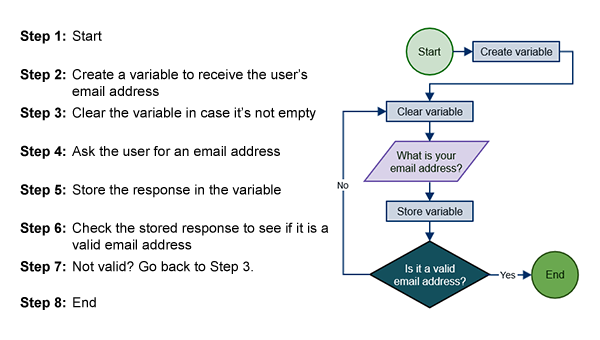
++++++++++++++
more on Parler in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=parler
Tag: media literacy
media-making skills
Students can hone their media-making skills while creating personal narrative videos as part of PBS American Portrait.
— PBS Teachers (@pbsteachers) November 17, 2020
https://tpt.pbslearningmedia.org/collection/american-portrait/
algorithm literacy
Report: Colleges Must Teach ‘Algorithm Literacy’ to Help Students Navigate Internet
By Rebecca Koenig Jan 16, 2020
Project Information Literacy, a nonprofit research institution that explores how college students find, evaluate and use information. It was commissioned by the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation and The Harvard Graduate School of Education.
focus groups and interviews with 103 undergraduates and 37 faculty members from eight U.S. colleges.
To better equip students for the modern information environment, the report recommends that faculty teach algorithm literacy in their classrooms. And given students’ reliance on learning from their peers when it comes to technology, the authors also suggest that students help co-design these learning experiences.
Algorithms and Media Literacy
+++++++++++++++++++
++++++++++++++++++++
++++++++++++++++++++
+++++++++++++
more on media literacy in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=media+literacy
more on news literacy in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=news+literate
reliable information sources
10 Journalism Brands Where You Find Real Facts Rather Than Alternative Facts
Feb 1, 2017 Paul Glader
The Poynter Institute – an enlightened non-profit in St. Petersburg, Fla., that has an ownership role in the Tampa Bay Times and provides research, training and educational resources on journalism – provides many excellent online modules to help citizens improve their news media literacy.
citizens should support local and regional publications that hew to ethical journalism standards and cover local government entities.
- https://www.nytimes.com/
- https://www.wsj.com/
- https://www.washingtonpost.com/
- http://www.bbc.com/news
- http://www.economist.com/
- http://www.newyorker.com/
- Wire Services: The Associated Press, Reuters, Bloomberg News
- https://www.foreignaffairs.com/
- https://www.theatlantic.com/
- http://www.politico.com/
Runners Up:
– National Public Radio
– TIME magazine
-The Christian Science Monitor
– The Los Angeles Times (and many other regional, metropolitan daily newspapers)
– USA Today
– CNN
– NBC News
– CBS News
– ABC News
Business News Sources:
– FORBES magazine
– Bloomberg BusinessWeek magazine
– Fortune magazine
– The Financial Times newspaper
Sources of reporting and opinion from the right of the political spectrum:
- National Review
- The Weekly Standard
Sources of reporting and opinion from the left of the political spectrum:
– The New Republic
– The Nation
+++++++++++
more on fake news in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=fake+news
video games and social-emotional learning
social-emotional learning (SEL) skills
the intersection of teacher education, learning technologies and game-based learning. He thinks educators shouldn’t ignore video games if they want students to be media-literate, because they are the “storytelling medium of the 21st century.”
gaming can help build other SEL skills, such as empathy.
Video games are good for teaching kids problem-solving and ethical decision-making
Some experts have expressed concern about how video games affect children. According to the Washington Post, the World Health Organization has recognized “gaming disorder”—characterized as a lasting addiction to video games—as a condition. Yet, not all experts agree that “game addiction” should be pathologized.
+++++++++++
more on video games in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=video+games
ICT information and communication technology literacy
The Role of Librarians in Supporting ICT Literacy
May 9, 2019,
https://er.educause.edu/blogs/2019/5/the-role-of-librarians-in-supporting-ict-literacy
Academic librarians increasingly provide guidance to faculty and students for the integration of digital information into the learning experience.
TPACK: Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge
Many librarians have shied away from ICT literacy, concerned that they may be asked how to format a digital document or show students how to create a formula in a spreadsheet. These technical skills focus more on a specific tool than on the underlying nature of information.
librarians have begun to use an embedded model as a way to deepen their connection with instructors and offer more systematic collection development and instruction. That is, librarians focus more on their partnerships with course instructors than on a separate library entity.
If TPACK is applied to instruction within a course, theoretically several people could be contributing this knowledge to the course. A good exercise is for librarians to map their knowledge onto TPACK.
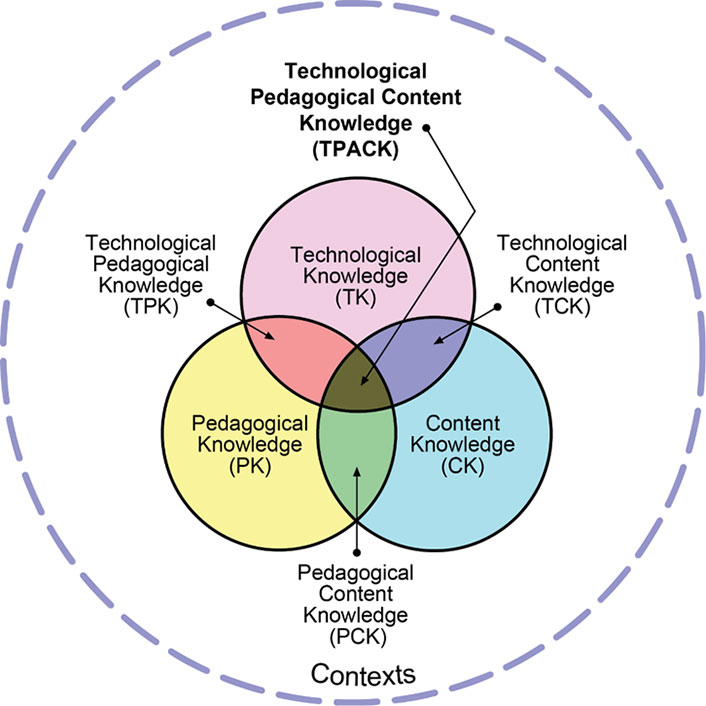
ICT reflects the learner side of a course. However, ICT literacy can be difficult to integrate because it does not constitute a core element of any academic domain. Whereas many academic disciplines deal with key resources in their field, such as vocabulary, critical thinking, and research methodologies, they tend not to address issues of information seeking or collaboration strategies, let alone technological tools for organizing and managing information.
Instructional design for online education provides an optimal opportunity for librarians to fully collaborate with instructors.
The outcomes can include identifying the level of ICT literacy needed to achieve those learning outcomes, a task that typically requires collaboration between the librarian and the program’s faculty member. Librarians can also help faculty identify appropriate resources that students need to build their knowledge and skills. As education administrators encourage faculty to use open educational resources (OERs) to save students money, librarians can facilitate locating and evaluating relevant resources. These OERs not only include digital textbooks but also learning objects such as simulations, case studies, tutorials, and videos.
Reading online text differs from reading print both physically and cognitively. For example, students scroll down rather than turn online pages. And online text often includes hyperlinks, which can lead to deeper coverage—as well as distraction or loss of continuity of thought. Also, most online text does not allow for marginalia that can help students reflect on the content. Teachers and students often do not realize that these differences can impact learning and retention. To address this issue, librarians can suggest resources to include in the course that provide guidance on reading online.
My note – why specialist like Tom Hergert and the entire IMS is crucial for the SCSU library and librarians and how neglecting the IMS role hurts the SCSU library –
Similarly, other types of media need to be evaluated, comprehended, and interpreted in light of their critical features or “grammar.” For example, camera angles can suggest a person’s status (as in looking up to someone), music can set the metaphorical tone of a movie, and color choices can be associated with specific genres (e.g., pastels for romances or children’s literature, dark hues for thrillers). Librarians can explain these media literacy concepts to students (and even faculty) or at least suggest including resources that describe these features
My note – on years-long repetition of the disconnect between SCSU ATT, SCSU library and IMS –
instructors need to make sure that students have the technical skills to produce these products. Although librarians might understand how media impacts the representation of knowledge, they aren’t necessarily technology specialists. However, instructors and librarians can collaborate with technology specialists to provide that expertise. While librarians can locate online resources—general ones such as Lynda.com or tool-specific guidance—technology specialists can quickly identify digital resources that teach technical skills (my note: in this case IMS). My note: we do not have IDs, another years-long reminder to middle and upper management. Many instructors and librarians have not had formal courses on instructional design, so collaborations can provide an authentic means to gain competency in this process.
My note: Tom and I for years have tried to make aware SCSU about this combo –
Instructors likely have high content knowledge (CK) and satisfactory technological content knowledge (TCK) and technological knowledge (TK) for personal use. But even though newer instructors acquire pedagogical knowledge (PK), pedagogical content knowledge (PCK), and technological pedagogical knowledge (TPK) early in their careers, veteran instructors may not have received this training. The same limitations can apply to librarians, but technology has become more central in their professional lives. Librarians usually have strong one-to-one instruction skills (an aspect of PK), but until recently they were less likely to have instructional design knowledge. ICT literacy constitutes part of their CK, at least for newly minted professionals. Instructional designers are strong in TK, PK, and TPK, and the level of their CK (and TCK and TPK) will depend on their academic background. And technology specialists have the corner on TK and TCK (and hopefully TPK if they are working in educational settings), but they may not have deep knowledge about ICT literacy.
Therefore, an ideal team for ICT literacy integration consists of the instructor, the librarian, the instructional designer, and the technology specialist. Each member can contribute expertise and cross-train the teammates. Eventually, the instructor can carry the load of ICT literacy, with the benefit of specific just-in-time support from the librarian and instructional designer.
My note: I have been working for more then six years as embedded librarian in the doctoral cohort and had made aware the current library administrator (without any response) about my work, as well as providing lengthy bibliography (e.g. https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/08/24/embedded-librarian-qualifications/ and have had meeting with the current SOE administrator and the library administrator (without any response).
I also have delivered discussions to other institutions (https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/04/12/embedded-librarian-and-gamification-in-libraries/)
Librarians should seriously consider TPACK as a way to embed themselves into the classroom to incorporate information and ICT literacy.
+++++++++++++
more about academic library in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=academic+library
more on SAMR and TRACK models in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/05/17/transform-education-digital-tools/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/07/29/mn-esummit-2015/
digital literacy ENGL 101
English 101 materials for discussion on digital literacy.
Jamie Heiman.
All materials on #DigitalLiteracy in the IMS blog here: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=digital+literacy
Scenario for digital literacy in English classes:
What do virtual reality, BuzzFeed quizzes and essay writing have in common?
July 18, 2018
high school students now create infographics, BuzzFeed-like quizzes and even virtual reality (VR) experiences to illustrate how they can research, write and express their thoughts.
technology — using sites like CoSpaces Edu and content learning system Schoology (my note: the equivalnet of D2L at SCSU) — to engage and empower her students.
Thinklink, during a session called “Virtually Not an Essay: Technological Alternatives to a standard essay assignment.” (see this blog materials on ThingLink and like here: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=thinglink. The author made typo by calling the app “ThinKlink, instead of ThinGlink. Also, to use Thinglink’s Video 360 editor, the free account is not sufficient and the $125/month upgrade is needed. Not a good solution for education)
Jamie: I would love to discuss with you #infographics and #Thinglink for use in your courses and the Departmental course.
Digital literacy (DL): options, ideas, possibilities
- definition
NMC: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/08/23/nmc-digital-literacy/
NMC 2016: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/10/25/nmc-on-digital-literacy/
ALA 2017: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/04/25/digital-literacy-ala/
ALA 2016: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/10/29/ala-on-digital-literacy/
Bryan Alexander: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/01/04/bryan-alexander-on-digital-literacy/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/02/10/rethinking-digital-literacy/
visuals: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/11/12/digital-literacy-3/
The government site: http://www.digitalliteracy.gov/
Digital literacy = technology use + critical thinking + social awareness : https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/03/15/digital-literacy-4/ - on [meta]literacies
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/11/27/reframing-informatioan-literacy-as-a-metaliteracy/
Topics from the European Conference on Information Literacy: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/12/19/ecil/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/09/19/digital-literacy/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/06/02/digital-literacy-can-technology-and-grammar-co-exist-in-class/
Media literacy: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/11/10/media-literacy-part-of-digital-citizenship/
digital assessment literacy: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/04/18/digital-assessment-literacy/
media literacy: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/04/24/media-literacy-guide/ (in conjunction with the #FakeNews materials: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/07/19/fake-news-materials-for-engl-101/)
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/06/05/media-literacy/
social media literacy: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/11/27/the-librarian-2-0-social-media-literacy/
functional literacy: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/09/17/first-year-experience-functional-literacy/
in response to “traditional” literacy: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/08/01/opinions-the-un-fallacy-of-balanced-literacy/ - DL and preparing students for the work place: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/05/23/digital-literacy-and-the-workplace/
- DL and SM (Social Media)
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/11/27/digital-literacy-practices-on-social-network-sites/ - Others
Digital forensics and news literacy (in conjunction with #FakeNews: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/07/19/fake-news-materials-for-engl-101/)
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2018/06/23/digital-forensics-and-news-literacy-education/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/12/02/digital-information-literacy/
digital game-based learning and digital literacies: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2015/05/31/dgbl-and-digital-literacies/ - Digital curation
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/12/02/digital-information-literacy/https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2016/12/06/digital-curation/ - Digital Storytelling
LIB 490/590 course: http://web.stcloudstate.edu/pmiltenoff/lib490/
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2017/04/12/digital-storytelling-for-edad-652/
media education differentiated instruction
Friezem, Y. (2017). THE MEDIA PRODUCTION HIVE: USING MEDIA EDUCATION FOR DIFFERENTIATED INSTRUCTION. Media Education, 8(1), 123-140
keywords: Media production, media literacy, Universal Design for Learning (UDL), executive
functioning, Media Production Hive
the theoretical framework of Universal Design for Learning (Rose & Meyer, 2002), teaching the same material via various strategies that cumulatively address needs and learning types of each student in the classroom (p. 126). acknowledge all the various types of learners in his class, such as visual learners, auditory learners, write-read learners, and kinesthetic learners, following Gardner’s (1983) multiple intelligence theory.
various ways of receiving, processing, and expressing information by different learners
various ways students can chose to engage in the process of learning
(p. 127) multiple means of representation guarantees each learner processes information in the best way they can, but it also provides repetition of the topic in various ways to deepen understanding
Students need to organize recently acquired knowledge in a strategic way and communicate their understanding to the teacher. Rose and Meyer (2002) created a detailed pathway for teachers to apply UDL using assistive technology.
Media education practices involve demystifying media messages and learning to use
media wisely through activities of evaluation, composition, introspection, and civic engagement. the links between the instructional design of lessons for all students and
the critical analysis, expression, and reflection on media messages are gradually
explored (Dalton, 2017).
Dalton, E. M. (2017). Universal design for learning: Guiding principles to reduce
barriers to digital & media literacy competence. Journal of Media Literacy Education, 9(2).
p. 128 Media production is the process of composing a message via a single or various media platforms. Media production includes creating videos, podcasts, presentations, posters, drawings, and books. With the increasing use of digital devices and applications, students are engaged in various ways to convey their messages using multiple ways of expression and multiple types of representations.

digital and media literacy competencies (Hobbs, 2010)
p. 137 challenges
Group dynamics often reveal power struggles among team members (Friesem, 2014). The responsibility of the media educator, who is not a mediator by training, is to find the way to mitigate the tension caused by differences among group members (Friesem, 2010). In addition, students have the tendency to use media production as a transgressive practice (Moore, 2011; Grace & Tubin, 1998). Facilitating the process of production involves constant reflection on the classroom power relationship using critical and pragmatic lenses.
Grace, D., & Tobin, J. (1998). Butt jokes and mean-teacher parodies: Video production
in the elementary classroom. In D. Buckingham (Ed.), Teaching popular culture: Beyond radical pedagogy (pp. 42-62). London, UK: University College London Press.
The discourse about the implementations of UDL with digital technology has been broad and used for several research studies (Rose & Meyer, 2002).
Rose, D. H., & Meyer, A. (2002). Teaching every student in the digital age: Universal
design for learning. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
++++++++++++++++++++++
more on media literacy in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=media+literacy
more on instructional desing in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=instructional+design
media literacy guide
The Global Critical Media Literacy Educators’ Resource Guide
http://gcml.org/the-global-critical-media-literacy-educators-resource-guide/
- Introduction
- About the GCMLP
- Contacts for GCMLP Publication
- Methods of Media Manipulation
- Breaking the Corporate News Frame: Project Censored’s Networked News Commons
- Validated Independent News Story Assignment
- How to Find, Evaluate, and Summarize Validated Independent News Stories
- Validated Independent News Story Grading Rubric
- Validated Independent News Story Grading Criteria
- Student Guide For Evaluating Web Sources
- ‘Becoming the Media:’ Experiential Learning through Media Criticism and Political Activism During National Presidential Elections
- ACME Classroom Activities: Challenging Big Media and News Censorship
- Digging Deeper: Politico-Corporate Media Manipulation, Critical Thinking, and Democracy
- Service Learning: The SUNY Buffalo State and Project Censored Partnership
- Commodifying the Public Sphere Through Advertising and Commercial Media
- Group Advertisement Assignment
- Junk Food News Assignment
- News Abuse Assignment
- Meme Assignment
- Solutions Video Project
- Video Summary Assignment
- Ethics Alerts: Applied Learning Opportunity in Higher Education
- Ethics Alert Assignment
- Critical Analysis of Gender Stereotypes on Television Assignment
- Critical Analysis of Race, Ethnicity, and Class Stereotypes in Entertainment
- 18 Fun and Easy Classroom Activities for Media Education
- Five Ways to Flex Your Media Literacy Muscles
- List of Independent and Corporate News and News Criticism Outlets
- GCMLP Biographies and Participating Institutions
- GCMLP Event on Your Campus Instructions
- Sacred Heart University Graduate Program
- Media Education for a Digital Generation Book Flyer
Regular Pages: https://www.dropbox.com/s/jp5isqrn6ijv9lx/ACMEbookFINAL101215.pdf?dl=0
Spreads: https://www.dropbox.com/s/enya4iyyxahg8ik/ACMEbookFINAL101215SPREADS.pdf?dl=0
+++++++++++++
more on media literacy in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=media+literacy