Dec
2013
Translating Constructivism into Instructional Design: Potential and Limitations.
The goal, for instance, is not to teach a particular version of history, but to teach someone how to think like a historian.
Yiasemina Karagiorgi
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
Tips for Designing an Online Lesson Using the 5 Es Instructional Model | https://t.co/LY53NNlMes pic.twitter.com/y4fu55MCFM
— Ana Cristina Pratas (@AnaCristinaPrts) April 12, 2020
Tips for Designing an Online Learning Experience Using the 5 Es Instructional Model
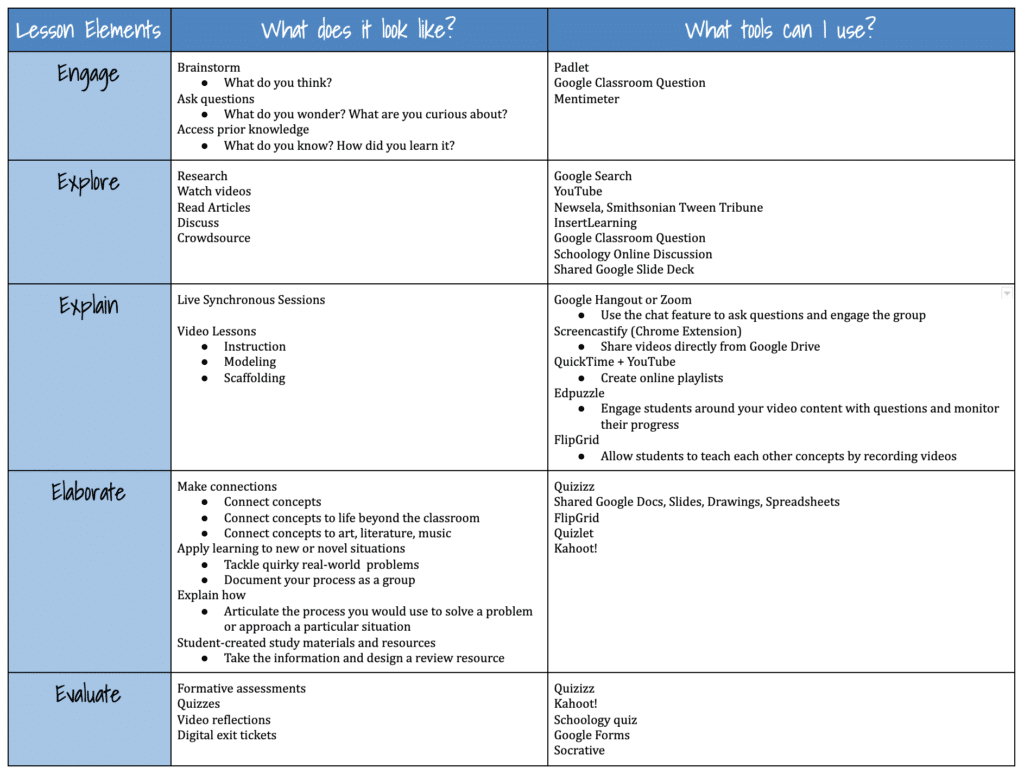
the Hyperdoc website and check out the templates and already-created hyperdocs available for teachers. Lisa Highfill, Kelly Hilton, and Sarah Landis are the authors of The Hyperdoc Handbook and have created a website full of free resources for teachers.
++++++++++++
more on instructional design and education in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=instructional+design+and+education
The eLearning Coach, at https://theelearningcoach.com/ for a multitude of free instructional design resources!
Heather Elizabeth Dodds
https://edtechbooks.org/id_highered/immersive_learning_e
The terms ‘extended reality’ or ‘cross reality’ refer to “technologies and applications that involve combinations of mixed reality (MR), augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and virtual worlds (VWs)” (Ziker, Truman, & Dodds, 2021, p. 56). Immersive learning definitions draw from Milgram and Kishino’s key taxonomy (1994) emphasizing the continuum of experiences that range from where a computer adds to a learner’s reality with overlays of information, or a computer experientially transports a learner to a different place and time by manipulating sight and sound.
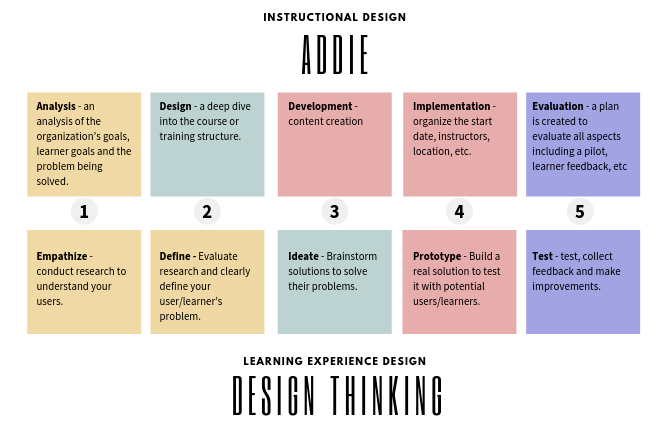
three different design models (see Figure 3): the ADDIE Design Model (Branson, 1978), Design Thinking (Brown & Wyatt, 2010) from user experience (UX), and the 3D Learning Experience Design Model (Kapp & O’Driscoll, 2009).
Serrat (2008) defines storytelling as “the vivid description of ideas, beliefs, personal experiences, and life-lessons through stories or narratives that evoke powerful emotions and insights” (p.1).
The foundational theory for most XR experiences is experiential learning theory. In cases where users create within XR, constructivist learning theory also applies.
XR experiences can include a story arc (See Appendix D), a tutorial of user affordances, intentional user actions, and place the user into first or third person experiences (Spillers, 2020).
***************
more on instructional design in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=instructional+design
A call for more inter-campus networking on learning design:https://t.co/9GIxMdtswE
— Bryan Alexander (@BryanAlexander) June 26, 2019
a new interdisciplinary field of learning innovation emerging.
Learning innovation, as conceptualized as an interdisciplinary field, attempts to claim a space at the intersection of design, technology, learning science and analytics — all in the unique context of higher education.
professional associations, such as POD, ELI, UPCEA, (https://upcea.edu/) OLC (https://onlinelearningconsortium.org/), ASU GSV (https://www.asugsvsummit.com/) and SXSW Edu (https://www.sxswedu.com/) — among many other conferences and events put on by professional associations.
A professional community of practice differs from that of an interdisciplinary academic network. Professional communities of practice are connected through shared professional goals. Where best practices and shared experiences form the basis of membership in professional associations, academic networks are situated within marketplaces for ideas. Academic networks run on the generation of new ideas and scholarly exchange. These two network models are different.
+++++++++++
https://elearningindustry.com/learning-experience-design-instructional-design-difference
“Learning Experience Design™ is a synthesis of Instructional Design, educational pedagogy, neuroscience, social sciences, design thinking, and User Experience Design.”
++++++++++++++
more on LX design in this iMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=learning+design
Part 1: March 7, 2018 | 1:00–2:30 p.m. ET
Part 2: March 14, 2018 | 1:00–2:30 p.m. ET
Part 3: March 21, 2018 | 1:00–2:30 p.m. ET
Faculty need a variety of instructional technology support—instructional design, content development, technology, training, and assessment—to name a few. They don’t want to go to one place for help, find out they’re in the wrong place, and be sent somewhere else—digitally or physically. Staff don’t want to provide help in silos or duplicate what other units are doing.
So, how can academic service providers collaborate to offer the right instructional technology support services, in the right place, at the right time, in the right way? In this course, instructional technologists, instructional designers, librarians, and instructional technology staff will learn to use a tool called the Service Center Canvas that does just that.
During this course, participants will:
NOTE: Participants will be asked to complete assignments in between the course segments that support the learning objectives stated below and will receive feedback and constructive critique from course facilitators on how to improve and shape their work.
 Elliot Felix, Founder and CEO, brightspot strategy
Elliot Felix, Founder and CEO, brightspot strategy
Felix founded and leads brightspot, a strategy consultancy that reimagines places, rethinks services, and redesigns organizations on university campuses so that people are better connected to a purpose, information, and each other. Felix is accomplished strategist, facilitator, and sense-maker who has helped transform over 70 colleges and universities.
 Adam Griff, Director, brightspot strategy
Adam Griff, Director, brightspot strategy
Adam Griff is a director at brightspot. He helps universities rethink their space, reinvent their service offerings, and redesign their organization to improve the experiences of their faculty, students, and staff, connecting people and processes to create simple and intuitive answers to complex questions. He has led projects with a wide range of higher education institutions including University of Wisconsin–Madison, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and University of California, Berkeley.
Special Interest Group: Learning Spaces and Instructional Technology (SIG) webinars are FREE and open to anyone. Please feel free to share this with others at your institution.
Notes from the previous session available here:
Of course, not all aspects of online course design require a team of specialists, a longer development time, and more funding. Some things can be done quickly, cheaply and by individuals with focused skill sets.
But technology can, when built with a deep understanding of how students learn, meet both of these needs. We can build online courses that provide students with hundreds of opportunities to test their knowledge. Using scientifically-based learning analytics, we can provide each learner with immediate, context-specific feedback. We can build software that constantly responds to each student’s cognitive and educational differences and serves up activities that address these differences.
Educator, technologist, researcher, and innovator in edtech, distance education, and faculty development
“Placing the burden on lone educators with minuscule (or non-existent) funding and who are not hired for their strengths in instructional media development is neither logical, nor fair. But more to the point, it’s a lost opportunity to leverage high-quality course design to drive improvements in learning outcomes.”
I could not agree more with this statement and the remainder of the article. I’ve long supported an instructional design partnership model where faculty occupy a leading role along with other professionals capable of making the interactions, activities, and rich-media meet the quality needs of an increasingly complex learning environment (and world).
Editor at Individual Basis
We need to start imagining new models for building, acquiring and sharing instructional media.
This has always been an issue. My students love activities that provide them with immediate feedback. I spend extra hours building a wide variety of different activities into each Learning module. It takes time and effort and if I am going to address different learning styles that is an entirely different issue. To create effective interactive learning tools that will not waste my students time and will challenge their skill level consumes more time than planning for a face to face class with different activities. I would love to talk to someone-be able to explain what I want my students to learn, suggest a few interactive choices, and come back later to find age related learning activities that fit different learning styles.
Owner, MyMeemz
There is going to be a fight because this model is more like a business product that educators contribute to, rather than own. Perhaps this is the true industrialization of education, replacing the craft model of individual teaching with standardized, high quality product?
Enrollment Advisor – Pearson Embanet
I have forwarded this article on to members of the course development team within Pearson for their feedback. I am curious to see their impression of the article versus mine, considering I predominantly am a part of recruitment services for Pearson specifically. Within our academic partnerships platform, we do contend with faculty, should they employ our course development team, to this vein because the ownership usually rests with the instructor solely. Editing course content or abridging related material so that it could be received potentially as more either user-friendly or technologically savvy can be a source of major contention with faculty members. I do agree that this is an industrialization of education to an extent, but it also pushes the ownership of traditional education past the instructor, a predominantly sole proprietorship environment, to an completely different team effort. The natural technological growing pains coupled with role expansion and differentiation are also issues needing to be addressed as well.
Owner, MyMeemz
Suppose one was to take this seriously. What might such a course look like – for a subject like Biology? Could it be built on existing LMS platforms, or is a new platform required?
Editor at Individual Basis
I think that both individual ownership and team collaboration are important to the development of successful online learning. We (hopefully) use the concepts of group and team learning in our classroom environments. We should not be afraid to open ourselves up to some of the positive opportunities that could develop from participating in these practices. It does not mean giving up our ownership of content and presentation. I see it as a marketplace of choice where instructors can decide what kinds of activities, helps, prompts, extra materials, and resources they want to add to their class content. The choices could be categorized by learning styles or how they fit into learning paradigms. I think we must face the reality that some parts of education will have to be more industrialized than others just because of the delivery method. This does not have to be a negative issue if there are enough choices to help instructors develop the rigorous content they want to deliver without sacrificing their entire life to the project.
Good morning all,
Please consider one-on-one and/or team sessions regarding the use of the Adobe Creative Suite as well as the use of other technologies in the educational process.
Please contact InforMedia Services (IMS), ims@stcloudstate.edu, for any questions, scheduling etc.
IMS (http://lrts.stcloudstate.edu/library/general/ims/default.asp) consists of faculty, who are willing and able to help faculty, staff and students with their academic endeavors in technology. We offer one-on-one sessions, workshops, instructional sessions and in-class technology instructions.
Follow us:
IMS blog: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/ (keyword: mobile devices)
Twitter: https://twitter.com/SCSUtechinstruc
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/InforMediaServices?ref=hl
Pinterest: http://www.pinterest.com/scsutechnology/
Instagram: http://instagram.com/scsutechinstruct
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC_UMIE5r6YB8KzTF5nZJFyA
Google +: https://plus.google.com/u/0/115966710162153290760/posts/p/pub
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/scsuinstructionaltechnology
Since IMS does not have access to the FacultyStaffAll listserv and cannot reach all campus as the message below, please feel welcome and encouraged to forward this email to your colleagues across unions.
Have a successful new academic year.
From: SCSU Information Technology
Sent: Tuesday, August 26, 2014 8:26 AM
To: FacultyStaffAll
Subject: Adobe Creative Cloud Site License
We are pleased to announce that we have renewed the Adobe site license for university-owned computers on campus. This means that the Adobe Creative Cloud Master Collection (includes Acrobat, Photoshop, InDesign, Illustrator, Dreamweaver, After Effects, Premier Pro, Fireworks, Flash, Lightroom, and more) is able to be installed on any university-owned computer at no additional cost to you.
Campus Use
If you would like the use of these applications, please email huskytech@stcloudstate.edu with the details of which applications you would like installed on your university-owned computer. Because it is the first week of the semester and technicians are quite busy right now, we ask for your patience with these installations.
NOTE: Not all campus computers are capable of running these programs. A technician will work with you to make sure your computer is capable of running this software before installing.
Personal Use
In addition, this campus site license includes a copy of Adobe Master Collection that can be installed on a faculty or staff person’s home computer for a yearly fee of $9.75.
Link to purchase personal version: http://stcloudstate.onthehub.com/WebStore/OfferingDetails.aspx?o=c7e8f835-08b1-e311-93fb-b8ca3a5db7a1
NOTE: Students are NOT eligible for this at-home use. Students can purchase Adobe Creative Cloud for a monthly fee of $19.99.
Please contact HuskyTech at 320-308-7000 or huskytech@stcloudstate.edu with any questions!
Thank you,
Casey Gordon
Technology Support Services Director
Information Technology Services
MC 112C | 320-308-4711 | cjgordon@stcloudstate.edu
St. Cloud State University