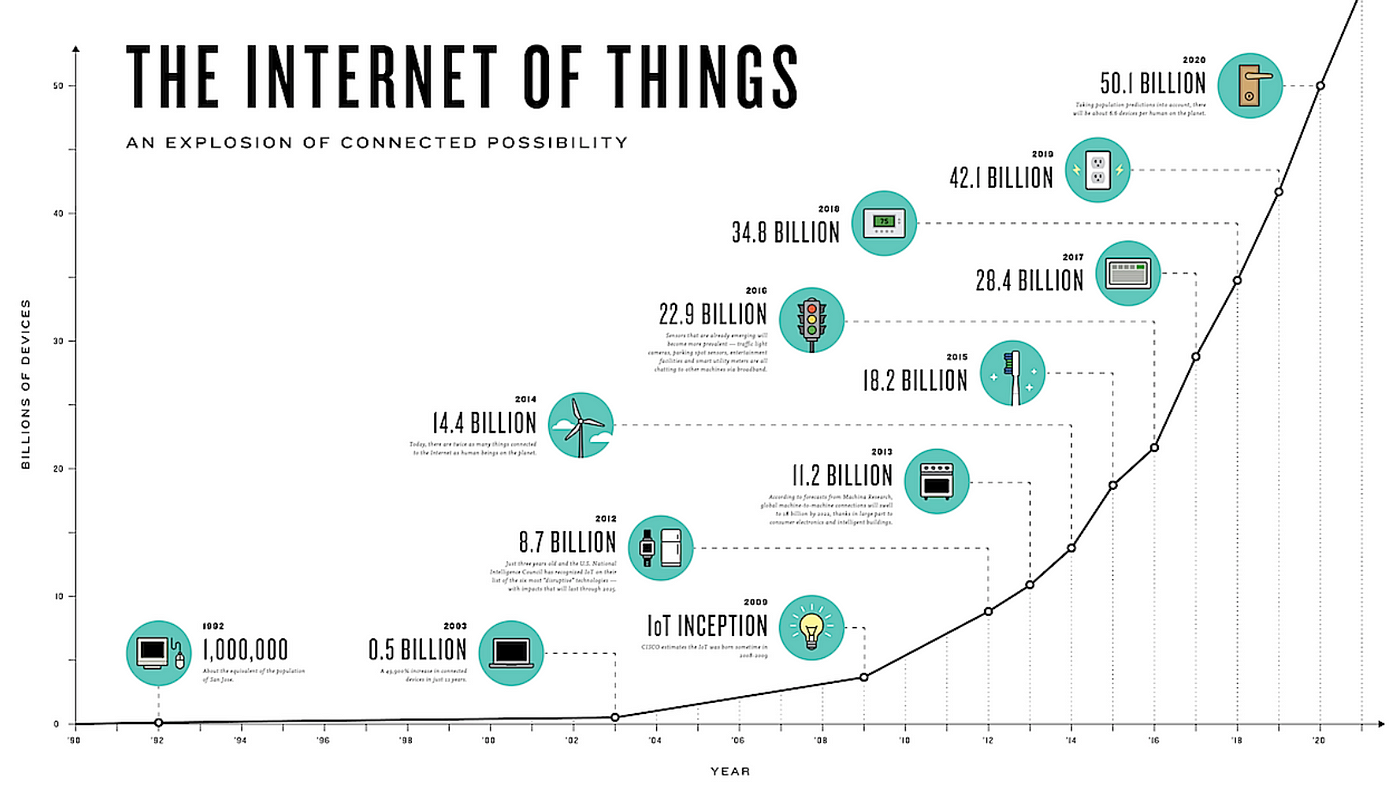
p. 48 IoT
beacons are another iteration of the IoT that libraries have adopted; these small wireless devices transmit a small package of data continuously so that when devices come into proximity of the beacon’s transmission, functions are triggered based on a related application.340 Aruba Bluetooth low-energy beacons to link digital resources to physical locations, guiding patrons to these resources through their custom navigation app and augmenting the user experience with location-based information, tutorials, and videos.
students and their computer science professor have partnered with Bavaria’s State Library to develop a library app that triggers supplementary information about its art collection or other points of interest as users explore the space
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
more on Horizon Reports in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=horizon+report