Apr
2016
Digital Literacy for St. Cloud State University
purpose: draft a document for the provost to plan for charting the future goal 3.12 “develop a comprehensive strategy to increase awareness and development of e-textbooks and open educational resources (OERs)”
\\STCLOUDSTATE\HuskyNet\DeptFiles\LRS\ETextbooks
SCSU goal: to reduce the cost of textbooks as an affordable learning initiative. Amount of reduction is undetermined
my notes based on the material below:
responses from colleagues:
Scott Robison, sarobison@mail.plymouth.edu: sparc-liboer@arl.org listserv
Jeff Gallant, Jeff.Gallant@usg.edu: David Ernst with the U and Ashley Miller from Ohio State U: dernst@umn.edu. Ashley’s is miller.6275@osu.edu.
Definition of: e-book
my note: there is no good definition about e-textbook in terms of the complexity, which e-textbook on campus might involve.
Considering Wimmer et al (2014) account on their campus experience in publishing e-textbook, a textbook may involve an LMS (Canvas) and blog (WordPress). Per my proposal during the F2F meeting, and following Rachel’s suggestion about discrimination of the different types of e-textbooks, here is an outline of e-textbook definition:
*******************
working definition for e-textbook for the purposes of SCSU:
e-textbook is a compilation of textual, multimedia and interactive material, which can be viewed on various electronic devices. E-textbook can: 1. be purchased from a publisher; 2. compiled in HTML format on faculty or group web space; 3. compiled on the content module of LMS (BB, D2L, Canvas, Moodle, etc.) 4. compiled on LMS (BB, D2L, Canvas, Moodle, etc.) and including all interactive materials: e.g. hyperlinks to MediaSpace multimedia, quizzes, etc.; 5. compiled on special apps, such as iBook Author, eCub, Sigil.
*******************
(Electronic-BOOK) The electronic counterpart of a printed book, which can be viewed on a desktop computer, laptop, smartphone, tablet or e-book reader (e-reader). When traveling, a huge number of e-books can be stored in portable units, dramatically eliminating weight and volume compared to paper. Electronic bookmarks make referencing easier, and e-book readers may allow the user to annotate pages.
Although fiction and non-fiction books come in e-book formats, technical material is especially suited for e-book delivery because it can be searched. In addition, programming code examples can be copied, which is why CD-ROMs that contained examples or the entire text were often packaged inside technical paper books.
E-Book Formats
Wimmer, Morrow, & Weber: Collaboration in eTextbook Publishing
There are several e-book formats on the market, including EPUB, Mobipocket (PRC, MOBI), eReader (PDB), Kindle (AZW, KF8) and Apple iBook (EPUB variation). Many e-readers also accept generic formats, including Adobe PDF and plain text (TXT).
Oxford dictionary, an electronic book or e-book is “an electronic version of a printed book that can be read on a computer or handheld device designed specifically for this purpose.” An e-textbook is defined as an e-book used for instructional or educational purposes and often includes features such as bookmarking, searching, highlighting, and note-taking as well as built-in dictionaries and pronunciation guides, embedded video-clips, embedded hyperlinks, and animated graphics.
E-textbooks have moved from occasional usage to a mainstream technology on college campuses. According to the Association of American Publishers, sales of e-books hit over $90 million; this is up over 200% when compared to the same month the previous year. When the cost of textbooks and the availability of formats are considered, the use of an e-textbook in the classroom may be the reasonable choice.
—————–
Despite the advantages that e-textbooks pose, such as interactive features and accessibility on mobile devices, several barriers exist regarding implementation in higher education, namely non-standardization of the platform, limited use by students, and the unclear role of the instructor in adoption.
a survey questionnaire in 2012 that explored basic usage and attitudes regarding e-textbooks.
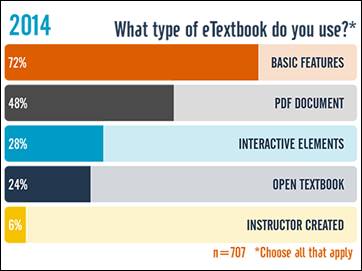
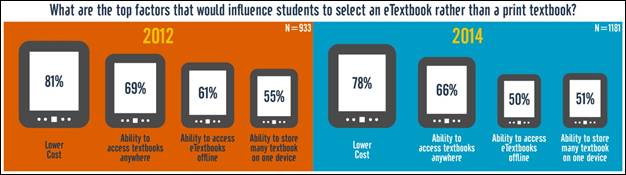
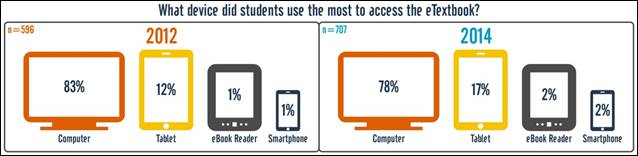
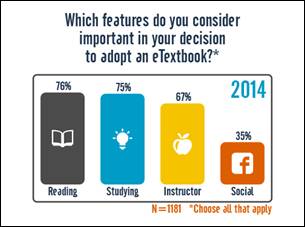

—————————–
Bossaller, J., & Kammer, J. (2014). Faculty Views on eTextbooks: A Narrative Study. College Teaching, 62(2), 68-75. doi:10.1080/87567555.2014.885877
Implementing eTexts into a Course:
This qualitative study gives insight into the experiences instructors have when working with publishers to integrate electronic content and technology into their courses.
Baek, E., & Monaghan, J. (2013). Journey to Textbook Affordability: An Investigation of Students’ Use of eTextbooks at Multiple Campuses. International Review Of Research In Open And Distance Learning, 14(3), 1-26.
http://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1017493
the Advisory Committee on Student Financial Assistance (2007) reported that textbook prices represent a significant barrier to students’ accessibility to textbooks. The report concluded that textbooks cost between $700-$1000 per year; textbook prices have risen much faster than other commodities; and that college aid fails to cover textbook expenses. Textbook costs are equivalent to 26% of tuition costs for an average four-year public university student and 72% of tuition costs for an average community college student. In fact, the California State Auditor (2008) reported that textbook costs grew more rapidly than student fees in academic year 2007–08.
++++++++++++
Wimmer, E. e., Morrow, A. a., & Weber, A. a. (2014). Collaboration in eTextbook Publishing: A Case Study.Collaborative Librarianship, 6(2), 82-86.
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dllf%26AN%3d108762075%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite

Distance education, e-learning, education and training. (2015). Clinical Chemistry & Laboratory Medicine, 53s557-s559. doi:10.1515/cclm-2015-5015
onto Youtube so that the user could access these via the internet.
Horejsi, M. (2014). Textbooks 2.0. Science Teacher, 81(3), 8. http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3daph%26AN%3d94603788%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
++++++++++++++
pedagogy
two Eastern Europeans (Moldova, Serbia) raise serious concerns about electronic textbooks
Španović, S. (2010). PEDAGOGICAL ASPECTS OF E-TEXTBOOKS. Odgojne znanosti. 12(2). 459-470.
Railean, E. (2015). https://prezi.com/sbidiadctrzo/beyond-textbook-digital-textbook-use-and-development/
http://www.governance.ualberta.ca/en/GeneralFacultiesCouncil/CommitteeontheLearningEnvironm/~/media/Governance/Documents/GO05/LEA/15-16/WEB/Item-4-eTextbook-Subcommittee-Report-CLE-TLAT.pdf :
ICWL (Conference) (13th : 2014 : Tallinn, E., & Cao, Y. (2014). New horizons in web based learning: ICWL 2014 international workshops, SPeL, PRASAE, IWMPL, OBIE, and KMEL, FET, Tallinn, Estonia, August 14-17, 2014, revised selected papers. Cham: Springer.
++++++++++++++++++++
MnSCU will by as Content Authoring Tool – SoftChalk. Here is a promo from Softchalk (my bold):
NEW SoftChalk Create 10 and SoftChalk Cloud eBook publishing features will arrive on April 25th! Come check out the latest enhancements at our upcoming webinars!
Sleek Designer Headers and Callout Boxes – Add some new pizazz to your SoftChalk lessons!
Three New Quiz Types – Test your students’ understanding with Sentence Completion, Multiple Blanks and Feedback Questions.
Polished New QuizPopper and Activity displays – With an enhanced interface for instructors and students.
Accessibility enhancements – Make your lessons available to everyone with even more accessibility enhancements.
NEW SoftChalk Cloud eBook creation and publishing – Includes a totally re-vamped, easier eBook creation and management. New SoftChalk eReader apps available for free download in the iOS, Android, Chromebook and Windows app stores. (Cloud Only)
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
are any faculty really going digital? Which content distributors will thrive? What are the implementation concerns? And when will going digital really happen?
two massive surveys and reports by the National Association of College Stores (NACS) and the Independent College Bookstore Association (ICBA) in partnership with the Campus Computing Survey (CCS),
More on flipped classroom in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=flipped&submit=Search
Flipped classroom. (2016, March 22). In Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Flipped_classroom&oldid=711368580

The Flipped Class: Overcoming Common Hurdles by Edutopia:
http://www.edutopia.org/blog/flipped-learning-toolkit-common-hurdles-jon-bergmann
Helps kids who were absent, stay current.
Helps kids who don’t get the lesson the first time in class.
Good resource for teacher assistants or student support staff who may not know the curriculum or may not know what to focus on.
Can attach Google spreadsheets or other online quizzes to check for comprehension, along with the video link sent to students
Zuber, W. J. (2016). The flipped classroom, a review of the literature. Industrial & Commercial Training, 48(2), 97-103. doi:10.1108/ICT-05-2015-0039 http://www.emeraldinsight.com/doi/full/10.1108/ICT-05-2015-0039
although learning styletheories serve as a justification for different learning activities it does not provide the necessarytheoretical framework as to how the activities need to be structured (Bishop and Verleger, 2013). p. 99
One observation from the literature is there is a lack of consistency of models of the FCM (Davieset al.,2013, p. 565) in addition to a lack of research into student performance, (Findlay-Thompson andMombourquette, 2014, p. 65; Euniceet al., 2013) broader impacts on taking up too much of thestudents’time and studies of broader student demographics. In another literature review of the FCM,Bishop and Verleger concur with the observation that there is a lack of consensus as to the definitionof the method and the theoretical frameworks (Bishop and Verleger, 2013). p. 99
Flipped Classrooms’ may not have any impact on learning:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/2013/10/23/flipped-classrooms-may-not-have-any-impact-on-learning/
Gross, B., Marinari, M., Hoffman, M., DeSimone, K., & Burke, P. (2015). Flipped @ SBU: Student Satisfaction and the College Classroom. Educational Research Quarterly, 39(2), 36-52.
we found that high levels of student engagement and course satisfaction characterised the students in the flipped courses, without any observable reduction in academic performance.
Hotle, S. L., & Garrow, L. A. (2016). Effects of the Traditional and Flipped Classrooms on Undergraduate Student Opinions and Success. Journal Of Professional Issues In Engineering Education & Practice, 142(1), 1-11. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)EI.1943-5541.0000259
It was found that student performance on quizzes was not significantly different across the traditional and flipped classrooms. A key shortcoming noted with the flipped classroom was students’ inability to ask questions during lectures. Students in flipped classrooms were more likely to attend office hours compared to traditional classroom students, but the difference was not statistically significant.
Heyborne, W. H., & Perrett, J. J. (2016). To Flip or Not to Flip? Analysis of a Flipped Classroom Pedagogy in a General Biology Course. Journal Of College Science Teaching, 45(4), 31-37.
Although the outcomes were mixed, regarding the superiority of either pedagogical approach, there does seem to be a trend toward performance gains using the flipped pedagogy. We strongly advocate for a larger multiclass study to further clarify this important pedagogical question.
Tomory, A., & Watson, S. (2015). Flipped Classrooms for Advanced Science Courses. Journal Of Science Education & Technology, 24(6), 875-887. doi:10.1007/s10956-015-9570-8
http://blog.learnlets.com/?p=4832
I happened to hear a gamification expert talk, and he pointed out some rules about what he termed ‘goal science’. He had five pillars:
More on gamification in this IMS blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=gamification&submit=Search
Special Interest Group: Learning Spaces and Instructional Technology (SIG) webinars are FREE and open to anyone. Please feel free to share this with others at your institution.
Notes from the previous session available here:
Here are five different ways to apply the same rubric in your classroom.
1. A Rubric for Thinking (Invention Activity)
2. A Rubric for Peer Feedback (Drafting Activity)
3. A Rubric for Teacher Feedback (Revision Activity)
4. A Rubric for Mini-Lessons (Data Indicate a Teachable Moment)
5. A Rubric for Making Grades Visible (Student Investment in Grading)
How often have we heard that students believe grades to be arbitrary or capricious? Repeated use of a single rubric is good for both students and instructors. Switching roles between author and editor results in students’ increased familiarity with the process and the components of good writing. Over the course of the semester, students will synthesize the rubric’s components into effective communication. The instructor, too, will shift from “sage on the stage” to “guide on the side,” answering fewer questions (and answering the same question fewer times). In other words, students will gain greater independence as writers and thinkers. And this is good for all of us.
For more detailed information, go to the full version of the article: http://www.facultyfocus.com/articles/effective-teaching-strategies/rubrics-an-undervalued-teaching-tool/
More on rubrics in this blog
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=rubrics&submit=Search
Luther Rotto
For what it’s worth, here’s something I used ‘long ago’ on rubrics:
http://web.stcloudstate.edu/LRotto/im4-522/assignments/rubrics.htm
Links to information about rubrics:
Creating Rubrics
The folks at TeacherVision.com weigh in on rubrics.
http://www.teachervision.com/lesson-plans/lesson-4521.html
How to create a Rubric
The Chicago Public Schools page on writing rubrics from scratch
http://intranet.cps.k12.il.us/Assessments/Ideas_and_Rubrics/Create_Rubric/create_rubric.html
The Rubric Bank
The Chicago Schools again with a list of rubrics for various subject areas
http://intranet.cps.k12.il.us/Assessments/Ideas_and_Rubrics/Rubric_Bank/rubric_bank.html
Rubrics Resources – Westfield (MA) Public Schools
A links page to many other sources about using rubrics to improve instruction.
http://www.k12.westfield.ma.us:591/technology/pdev/rubric_resources.htm
Kathy Schrock’s Guide for Educators – Assessment Rubrics
Kathy Schrock’s links listing for rubrics – examples and about them
http://school.discovery.com/schrockguide/assess.html
Rubric How-To’s – MidLink’s Teacher Resource Room
Caroline McCullen’s (a multimedia teacher) page about rubrics with links to other sources on the topic
http://www.ncsu.edu/midlink/rubrics/
Rubrics by Bernie Dodge
The Master details how rubrics and WebQuests dovetail nicely.
http://webquest.sdsu.edu/rubrics/weblessons.htm
RubiStar site
An example of a web-based tool that can generate rubrics at the click of a button.
http://rubistar.4teachers.org/index.shtml
TeAch-nology.com’s Teacher Rubric Makers
Yet another example of a web-based tool that promises to generate rubrics.
http://www.teach-nology.com/web_tools/rubrics
221 HONORS.
The Honor System:
A Comparison Between the U.S. South and the Mediterranean World
Plamen Miltenoff, MLIS, Ph.D.
5:00 pm – 7:30 pm Wednesdays Miller Center 206
Contact Information |
Back to Top |
The best way to contact me is through email, but you can use any of the options below.
| Email: | pmiltenoff@stcloudstate.edu |
| Phone: | 320-308-3072 |
| Web Site: | http://web.stcloudstate.edu/pmiltenoff/faculty |
| Office Location: | Miller Center, 204-J |
The Honor system is a phenomenon well known in many cultures across the globe and strongly presented in cultures since Ancient Greece and Rome. The concepts of honor and shame have long been associated with cultures in the Mediterranean region mostly because the first scholars to study the social impact of these concepts did so in Southern Europe. Honor has two fundamental components: birth and morality. People could gain or lose their honor by the morality of their conduct. Despite the scholarly emphasis on the Mediterranean, the concept of honor influenced social systems all over the world, and historians are beginning to detect its traces in places as different as China and Africa. The Southern Honor system can firmly be traced back in the European roots and determined to a great degree the American history of the 19th century.
This course will study the geography, history, sociology and religions, cultural and political systems of two worlds and learn to compare the findings. Based on those comparisons, lessons in gender, culture and politics will be drawn.
Students in this course will
Attendance/Discussion Requirements
Course Policies |
Back to Top |
Late Assignment Policy |
All assignments should be submitted by midnight of the date on which they are due. Ten percent of an assignment’s point value will be removed for each day an assignment is late. This policy will be adjusted on a case-by-case basis if emergencies prevent you from submitting an assignment on time. In these situations, contact me as soon as is reasonable to determine how this policy can be adjusted in a way that meets your needs and is still fair to other students.
Grading |
Back to Top |
The grade book in D2L will be used to show detailed information about grades in this course. The table below shows the value of each assignment and the total number of points available.
| Overall Grade | |
| 94% – 100% = A | |
| 90 % – 93.99% = A- | |
| 86% – 89.99% = B+ | |
| 83% – 85.99% = B | |
| 80% – 82.99% = B- | |
| 70% – 79.99% = C | |
| 60% – 69.99% = D | |
| 59.99% or lower = F |
Assignments Schedule
| WEEK 1. August 28 Reading[s]: Peruse through all articles in the D2L content area. Choose one article to your liking and be ready to reflect on it.Assignment[s]: 1. complete entry survey. 2. Prepare to present in coherent and concise manner your understanding of Honors and Shame and discuss the goals for this course. 3. Enter a short essay in the D2L discussion on how do you see applying the knowledge from this course in your future studies, research and work |
||
| Introduction. Orientation, class parameters and familiarizing with the syllabus. Questions and issues. Course goals | What is an/the Honor System? Entry Interview (D2L survey is completed and analyzed). Why explore this topic and these vastly different geographic entities (US South and the Mediterranean). Define interest in this class and interest for a project; how this class can help your studies? Your career? All over as a human being? | |
| WEEK 2.Sept 4
Reading[s]: Assignment[s]: 1. Find an article on Honor and Shame. 2. Outline in two paragraphs the content of one of the three articles and in a third paragraph compare to your findings; use academic style to log your responses. If you have hesitation about your style, please check with the Write Place, your peers and me. |
||
| Why research? Work on the reading material for class
Find articles for the course. |
What is academic research? What is a peer-review article? When and how research the Internet. How do I access and keep track of resources. RefWorks versus Zotero and Mendeley What is an academic paper. How do I write an academic paper. The Write place. Making plans: final project |
|
| WEEK 3. Sept 11
Reading[s]: Assignment[s]: |
||
| Honors and Shame from a historical perspective | Do we have a robust theory/notion about the Honor/Shame system through the centuries? Do you think tracking that model through centuries helps in the 21st century? If yes, how and if no, why? | |
| WEEK 4. Sept 18
Reading[s]: Fernand Braudel (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fernand_Braudel) and the Annales School Assignment[s]: |
||
| Honors and Shame from a geographic perspective | Is there a “southern” connection (Mediterranean is the European South)? Can be Annale School be right (geography and relief determines history)? To what degree geography and geographical conditions determine such models (Honor/Shame)? | |
| WEEK 5. Sept 25
Reading[s]: Crook, Z. (2009). Honor, Shame, and Social Status Revisited. Journal of Biblical Literature, 128(3), 591–611. Assignment[s]: |
||
| Honors and Shame from a cultural perspective. Gender roles, Masculinity | Does the Honor/Shame model help understand gender roles, social status, masculinity etc.? | |
| WEEK 6. Oct 2
Reading[s]: Assignment[s]: |
||
| Honors and Shame from a political and social perspective | Can Honor/Shame be connected with the current political situation in Egypt, Syria, Turkey? Did Honor/Shame system influence decision in American history? | |
| WEEK 7. Wednesday Oct 9
Assignment[s]: final project details |
||
| Start working on the final project | Present and discuss your final project: 1. Finalized title 2. Outline 3. Plan 4. Clear work distribution among group members 5. Clear way for peer assessment. | |
| WEEK 8. Wednesday Oct 16 Assignment[s]: details on final project |
||
| Final brainstorming and start working on the project | Meeting as a whole: 1. Present group’s plan to class. 2. Share group’s ideas with class. 3. Share technology 4. Share sources 5. Share means for peer assessment | |
| WEEK 9. Wednesday Oct 23
Assignment[s]: draft of bibliography |
||
| Class as a whole: peer review and brainstorming | Meeting as a whole: 1. Are sources reliable? 2. Are sources of academic origin (peer-reviewed)? 3. Is the bibliography adhering correctly to the formats (APA, Chicago, ALA) | |
| WEEK 10. Wednesday Oct 30
Assignment[s]: details on presentation |
||
| Work on the final project | Meeting as a whole: 1. Presentation format 2. Share technology 3. Share ideas | |
| WEEK 11. Wednesday Nov 6 Assignment[s]: paper draft due in D2L dropbox |
||
| Work on final project | Meeting as a whole: share group’s progress and seek other group’s feedback | |
| WEEK 12. Wednesday Nov 13 Assignment[s]: paper draft and presentation |
||
| Work on project | Meeting as a whole: share group’s progress and seek other group’s feedback | |
| WEEK 13. Wednesday Nov 20 Assignment[s]: paper draft due in D2L dropbox |
||
| Work on project | Meeting as a whole: share group’s progress and seek other group’s feedback | |
| WEEK 13. Wednesday Nov 27 | ||
| Work on project | Meeting as a whole: share group’s progress and seek other group’s feedback | |
| WEEK 13. Wednesday Dec 4 Assignment[s]: paper final draft due in D2L dropbox |
||
| presentations | Class presentations of the final projects | |
| WEEK 13. Wednesday Dec 11 | ||
| presentations | Class presentations of the final projects | |
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
Bertram Wyatt-Brown. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://personal.tcu.edu/swoodworth/Wyatt-Brown.htm
Brayford, S. A. (1999). TO SHAME OR NOT TO SHAME: SEXUALITY IN THE MEDITERRANEAN DIASPORA. Semeia, (87), 163.
BUSATTA, S. (2006). Honour and Shame in the Mediterranean. Antrocom, 2(2). 75-78. Retrieved March 19, 2013, from http://www.academia.edu/524890/Honour_and_Shame_in_the_Mediterranean
Cohen, D. (n.d.). Insult, Aggression, and the Southern Culture of Honor: An “Experimental Ethnography.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 70(5), 945–960.
Crook, Z. (2009). Honor, Shame, and Social Status Revisited. Journal of Biblical Literature, 128(3), 591–611.
Culture of honor (Southern United States). (n.d.). Retrieved from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Culture_of_honor_(Southern_United_States)
Dussere, E. (2001). The Debts of History: Southern Honor, Affirmative Action, and Faulkner’s Intruder in the Dust. Faulkner Journal, 17(1), 37–57.
Esmer, T. U. (n.d.). Honor in Ottoman and Contemporary Mediterranean Societies: Controversies, Continuities, and New Directions. conference announcement. Retrieved from http://www.h-net.org/announce/show.cgi?ID=196551
Family, Patronage, and Social Contests.pdf. (n.d.).
Hall, J. L. (1907). Half-hours in southern history. B. F. Johnson publishing co.
Harrell, L. A. (2009, December 4). It’s an honorable choice: Rebellions Against Southern Honor in William Styron’s The Confessions of Nat Turner. Retrieved from http://www.lib.ncsu.edu/resolver/1840.16/2614
Harris, J. W. (2002). Honor, Grace, and War (But Not Slavery?) in Southern Culture. Reviews in American History, 30(1), 1–7. doi:10.2307/30031707
Hellerman. (n.d.). Reconstructing Honor in Roman Philippi. Cambridge University Press.
Herzfeld, M. (1980). Honour and Shame: Problems in the Comparative Analysis of Moral Systems. Man, 15(2), 339–351. doi:10.2307/2801675
Honor, Shame, and Social Status.pdf. (n.d.).
honor-04-Antrocom_Honour and Shame in the Mediterranean_S.pdf. (n.d.).
Honors and Shame and the Unity of the Mediterranean. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/3317790
Honour and shame (Anthropology). (n.d.). Retrieved from http://what-when-how.com/social-and-cultural-anthropology/honour-and-shame-anthropology/
Lever, A. (1986). Honour as a Red Herring. Critique of Anthropology, 6(3), 83–106. doi:10.1177/0308275X8600600305
Manly Honor Part V: Honor in the American South. (n.d.). The Art of Manliness. Retrieved August 15, 2013, from http://www.artofmanliness.com/2012/11/26/manly-honor-part-v-honor-in-the-american-south/
Moxnes, V. (1996). Honor and Shame. In R. L. Rohrbaugh (Ed.). The Social Sciences and New Testament Interpretation (pp. 19-40). Peabody, Mass.: Hendrickson. http://tinyurl.com/qdvc499
Murder in Jerba_ Honour, Shame and.pdf. (n.d.).
Osiek, C. (2008). Women, honor, and context in Mediterranean antiquity, 64(1), 323–337. doi:10.4102/hts.v64i1.2
Peoples and Cultures of the Mediterranean. (n.d.). Retrieved March 19, 2013, from http://www.academia.edu/2437701/Peoples_and_Cultures_of_the_Mediterranean
Rabichev, R. (n.d.). The Mediterranean concepts of honour and shame as seen in the depiction of the biblical women. Retrieved from http://prophetess.lstc.edu/~rklein/Doc6/renata.htm
Santos, N. F. (2008). Family, Patronage, and Social Contests: Narrative Reversals in the Gospel of Mark. S&J, (2).
Slavery and Southern Honor. (n.d.). StudyMode. Education. Retrieved from http://www.studymode.com/essays/Slavery-Southern-Honor-72644.html
Smith, A. (2004). Murder in Jerba: Honour, Shame and Hospitality among Maltese in Ottoman Tunisia. History and Anthropology Routledge, 15(2), 107–132.
Stewart,, Y. (n.d.). Mursi: A Study in Honor-Shame dynamics. CATEGORY ARCHIVES: HONOR-SHAME CULTURE. Retrieved from http://www.theaugeanstables.com/category/honor-shame-culture/
TO SHAME OR NOT TO SHAME_ SEXUALITY IN THE MEDITERRANEAN DIASPORA..pdf. (n.d.).
Weir, D. (n.d.). Honour and Shame. Islam Watch. Retrieved from http://www.islam-watch.org/Others/Honour-and-Shame-in-Islam.htm
Women, honor, and context in Mediterranean antiquity.pdf. (n.d.).
Wyatt-Brown, B. & Milbauer, Richard J. (2004). Honor, Shame, and Iraq in American Foreign Policy. In Note prepared for the Workshop on Humiliation and Violent Conflict, Columbia University, New York, November 18-19, 2004. Presented at the Workshop on Humiliation and Violent Conflict, Columbia University, New York,. Retrieved from http://www.humiliationstudies.org/documents/WyattBrownNY04meeting.pdf
What does Research Tell Us about Classroom Discussion? Jay Howard
http://digitalcommons.butler.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1163&context=facsch_papers
Do College Students Participate More in Discussion in Traditional Delivery Courses or in Interactive Telecourses?
https://muse.jhu.edu/journals/journal_of_higher_education/v073/73.6howard.html
facts from sociological research:
Traditional forms and techniques for discussion and participation
Weih, T. G. (2015). Discussion Strategies for the Inclusion of ALL Students. Online Submission,
http://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED561060
Does the instructor really care of what students have to say
lecturing does not predispose to discussion
Simich-Dudgeon, C., & National Clearinghouse for Bilingual Education, W. D. (1998). Classroom Strategies for Encouraging Collaborative Discussion. Directions in Language and Education. http://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED435188
Chen, W., & Looi, C. (2007). Incorporating Online Discussion in Face to Face Classroom Learning: A New Blended Learning Approach. Australasian Journal Of Educational Technology, 23(3), 307-326.
Discussions and participation in hybrid environment
Jinhong, J., & Gilson, T. A. (2014). Online Threaded Discussion: Benefits, Issues, and Strategies. Kinesiology Review, 3(4), 241-246.
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3ds3h%26AN%3d100248254%26site%3dehost-live%26scope%3dsite
For each OTD topic, the instructor randomly assigns two to four student discussion leaders who are in charge of organizing OTD for the assigned week. Each of the discussion leaders is asked to generate one or two discussion questions related to the topic based on reading assignments. The use of student discussion leaders is a strategy to encourage active participation and help develop ownership of learning. Once student discussion leaders post their questions, other students are encouraged to contribute to the discussion by answering each question, commenting on the ideas of others, or asking questions of peers or the instructor for the next two days. When the week’s discussion is complete, the student leaders and instructor work together to summarize the discussion and evaluate each student’s participation and contribution to the discussion using a scoring rubric. (p.242)
Implementation (p. 243):
Discussions and participation in online environment
Darabi, A., Liang, X., Suryavanshi, R., & Yurekli, H. (2013). Effectiveness of Online Discussion Strategies: A Meta-Analysis. American Journal Of Distance Education, 27(4), 228-241. doi:10.1080/08923647.2013.837651
Lin, P., Hou, H., Wang, S., & Chang, K. (2013). Analyzing knowledge dimensions and cognitive process of a project-based online discussion instructional activity using Facebook in an adult and continuing education course. Computers & Education, 60(1), 110-121. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2012.07.017
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360131512001819
In the process of project-based learning, learners must utilize different kinds of knowledge (e.g., discrete declarative knowledge and dynamic procedural knowledge) (Lou, 2004). Meanwhile, students can develop higher level of cognitive skills for a specific domain as well as the ability to apply adequate knowledge to a specific domain or context during PBL (Barron et al., 1998; Blumenfeld et al., 1991).
social interaction, which was considered as irrelevant discussion, may also leading to meaningful thinking and echoes the viewpoints from previous studies, which suggest social interaction can be a critical element in the CSCL environment (Abedin et al., 2011a, 2011b).
This paper discusses an innovative blended learning strategy which incorporates online discussion in both in-class face to face, and off-classroom settings. Online discussion in a face to face class is compared with its two counterparts, off-class online discussion as well as in-class, face to face oral discussion, to examine the advantages and disadvantages of the proposed strategy. By integrating online discussion into the flow of the classroom, learners are given dedicated time to foster a habit of critical thinking, reflection and articulating these online, which can subsequently seed further in-class oral discussions, and off-class online discussions. It is found that in-class, online discussion can provide a wider spectrum of discussion perspectives, equalise participation in discussion, and promote cognitive thinking skills and in depth information processing. However, the lack of face to face interactions and the need for sufficient time to do online postings pose challenges in implementing online discussion for face to face classroom learning.
=============
More on classroom discussions in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=discussions&submit=Search
Saint Leo University uses a game-based storyline to invigorate professional learning.
By Dennis Pierce, 01/27/16
Borden and his colleagues teamed up with Edchat Interactive, a company that is working to transform online professional development into a more interactive experience that reflects how people learn best, and Games4Ed, a nonprofit organization that brings together educators, researchers, game developers, and publishers to advance the use of games and other immersive learning strategies in education.
“People don’t learn by watching somebody discuss a series of slides; they learn best by interacting with others and reflecting. Great teachers always have people break into groups to accomplish a task, and then the different groups all report back to the group as a whole. That should be replicable online.”
Adult Learning Through Play
Using simulations for professional development is fairly common. For instance, in SimSchool, a program developed by educational scientists at the University of North Texas and the University of Vermont, new and pre-service teachers can try out their craft in a simulated classroom environment, doing the same activities as actual teachers but getting real-time feedback from the simulated program and their instructors.
Christopher Like, a science teacher and STEAM coordinator for the Bettendorf Community School District in Iowa, developed a game-based model for ed tech professional development that has been adapted by K-12 school districts across the nation. His game, Mission Possible, has teachers complete 15-minute “missions” in which they learn technology skills and advance to successively higher levels. “It engages teachers’ competitive nature just like Call of Duty does with my eldest son,” he wrote in a blog post.
From the Blended and Online Learning discussion list:
We’re working on a grant program at my unit to improve these lec-capture courses. One of the ways is to train faculty:
Chunking of videos includes preplanning and post production tasks. Faculty can be trained to script their lectures more, create lecture based on “topics” to make chunking and tagging easier. Need to focus on end user experience (online student).
These are some of the ideas. We plan to start implementing them this summer. I’ll share with you our progress. 🙂
Rema
———————————————————–
Rema Nilakanta, Ph.D.
Director of Design & Delivery|
Engineering-LAS Online Learning
1328 Howe Hall
515-294-9259 (office)
515-294-6184 (fax)
http://www.elo.iastate.edu
—————————-
On Wed, Jan 27, 2016 at 8:48 AM, Nilakanta, Rema [ELO] <rema@iastate.edu> wrote:
Good Morning!
Thank you all for filling out the survey on the use of lecture capture in higher education. I appreciate your time and interest in this subject.
Attached are the results. I’ve also provided an overview below. The main purpose of this survey was to get an overall idea of how lecture capture is used in HE. I was just curious to see if the way we use it is pretty much similar at other institutions. The finding was inconclusive. My next step is to dig a little deeper – perhaps repurpose this survey for faculty and students. The final goal is to improve these courses – make them as pedagogically sound as possible, given that this technology is here to stay at our campus, at least for the near future. It will certainly require designing faculty training, but I would also like to explore innovative and efficient ways of chunking lecture videos pre and post production.
Let me know if you have any questions or need further information.
Rema
OVERVIEW OF “USE OF LECTURE CAPTURE IN HE” SURVEY RESULTS & FINDINGS
By Rema Nilakanta
I’ve listed some of the findings that impressed me. They do not follow the order of the questions in the survey. For details, please view the attached report.
Just a quick note – There were 39 respondents, but not all responded to every question. The respondents included instructional and IT support staff and administrators at all levels generally from 4-year public and private universities.
FINDINGS & THEMES
o review of in-class lectures
o training and advising
o student presentations (students use the technology to create their presentations/demos/assignments)
o live streaming of seminars and on-site hosting of conferences for remote students and audiences.
o For people satisfied with the setup, there were quite a few users of Echo 360 and Panopto.
o Panopto seemed to rise above the rest for its promptness and quality of service. Mediasite got mixed response.
o There seems to be an awareness of the need to get the lectures captioned.
o Along with automated lecture capture technology, there seems to be a rise in old ways of doing things – manual (human) recording of events continues and seems preferable, especially in the face of rising costs of lecture capture technology.
o Training faculty to use the technology – turn on the mic, no recording of white board, do not change settings, take time to learn the technology.
o Funding and support
o Ensuring best practices
o Captioning
o IP concerns
OPERATIONS
– Keep mic on all the time
– Use of media asset management systems, like Kaltura (MediaSite)
– Admins trained to check settings for rooms
– Disable download of recordings as default setting (addressed IP concerns)
TRAINING
– Create user groups around technologies
– Promote communication among instructors using a particular room
– Training of faculty by instructional design teams on the use of technology and best practices
here is more on lecture capture in this IMS blog:
https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/?s=lecture+capture&submit=Search