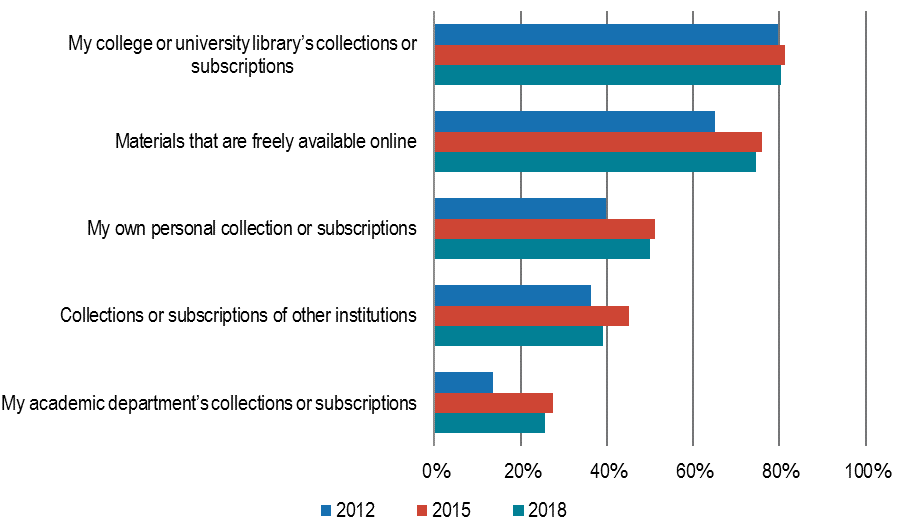THE VALUE OF ACADEMIC LIBRARIES
A Comprehensive Research Review and Report. Megan Oakleaf
http://www.ala.org/acrl/sites/ala.org.acrl/files/content/issues/value/val_report.pdf
Librarians in universities, colleges, and community colleges can establish, assess, and link
academic library outcomes to institutional outcomes related to the following areas:
student enrollment, student retention and graduation rates, student success, student
achievement, student learning, student engagement, faculty research productivity,
faculty teaching, service, and overarching institutional quality.
Assessment management systems help higher education educators, including librarians, manage their outcomes, record and maintain data on each outcome, facilitate connections to
similar outcomes throughout an institution, and generate reports.
Assessment management systems are helpful for documenting progress toward
strategic/organizational goals, but their real strength lies in managing learning
outcomes assessments.
to determine the impact of library interactions on users, libraries can collect data on how individual users engage with library resources and services.
increase library impact on student enrollment.
p. 13-14improved student retention and graduation rates. High -impact practices include: first -year seminars and experiences, common intellectual experiences, learning communities, writing – intensive courses, collaborative assignments and projects, undergraduate research, Value of Academic Libraries diversity/global learning, service learning/community -based learning, internships, capstone courses and projects
p. 14
Libraries support students’ ability to do well in internships, secure job placements, earn salaries, gain acceptance to graduate/professional schools, and obtain marketable skills.
librarians can investigate correlations between student library interactions and their GPA well as conduct test item audits of major professional/educational tests to determine correlations between library services or resources and specific test items.
p. 15 Review course content, readings, reserves, and assignments.
Track and increase library contributions to faculty research productivity.
Continue to investigate library impact on faculty grant proposals and funding, a means of generating institutional income. Librarians contribute to faculty grant proposals in a number of ways.
Demonstrate and improve library support of faculty teaching.
p. 20 Internal Focus: ROI – lib value = perceived benefits / perceived costs
production of a commodity – value=quantity of commodity produced × price per unit of commodity
p. 21 External focus
a fourth definition of value focuses on library impact on users. It asks, “What is the library trying to achieve? How can librarians tell if they have made a difference?” In universities, colleges, and community colleges, libraries impact learning, teaching, research, and service. A main method for measuring impact is to “observe what the [users] are actually doing and what they are producing as a result”
A fifth definition of value is based on user perceptions of the library in relation to competing alternatives. A related definition is “desired value” or “what a [user] wants to have happen when interacting with a [library] and/or using a [library’s] product or service” (Flint, Woodruff and Fisher Gardial 2002) . Both “impact” and “competing alternatives” approaches to value require libraries to gain new understanding of their users’ goals as well as the results of their interactions with academic libraries.
p. 23 Increasingly, academic library value is linked to service, rather than products. Because information products are generally produced outside of libraries, library value is increasingly invested in service aspects and librarian expertise.
service delivery supported by librarian expertise is an important library value.
p. 25 methodology based only on literature? weak!
p. 26 review and analysis of the literature: language and literature are old (e.g. educational administrators vs ed leaders).
G government often sees higher education as unresponsive to these economic demands. Other stakeholder groups —students, pa rents, communities, employers, and graduate/professional schools —expect higher education to make impacts in ways that are not primarily financial.
p. 29
Because institutional missions vary (Keeling, et al. 2008, 86; Fraser, McClure and
Leahy 2002, 512), the methods by which academic libraries contribute value vary as
well. Consequently, each academic library must determine the unique ways in which they contribute to the mission of their institution and use that information to guide planning and decision making (Hernon and Altman, Assessing Service Quality 1998, 31) . For example, the University of Minnesota Libraries has rewritten their mission and vision to increase alignment with their overarching institution’s goals and emphasis on strategic engagement (Lougee 2009, allow institutional missions to guide library assessment
Assessment vs. Research
In community colleges, colleges, and universities, assessment is about defining the
purpose of higher education and determining the nature of quality (Astin 1987)
.
Academic libraries serve a number of purposes, often to the point of being
overextended.
Assessment “strives to know…what is” and then uses that information to change the
status quo (Keeling, et al. 2008, 28); in contrast, research is designed to test
hypotheses. Assessment focuses on observations of change; research is concerned with the degree of correlation or causation among variables (Keeling, et al. 2008, 35) . Assessment “virtually always occurs in a political context ,” while research attempts to be apolitical” (Upcraft and Schuh 2002, 19) .
p. 31 Assessment seeks to document observations, but research seeks to prove or disprove ideas. Assessors have to complete assessment projects, even when there are significant design flaws (e.g., resource limitations, time limitations, organizational contexts, design limitations, or political contexts); whereas researchers can start over (Upcraft and Schuh 2002, 19) . Assessors cannot always attain “perfect” studies, but must make do with “good enough” (Upcraft and Schuh 2002, 18) . Of course, assessments should be well planned, be based on clear outcomes (Gorman 2009, 9- 10) , and use appropriate methods (Keeling, et al. 2008, 39) ; but they “must be comfortable with saying ‘after’ as well as ‘as a result of’…experiences” (Ke eling, et al. 2008, 35) .
Two multiple measure approaches are most significant for library assessment: 1) triangulation “where multiple methods are used to find areas of convergence of data from different methods with an aim of overcoming the biases or limitations of data gathered from any one particular method” (Keeling, et al. 2008, 53) and 2) complementary mixed methods , which “seek to use data from multiple methods to build upon each other by clarifying, enhancing, or illuminating findings between or among methods” (Keeling, et al. 2008, 53) .
p. 34 Academic libraries can help higher education institutions retain and graduate students, a keystone part of institutional missions (Mezick 2007, 561) , but the challenge lies in determining how libraries can contribute and then document their contribution
p. 35. Student Engagement: In recent years, academic libraries have been transformed to provide “technology and content ubiquity” as well as individualized support
My Note: I read the “technology and content ubiquity” as digital literacy / metaliteracies, where basic technology instructional sessions (everything that IMS offers for years) is included, but this library still clenches to information literacy only.
p. 37 Student Learning
In the past, academic libraries functioned primarily as information repositories; now they are becoming learning enterprises (Bennett 2009, 194) . This shift requires academic librarians to embed library services and resources in the teaching and learning activities of their institutions (Lewis 2007) . In the new paradigm, librarians focus on information skills, not information access (Bundy 2004, 3); they think like educators, not service providers (Bennett 2009, 194) .
p. 38. For librarians, the main content area of student learning is information literacy; however, they are not alone in their interest in student inform ation literacy skills (Oakleaf, Are They Learning? 2011).
My note: Yep. it was. 20 years ago. Metaliteracies is now.
p. 41 surrogates for student learning in Table 3.
p. 42 strategic planning for learning:
According to Kantor, the university library “exists to benefit the students of the educational institution as individuals ” (Library as an Information Utility 1976 , 101) . In contrast, academic libraries tend to assess learning outcomes using groups of students
p. 45 Assessment Management Systems
Tk20
Each assessment management system has a slightly different set of capabilities. Some guide outcomes creation, some develop rubrics, some score student work, or support student portfolios. All manage, maintain, and report assessment data
p. 46 faculty teaching
However, as online collections grow and discovery tools evolve, that role has become less critical (Schonfeld and Housewright 2010; Housewright and Schonfeld, Ithaka’s 2006 Studies of Key Stakeholders 2008, 256) . Now, libraries serve as research consultants, project managers, technical support professionals, purchasers , and archivists (Housewright, Themes of Change 2009, 256; Case 2008) .
Librarians can count citations of faculty publications (Dominguez 2005)
.
+++++++++++++
Tenopir, C. (2012). Beyond usage: measuring library outcomes and value. Library Management, 33(1/2), 5-13.
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dllf%26AN%3d70921798%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
methods that can be used to measure the value of library products and services. (Oakleaf, 2010; Tenopir and King, 2007): three main categories
- Implicit value. Measuring usage through downloads or usage logs provide an implicit measure of value. It is assumed that because libraries are used, they are of value to the users. Usage of e-resources is relatively easy to measure on an ongoing basis and is especially useful in collection development decisions and comparison of specific journal titles or use across subject disciplines.
do not show purpose, satisfaction, or outcomes of use (or whether what is downloaded is actually read).
- Explicit methods of measuring value include qualitative interview techniques that ask faculty members, students, or others specifically about the value or outcomes attributed to their use of the library collections or services and surveys or interviews that focus on a specific (critical) incident of use.
- Derived values, such as Return on Investment (ROI), use multiple types of data collected on both the returns (benefits) and the library and user costs (investment) to explain value in monetary terms.
++++++++++++++++++
more on ROI in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2014/11/02/roi-of-social-media/
Survey Highlights Digitization’s Impact on Campus Libraries
By David Raths 05/22/17
https://campustechnology.com/articles/2017/05/22/survey-highlights-digitizations-impact-on-campus-libraries.aspx
nonprofit Ithaka S+R. The study, Ithaka S+R Library Survey 2016, highlighted a number of challenges facing library directors in an era of increased digitization. Future Trends Forum video chat May 19 hosted by Bryan Alexander.
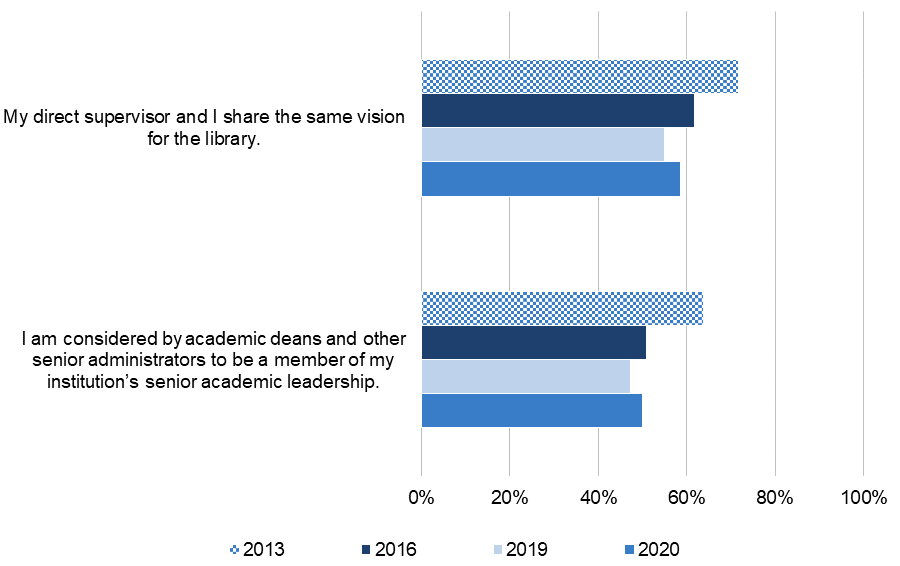
Alexander zeroed in on the finding that library directors feel increasingly less valued by supervisors such as chief academic officers.
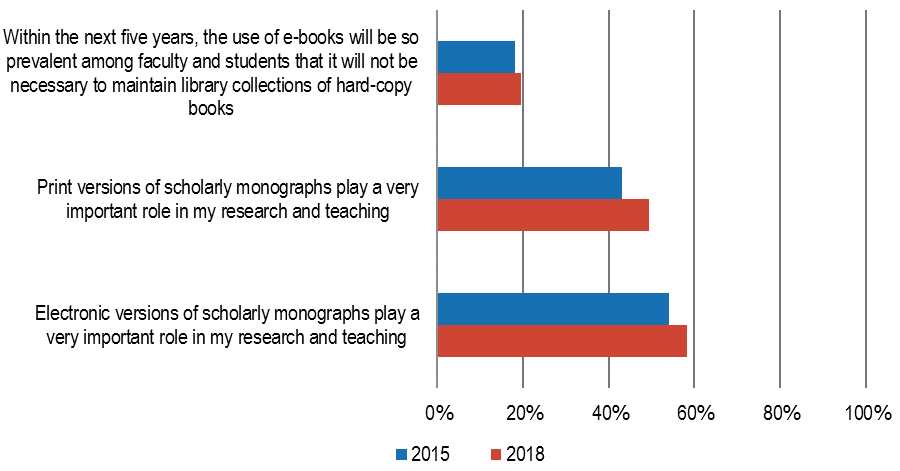
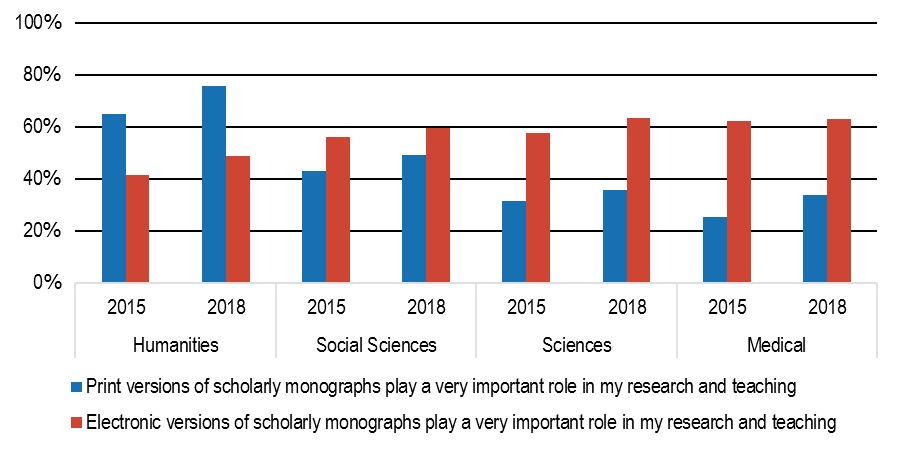
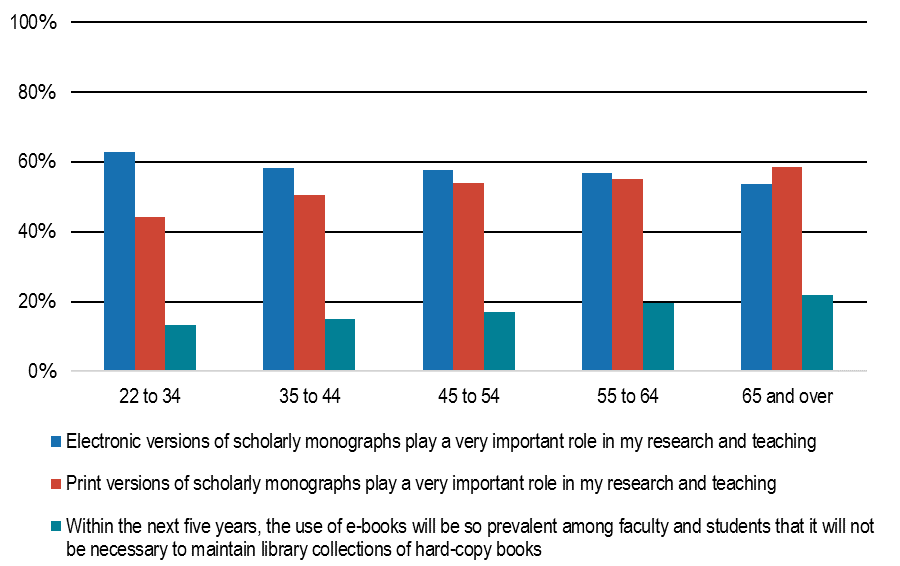
Not surprisingly, the survey illustrates a broad shift toward electronic resources, Wolff-Eisenberg noted, with an increasing number of libraries developing policies for de-accessioning print materials that are also available digitally.
library directors are increasingly recognizing that discovery does not always happen in the library. Compared to the 2013 survey results, fewer library directors believe that it is important that the library is seen by its users as the first place that they go to discover content, and fewer believe that the library is always the best place for researchers at their institution to start their research.
There is also a substantial gap between how faculty members and library directors perceive the library’s contribution in supporting student learning. Both tend to agree that students have poor research skills, Wolff-Eisenberg noted. The faculty members see it as more of a problem, but they are less likely than library directors to see librarians contributing to student learning by helping them to develop research skills
The positions for which respondents anticipate the most growth in the next five years are related to instructional design (my note: this is IMS), information literacy and specialized faculty research support involving digital humanities, geographical information systems (GIS) and data management.
++++++++++++++++++++++
more on digitization in academic libraries in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims?s=digitization+library
The scholar-centric nature of the questionnaire ensures that potential changes in research and teaching inform our thinking, not only about academic libraries and scholarly publishing, but about changes in the educational enterprise more broadly.
My note:
By showcasing the diminishing role of physical presence and the increasing research using online methods, this study clearly proves that the 4/5 years debate if the reference librarians must sit on that desk (and answer the most popular question “where is the bathroom”) is futile.
What the study does not show, since it is conducted in its traditional (conservative) form, is that the library is NOT only the traditional library, where faculty and student search for information (being that in its physical appearance or in online access), but the library entails services, very close to the ones offered by IMS.
I see a discrepancy between literature (where libraries compel much more proactive approach regarding services) and the structure of this survey, which focuses on the traditional (conservative) role of the library as a gatekeeper to online resources [only]. Besides entrenching in 90’s practices of information literacy and/or “dressing up” old-fashioned information literacy with the new cloths of “digital literacy”as I witness at my workplace, the faculty must have been surveyed on the skills in metaliteacies, which the library can [must] provide, as per literature.