Archive of ‘Library and information science’ category
Please join us in exploring our mobile devices.
Minutes from the April 23, 2014 meeting
Pamela, Greg, Rachel and Plamen met at 3pM in MC 205 and discussed:
- ebooks
- different OS and gadgets – iOS, Windows Surface, Android Galaxy, Kindle
the differences. We determined that it is up to the user which one she/he prefers.
- what can be frustrating
Android – more difficult to organize. For an novice it is more difficult
- WIndows Surface come with Office and Surface has a mouse pointer and USB port, which makes easy connect external mouse.
- Pamela will buy different types of dongles (USB, VGA) for iOS, Android Galaxy and WIndows and they will be available to loan from the dean’s office.
- Siri, consensus on the poor quality. Cortana on WIndows is to be seen. Somebody on campus using Siri to text. Google Now is the Siri equivalent.
- Google Glass. waste of money? it has potential thought. battery is very limited. we are not sure if it connects to iPAD
- meet once a month. ask what worked from the last group and what didn’t to determine what can be discussed. Carol Rose has an app for passwords. How many people do NOT have access to a mobile device. What people do here, work related stuff (email, notes, calendar). A coordinator of this group monitoring free apps and suggesting to be tested in LRS. List from the former group with the apps for iOS, Android, Windows.
Log in your questions, suggestions and helpful information.
Plamen Miltenoff and Tom Hergert
InforMedia Services
informedia@stcloudstate.edu
pmiltenoff@stcloudstate.edu
trhergert@stcloudstate.edu
Contact us via social media:
IMS blog: https://blog.stcloudstate.edu/ims/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/SCSUtechinstruc
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/InforMediaServices?ref=hl
Pinterest: http://www.pinterest.com/scsutechnology/
Instagram: http://instagram.com/scsutechinstruct
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC_UMIE5r6YB8KzTF5nZJFyA
Google +: https://plus.google.com/u/0/115966710162153290760/posts/p/pub
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/scsuinstructionaltechnology
You know that you can export a Google Doc into a MS Word format.
Did you know that you can open a MS Word doc in Google Doc? Here is how:
http://practicaledtech.com/2014/04/21/practical-ed-tech-tip-of-the-week-templates-in-google-drive/
https://www.brainfuse.com/home/peers.asp
http://www.magazine.utoronto.ca/life-on-campus/donny-ouyang-online-peer-tutoring/
https://peers.aristotlecircle.com/page/1-to-1-in-home-tutoring
http://study-guide-services-review.toptenreviews.com/what-is-peer-to-peer-tutoring.html
http://www.azcentral.com/news/arizona/articles/20130426education-nation-peer-tutoring-gets-high-tech-makeover.html
http://jobs.aol.com/videos/job-search/rayku-p2p-online-tutoring-program-startup-presentation/517175995/
Peer reviewed (please consider LRS online dbase to retrieve):
Westera, W., De Bakker, G., & Wagemans, L. (2009). Self-arrangement of fleeting student pairs: a Web 2.0 approach for peer tutoring. Interactive Learning Environments, 17(4), 341-349. doi:10.1080/10494820903195249
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dkeh%26AN%3d45141111%26site%3deds-live%26scope%3dsite
http://ascilite.org.au/ajet/ajet26/mcloughlin.html
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S036013150600090X
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0740818807000448
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S8755461507000734
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/02602930410001689144#.U1J_MvldWSo
Interesting conference proceedings:
Gaofeng, R., & Yeyu, L. (2007). An Online Peer Assisted Learning Community Model and its Application in ZJNU.Online Submission,
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3deric%26AN%3dED500172%26site%3deds-live%26scope%3dsite
A model to consider, if you have a higher ed instution in the vicinity and replace freshman students with K12 ones. I like how the authors further classified the tutors into 3 categories:
De Smet, M., Van Keer, H., & Valcke, M. (2008). Blending asynchronous discussion groups and peer tutoring in higher education: An exploratory study of online peer tutoring behaviour. Computers & Education, 50207-223. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2006.05.001
http://eds.b.ebscohost.com.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/eds/detail?vid=4&sid=2fae304e-fee9-4a4f-8119-386670956bbb%40sessionmgr111&hid=106&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWRzLWxpdmUmc2NvcGU9c2l0ZQ%3d%3d#db=edselp&AN=S036013150600090X
This is the foundation, which the startup companies from Sillicon Valley are using to make money:
Hsiao, Y. P., Brouns, F., Kester, L., & Sloep, P. (2013). Cognitive load and knowledge sharing in Learning Networks. Interactive Learning Environments, 21(1), 89-100. doi:10.1080/10494820.2010.548068
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dkeh%26AN%3d85198881%26site%3deds-live%26scope%3dsite
this is old, but you can take the concepts and apply them right toward your research of using CAI
Dewey, D. P., & Cannon, A. E. (2006). Supporting technology instruction through peer tutoring, discussion boards and electronic journals. IALLT Journal Of Language Learning Technologies, 38(2), 17.
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dedo%26AN%3d24660100%26site%3deds-live%26scope%3dsite
this one goes towad
Mengping, T. (2014). Mathematics Synchronous Peer Tutoring System for Students with Learning Disabilities.Journal Of Educational Technology & Society, 17(1), 115-127.
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3dkeh%26AN%3d94937804%26site%3deds-live%26scope%3dsite
Tsuei, M. (2012). Using Synchronous Peer Tutoring System to Promote Elementary Students’ Learning in Mathematics. Computers & Education, 58(4), 1171-1182.
http://login.libproxy.stcloudstate.edu/login?qurl=http%3a%2f%2fsearch.ebscohost.com%2flogin.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26db%3deric%26AN%3dEJ955399%26site%3deds-live%26scope%3dsite
Good day everyone,
The rising prominence of mobile devices in education and our private lives prompts us to revisit the “tablets” group of 2012/2013. Back then LRS and ITS faculty and staff, who were given iPads and Android tablets, met monthly to share ideas and experience.
With Dean Vargas’s support we plan to reconvene this group. We recognize that many more of us now have mobile devices, including tablets and smart phones, so we invite anyone who has a mobile device (not only a tablet and not only using iOS or Android, but any mobile device or operating system) to meet with us and:
a. share experience and knowledge,
b. seek answers to questions and/or
c. brainstorm and develop ideas as to how we can use these tools more effectively at work and in our private lives.
The group is initially christened as SMUG (smart mobile users’ group, not for our attitude, but for fun). We expect the group to create its own personality and name.
Please contact us if you’re interested. Please have the Doodle poll https://doodle.com/2uaytxbth728sa9b for the initial meeting.
Thanks,
Tom Hergert and Plamen Miltenoff
The future of education lies in a healthy balance between teaching and technology. Digital literacy a the standard language of our world today, writes Andrew Marcinek. “As databases grow and information continues to evolve into paperless formats, it is essential to teach students how to question effectively and efficiently.” In addition, Marcinek advocates for educators to promote and encourage offline activities like socializing and traditional books alongside online learning.
In addition, Marcinek believes that educators should find applications that “promote and strengthen a variety of skill sets for students, not just one or two.” Learning goals and objective should still drive classroom engagement, not tools like devices and applications.
An administrator’s biggest mistake is to make technology seem like a mandated item.
For full story, see Edutopia.
Technology and Teaching: Finding a Balance
MARCH 11, 2014
Andrew MarcinekDirector of Technology & EducatorU.org Co-founder, Boston, MA
http://www.edutopia.org/blog/technology-and-teaching-finding-balance-andrew-marcinek
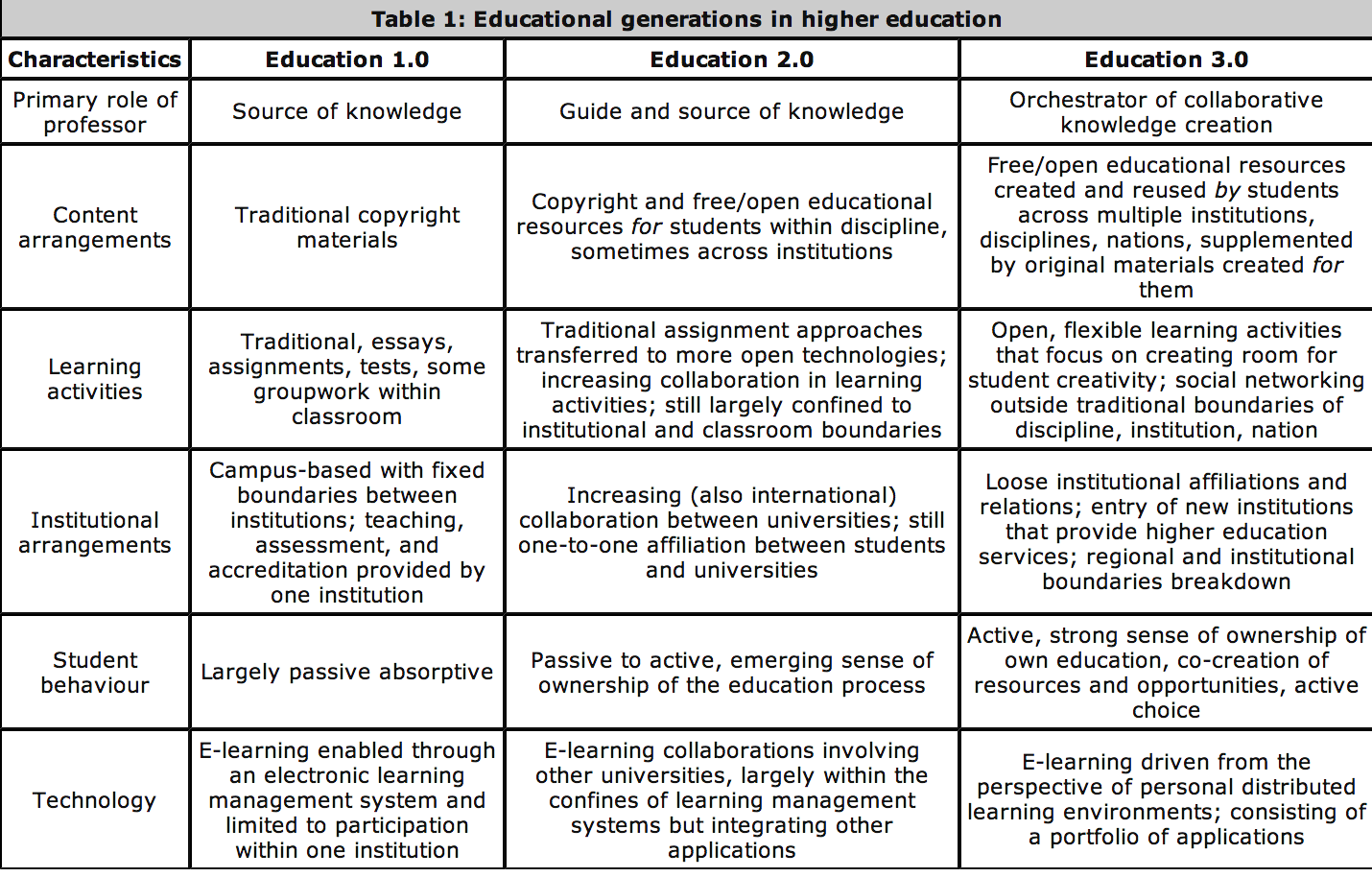
https://www.educatorstechnology.com/2013/11/education-10-vs-education-20-vs.html
Free Technology for Teachers: 5 Video Projects to Try With Your Students
http://www.freetech4teachers.com/2012/08/5-video-projects-to-try-with-your.html?m=1
Twitter, Rape and Privacy on Social Media – The Cut
http://nymag.com/thecut/2014/03/twitter-rape-and-privacy-on-social-media.html?mid=facebook_nymag
*****************
Three thoughtful and thought-provoking essays about teaching social media use:
“Why students should not be required to publicly participate online” online at http://prpost.wordpress.com/2010/04/25/why-students-should-not-be-required-to-publicly-participate-online/
“Notes on Student Privacy and Online Pedagogy” online at http://joshhonn.com/?p=65
“Why the Loon does not assign public social-media use” online at http://gavialib.com/2014/02/why-the-loon-does-not-assign-public-social-media-use/
I don’t necessarily advocate the point of view expressed in these posts, but I do think they merit both attention and discussion in a course focused on social media.
Keith Ewing
Professor, Library Systems & Digital Projects
Core Principles of MLE
http://namle.net/publications/core-principles/
The purpose of media literacy education is to help individuals of all ages develop the habits of inquiry and skills of expression that they need to be critical thinkers, effective communicators and active citizens in today’s world.
1. Media Literacy Education requires active inquiry and critical thinking about the messages
we receive and create.
2. Media Literacy Education expands the concept of literacy (i.e., reading and writing) to
include all forms of media.
3. Media Literacy Education builds and reinforces skills for learners of all ages. Like print
literacy, those skills necessitate integrated, interactive, and repeated practice.
4. Media Literacy Education develops informed, reflective and engaged participants essential
for a democratic society.
5. Media Literacy Education recognizes that media are a part of culture and function as
agents of socialization.
6. Media Literacy Education affirms that people use their individual skills,
http://namle.net/publications/media-literacy-definitions/:
The Basic Definition
Within North America, media literacy is seen to consist of a series of communication competencies, including the ability to ACCESS, ANALYZE,EVALUATE, and COMMUNICATE information in a variety of forms, including print and non-print messages.
Media literacy empowers people to be both critical thinkers and creative producers of an increasingly wide range of messages using image, language, and sound. It is the skillful application of literacy skills to media and technology messages.
